|
Urea Reduction Ratio
The urea reduction ratio (URR) is a dimensionless number used to quantify dialysis treatment adequacy. Definition URR = \frac \times 100\% Where: * Upre is the pre-dialysis urea level * Upost is the post-dialysis urea level Whereas the URR is formally defined as the urea reduction "ratio", in practice it is informally multiplied by 100% as shown in the formula above, and expressed as a percent. History and overview The URR was first popularized by Lowrie and Lew in 1991 as a method of measuring amount of dialysis that correlated with patient outcome. This method is very useful because of its simplicity. It permits easy monitoring of the amount of dialysis therapy delivered to individual patients, as well as across dialysis units, groups of units, states, regions, or countries, because monthly predialysis and postdialysis urea nitrogen values are routinely measured. It also permits quality control and improvement initiatives and regulatory oversight. ThUnited States Renal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensionless Number
A dimensionless quantity (also known as a bare quantity, pure quantity, or scalar quantity as well as quantity of dimension one) is a quantity to which no physical dimension is assigned, with a corresponding SI unit of measurement of one (or 1), ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. which is not explicitly shown. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in many fields, such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, engineering, and economics. Dimensionless quantities are distinct from quantities that have associated dimensions, such as time (measured in seconds). Dimensionless units are dimensionless values that serve as units of measurement for expressing other quantities, such as radians (rad) or steradians (sr) for plane angles and solid angles, respectively. For example, optical extent is defined as having units of metres multiplied by steradians. History Quantities having dimension one, ''dimensionless quantities'', regularly occur in sciences, and are formally treated within the fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis (from Greek , , 'dissolution'; from , , 'through', and , , 'loosening or splitting') is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney disease, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is 10–15% of normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler discovered that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials, which was an important conceptual milesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kt/V
In medicine, ''Kt/V'' is a number used to quantify hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis treatment adequacy. *''K'' – dialyzer clearance of urea *''t'' – dialysis time *''V'' – volume of distribution of urea, approximately equal to patient's total body water In the context of hemodialysis, Kt/V is a pseudo-dimensionless number; it is dependent on the pre- and post-dialysis concentration (see below). It is ''not'' the product of ''K'' and ''t'' divided by ''V'', as would be the case in a true dimensionless number. In peritoneal dialysis, it isn't dimensionless at all. It was developed by Frank Gotch and John Sargent as a way for measuring the dose of dialysis when they analyzed the data from the National Cooperative Dialysis Study. In hemodialysis the US National Kidney Foundation ''Kt''/''V'' target is ≥ 1.3, so that one can be sure that the delivered dose is at least 1.2. In peritoneal dialysis the target is ≥ 1.7/week. Despite the name, ''Kt''/''V'' is quit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clearance (medicine)
In pharmacology, clearance is a pharmacokinetic measurement of the volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed per unit time. Usually, clearance is measured in L/h or mL/min. The quantity reflects the rate of drug elimination divided by plasma concentration. Excretion, on the other hand, is a measurement of the amount of a substance removed from the body per unit time (e.g., mg/min, μg/min, etc.). While clearance and excretion of a substance are related, they are not the same thing. The concept of clearance was described by Thomas Addis, a graduate of the University of Edinburgh Medical School. Substances in the body can be cleared by various organs, including the kidneys, liver, lungs, etc. Thus, total body clearance is equal to the sum clearance of the substance by each organ (e.g., renal clearance + hepatic clearance + lung clearance = total body clearance). For many drugs, however, clearance is solely a function of renal excretion. In these cases, clearance is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
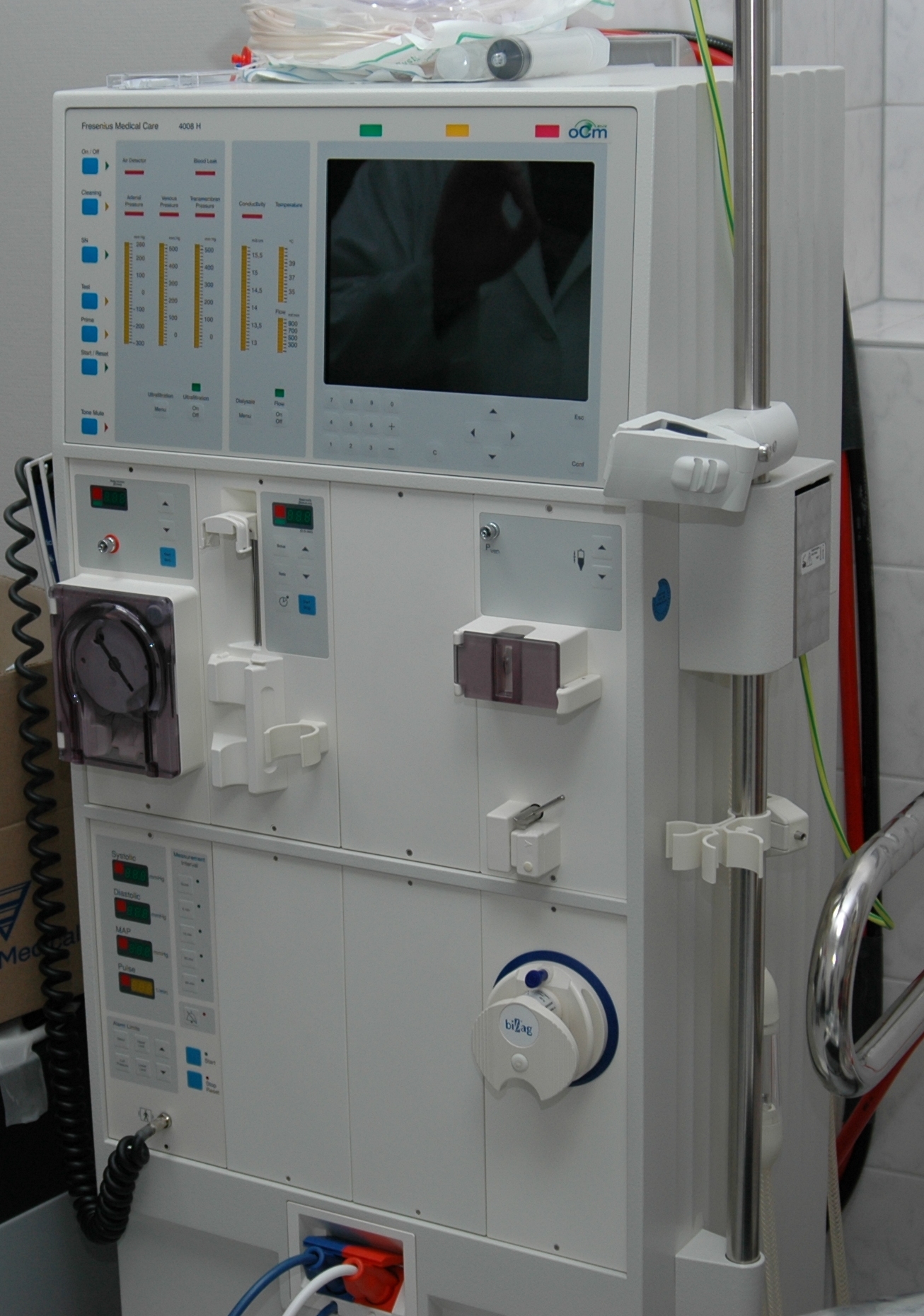
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies (the other two being kidney transplant and peritoneal dialysis). An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis. Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy. Routine hemodialysis is conducted in a dialysis outpatient facility, either a purpose-built room in a hospital or a dedicated, stand-alone clinic. Less frequently hemodialysis is done at home. Dialysis treatments in a clinic are initiated and managed by specialized staff made up of nurses and technicians; dialysis treatments at home can be self-initiated an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
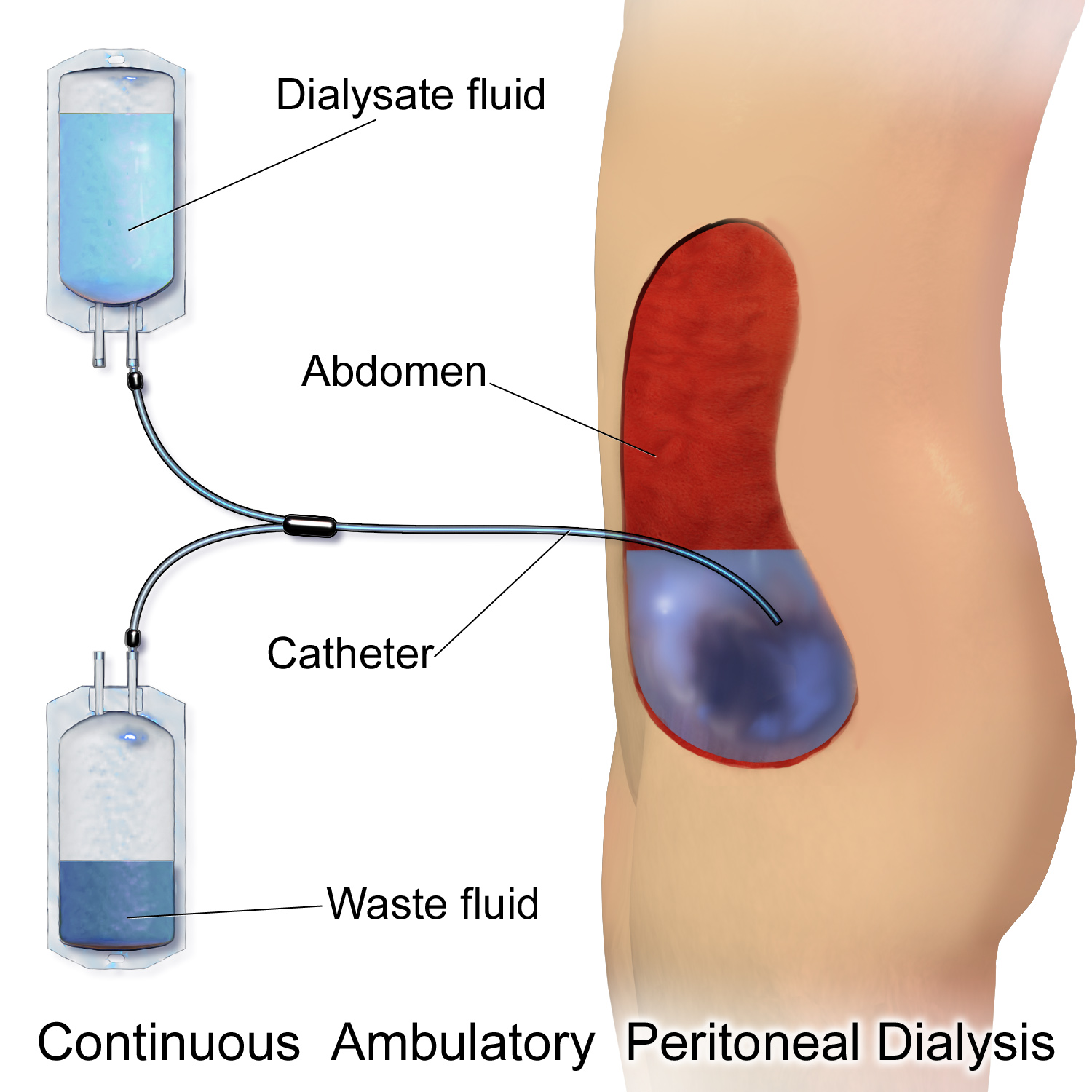
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis which uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first couple of years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease. Complications may include infections within the abdomen, hernias, high blood sugar, bleeding in the abdomen, and blockage of the catheter. Use is not possible in those with significant prior abdominal surgery or inflammatory bowel disease. It requires some degree of technical skill to be done properly. In peritoneal dialysis, a specific solution is introduced through a permanent tube in the lower abdomen and then removed. This may either occur at regular intervals throughout the day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |