|
Urination
Urination is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, pissing, and going number one. In healthy humans and other animals, the process of urination is under voluntary control. In infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury, urination may occur as a reflex. It is normal for adult humans to urinate up to seven times during the day. In some animals, in addition to expelling waste material, urination can mark territory or express submissiveness. Physiologically, urination involves coordination between the central, autonomic, and somatic nervous systems. Brain centres that regulate urination include the pontine micturition center, periaqueductal gray, and the cerebral cortex. In placental mammals, urine is drain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manneken Pis
''Manneken Pis'' (; ) is a landmark bronze fountain sculpture in central Brussels, Belgium, depicting a puer mingens; a naked little boy urinating into the fountain's basin. Though its existence is attested as early as the 15th century, it was designed in its current form by the Brabantine sculptor Jérôme Duquesnoy the Elder and put in place in 1618 or 1619. ''Manneken Pis'' has been repeatedly stolen or damaged throughout its history. The current statue is a replica dating from 1965, with the original being kept in the Brussels City Museum. Nowadays, it is one of the best-known symbols of Brussels and Belgium, inspiring many imitations and similar statues. The figure is regularly dressed up and its wardrobe consists of around one thousand different costumes. Due to its self-derisive nature, it is also an example of '' belgitude'' ( French; ), as well as of folk humour ('' zwanze'') popular in Brussels. ''Manneken Pis'' is an approximate five minutes' walk from the Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing life-long healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers and outpatient clinics located throughout the country. Non-healthcare benefits include disability compensation, vocational rehabilitation, education assistance, home loans, and life insurance. The VA also provides burial and memorial benefits to eligible veterans and family members at 135 national cemeteries. While veterans' benefits have been provided by the federal government since the American Revolutionary War, a veteran-specific federal agency was not established until 1930, as the Veterans Administration. In 1982, its mission was extended to a fourth mission to provide care to non-veterans and civilians in case of national emergencies. In 1989, the Veterans Administration became a cabinet-level Department of Veterans Affairs. The age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrum
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall it is concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The central part is curved outward toward the posterior, allowing greater room for the pel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response. Nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system arise from the central nervous system. Specific nerves include several cran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbar
In tetrapod anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means ''of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm and the sacrum.'' The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lower spine, or as an area of the back in its proximity. In human anatomy the five lumbar vertebrae (vertebrae in the lumbar region of the back) are the largest and strongest in the movable part of the spinal column, and can be distinguished by the absence of a foramen in the transverse process, and by the absence of facets on the sides of the body. In most mammals, the lumbar region of the spine curves outward. The actual spinal cord terminates between vertebrae one and two of this series, called L1 and L2. The nervous tissue that extends below this point are individual strands that collectively form the cauda equina. In between each lumbar vertebra a nerve root exits, and these nerve roots come together again to form the largest single nerve in the human body, the sciatic n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system functions to regulate the body's unconscious actions. The sympathetic nervous system's primary process is to stimulate the body's fight or flight response. It is, however, constantly active at a basic level to maintain homeostasis. The sympathetic nervous system is described as being antagonistic to the parasympathetic nervous system which stimulates the body to "feed and breed" and to (then) "rest-and-digest". Structure There are two kinds of neurons involved in the transmission of any signal through the sympathetic system: pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic. The shorter preganglionic neurons originate in the thoracolumbar division o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
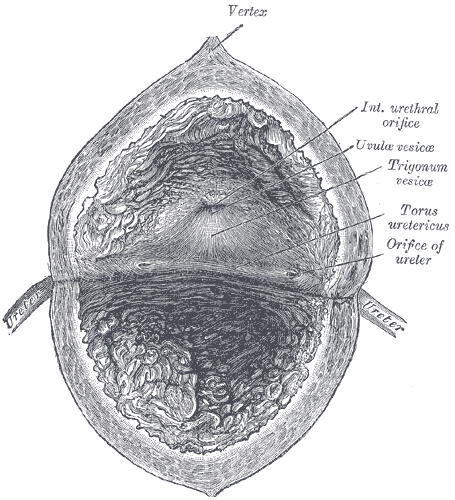
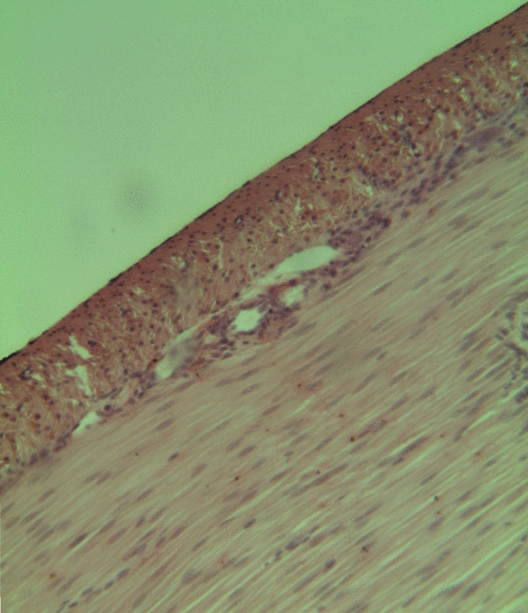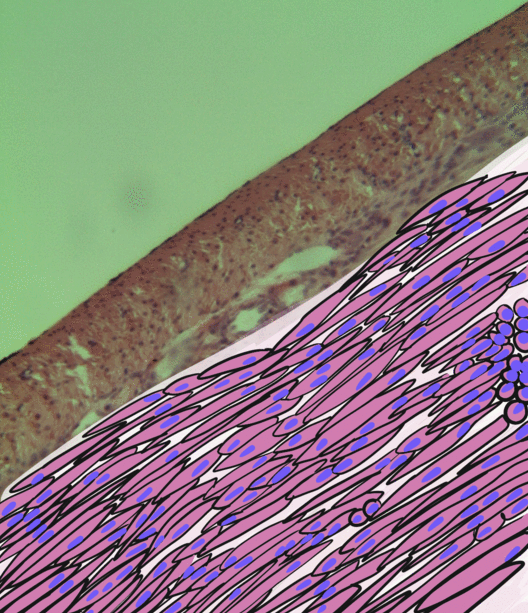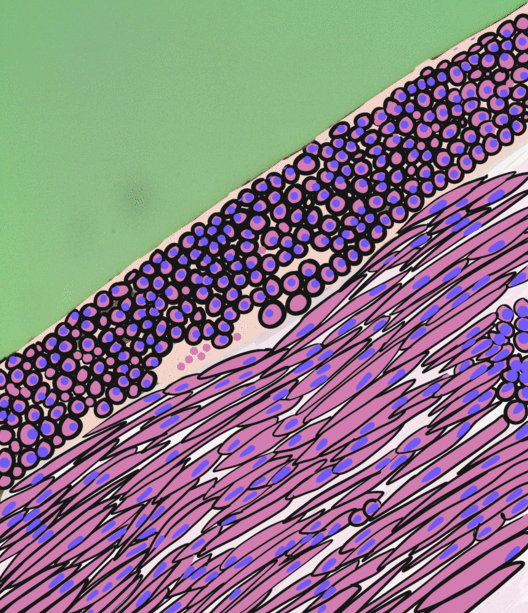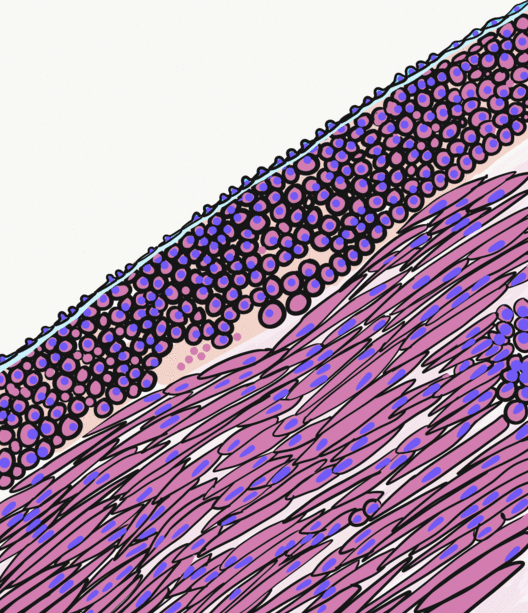
Detrusor
The detrusor muscle, also detrusor urinae muscle, muscularis propria of the urinary bladder and (less precise) muscularis propria, is smooth muscle found in the wall of the bladder. The detrusor muscle remains relaxed to allow the bladder to store urine, and contracts during urination to release urine. Related are the urethral sphincter muscles which envelop the urethra to control the flow of urine when they contract. Structure The fibers of the detrusor muscle arise from the posterior surface of the body of the pubis in both sexes (musculi pubovesicales), and in the male from the adjacent part of the prostate. These fibers pass, in a more or less longitudinal manner, up the inferior surface of the bladder, over its apex, and then descend along its fundus to become attached to the prostate in the male, and to the front of the vagina in the female. At the sides of the bladder the fibers are arranged obliquely and intersect one another. The 3 layers of muscles are arranged lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulval Vestibule
The vulval vestibule (or vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is a part of the vulva between the labia minora into which the urinary meatus (urethral opening) and the vaginal opening open. Its edge is marked by Hart's line. It represents the distal end of the urogenital sinus of the embryo.Manual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1–16. . Structure Structures opening in the vulval vestibule are the urethra, vagina, Bartholin's glands, and Skene's ducts. The external urethral orifice is placed about 25–30 millimetres (1–1.2 in) behind the clitoris and immediately in front of that of the vagina; it usually assumes the form of a short, sagittal cleft with slightly raised margins. Nearby are the openings of the Skene's ducts. The vaginal orifice is a median slit below and behind the opening of the urethra; its size varies inversely with that of the hymen. To the left and right of the vulval vestibule are the labia minora. Anterior to it are the clitoral hood, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |