|
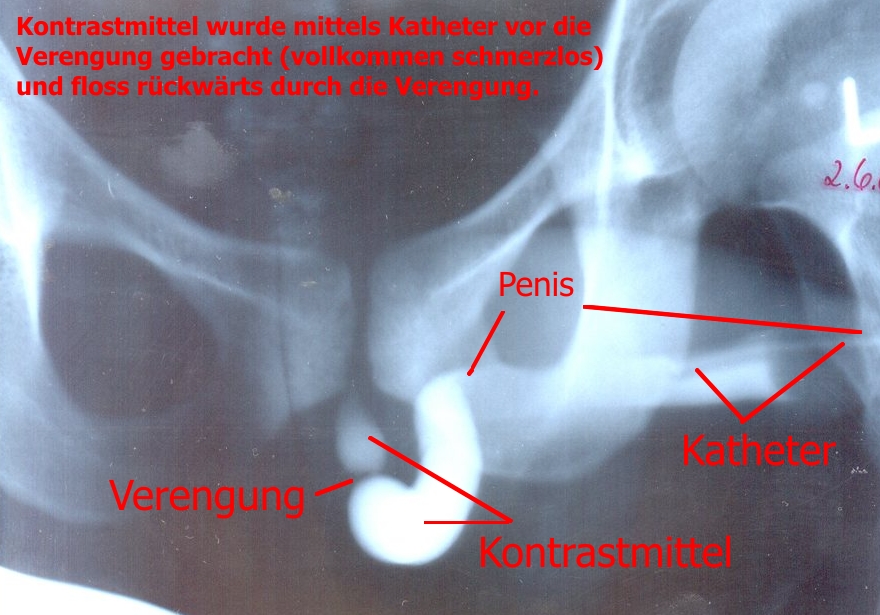
Urethrography
A retrograde urethrography is a routine radiologic procedure (most typically in males) used to image the integrity of the urethra. Hence a retrograde urethrogram is essential for diagnosis of urethral injury, or urethral stricture. Uses Some indications for retrograde urethrogram are: urethral stricture, urethral trauma, urethral fistula and congenital urethral abnormalities. There is no absolute contraindication for retrograde urethrogram. There are several relative contraindications such as: allergy to contrast agents, acute urinary tract infection, and recent instrumentation of urethra. Procedure A low osmolar contrast agent with concentration of 200 to 300 mg per ml with volume of 20 ml can be used in this study. Warming the contrast medium before infusion into the urethra can help to reduce the chance of getting spasm of external urethral sphincter. The subject lie down on supine position. An 8 Fr Foley catheter is connected to a 50 ml syringe. The syringe is flushed to rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiding Cystourethrography
In urology, voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) is a frequently performed technique for visualizing a person's urethra and urinary bladder while the person urinates (voids). It is used in the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux (kidney reflux), among other disorders. The technique consists of catheterizing the person in order to fill the bladder with a radiocontrast agent, typically diatrizoic acid. Under fluoroscopy (real time x-rays) the radiologist watches the contrast enter the bladder and looks at the anatomy of the patient. If the contrast moves into the ureters and back into the kidneys, the radiologist makes the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux, and gives the degree of severity a score. The exam ends when the person voids while the radiologist is watching under fluoroscopy. Consumption of fluid promotes excretion of contrast media after the procedure. It is important to watch the contrast during voiding, because this is when the bladder has the most pressure, and it is most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades, fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm. Fluoroscopy is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethral Stricture
A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra, the tube connected to the bladder that allows the passing of urine. The narrowing reduces the flow of urine and makes it more difficult or even painful to empty the bladder. Urethral stricture is caused by injury, instrumentation, infection, and certain non-infectious forms of urethritis The condition is more common in men due to their longer urethra. Signs and symptoms The hallmark sign of urethral stricture is a weak urinary stream. Other symptoms include: * Splaying of the urinary stream * Urinary frequency * Urinary urgency * Straining to urinate * Pain during urination * Urinary tract infection * Prostatitis * Inability to completely empty the bladder. Some people with severe urethral strictures are completely unable to urinate. This is referred to as acute urinary retention, and is a medical emergency. Hydronephrosis and kidney failure may also occur. Complications * Urinary retention * Prostatitis * Bladder dysfunc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Catheterisation
In urinary catheterization a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used for treatment or diagnosis of bladder conditions. A clinician, often a nurse, usually performs the procedure, but self-catheterization is also possible. A catheter may be in place for long periods of time (indwelling catheter) or removed after each use (intermittent catheterization). Catheter types Catheters come in several basic designs: *A Foley catheter ( indwelling urinary catheter) is retained by means of a balloon at the tip that is inflated with sterile water. The balloons typically come in two different sizes: 5 cm3 and 30 cm3. They are commonly made in silicone rubber or natural rubber. *An intermittent catheter/Robinson catheter is a flexible catheter that is removed after each use. Unlike the Foley catheter, it has n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectional Radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images are often examined by radiologists. Both the procedure and any resultant images are often simply called "X-ray". Plain radiography or roentgenography generally refers to projectional radiography (without the use of more advanced techniques such as computed tomography that can generate 3D-images). ''Plain radiography'' can also refer to radiography without a radiocontrast agent or radiography that generates single static images, as contrasted to fluoroscopy, which are technically also projectional. Equipment X-ray generator Projectional radiographs generally use X-rays created by X-ray generators, which generate X-rays from X-ray tubes. Grid An anti-scatter grid may be placed between the patient and the detector to reduce the quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrograde Ureteral
Ureteroscopy is an examination of the upper urinary tract, usually performed with a ureteroscope that is passed through the urethra and the bladder, and then directly into the ureter. The procedure is useful in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders such as kidney stones and urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Smaller stones in the bladder or lower ureter can be removed in one piece, while bigger ones are usually broken before removal during ureteroscopy. The examination may be performed with either a flexible, semi-rigid or rigid device while the patient is under anesthesia. In specific cases, the patient is free to go home after the examination.Ureteropyeloscopy. Baylor College of Medicine Baylor College of Medicine (BCM) is a medical school and research center in Houston, Texas, within the Texas Medical Center, the world's largest medical center. BCM is composed of four academic components: the School of Medicine, the Graduate S .... 2018 ccessed 2018 Mar 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membranous Urethra
The membranous urethra or intermediate part of male urethra is the shortest, least dilatable, and, with the exception of the urinary meatus, the narrowest part of the urethra. It extends downward and forward, with a slight anterior concavity, between the apex of the prostate and the bulb of the urethra, perforating the urogenital diaphragm about 2.5 cm below and behind the pubic symphysis. The hinder part of the urethral bulb lies in apposition with the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, but its upper portion diverges somewhat from this fascia: the anterior wall of the membranous urethra is thus prolonged for a short distance in front of the urogenital diaphragm; it measures about 2 cm in length, while the posterior wall which is between the two fasciæ of the diaphragm is only 1.25 cm long. The anatomical variation in membranous urethral length measurements in men have been reported to range from 0.5 cm to 3.4 cm. The membranous portion of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostatic Urethra
The prostatic urethra, the widest and most dilatable part of the urethra canal, is about 3 cm long. It runs almost vertically through the prostate from its base to its apex, lying nearer its anterior than its posterior surface; the form of the canal is spindle-shaped, being wider in the middle than at either extremity, and narrowest below, where it joins the membranous portion. A transverse section of the canal as it lies in the prostate is horse-shoe-shaped, with the convexity directed forward. The keyhole sign, in ultrasound, is associated with a dilated bladder and prostatic urethra. Additional images File:Illu prostate lobes.jpg, Lobes of prostate File:Illu prostate zones.jpg, Zones of prostate File:Illu penis.jpg, Structure of the penis File:Gray1156.png, Vertical section of bladder The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10.14 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico -'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad , a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spongy Urethra
The spongy urethra (cavernous portion of urethra, penile urethra) is the longest part of the male urethra, and is contained in the corpus spongiosum of the penis. It is about 15 cm long, and extends from the termination of the membranous portion to the external urethral orifice (male), external urethral orifice. Commencing below the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm it passes forward and upward to the front of the pubic symphysis; and then, in the flaccid condition of the penis, it bends downward and forward. It is narrow, and of uniform size in the body of the penis, measuring about 6 mm in diameter; it is dilated behind, within the bulb, and again anteriorly within the glans penis, where it forms the fossa navicularis urethrae. The spongy urethra runs along the length of the penis on its ventral (underneath) surface. It is about 15–16 cm in length, and travels through the corpus spongiosum. The ducts from the urethral gland (gland of Littre) enter h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |