|
Uranyl Sulfate
Uranyl sulfate describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula UO2SO4(H2O)n. These salts consist of sulfate, the uranyl ion, and water. They are lemon-yellow solids. Uranyl sulfates are intermediates in some extraction methods used for uranium ores. These compounds can also take the form of an anhydrous salt. Structure The structure of UO2(SO4)(H2O)3.5 is illustrative of the uranyl sulfates. The ''trans''-UO22+ centers are encased in a pentagonal bipyramidal coordination sphere. In the pentagonal plane are five oxygen ligands derived from sulfate and aquo ligands. The compound is a coordination polymer. Uses Aside from the large scale use in mining, uranyl sulfate finds some use as a negative stain in microscopy and tracer in biology. The Aqueous Homogeneous Reactor experiment, constructed in 1951, circulated a fuel composed of 565 grams of U-235 enriched to 14.7% in the form of uranyl sulfate. The acid process of milling uranium ores involves precipitating uranyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranyl Chloride
Uranyl chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula UO2Cl2(H2O)n where n = 0, 1, or 3. These are yellow-colored solids. Synthesis and structures The hydrates are obtained by dissolving uranyl sulfate or uranyl acetate in hydrochloric acid followed by crystallization from concentrated solutions. Depending on the method of drying, one obtains the mono- or the trihydrate. The monohydrate is described as a yellow, sulfur-like powder. It is very hygroscopic. The trihydrate is greenish-yellow. Both hydrates are fluorescent solids that are highly soluble in water. The anhydrous material can be obtained by the reaction of oxygen with uranium tetrachloride: :UCl4 + O2 → UO2Cl2 + Cl2 In terms of structures, all three of these compounds feature the uranyl center (''trans''-UO22+) bound to five additional ligands, which can include (bridging) chloride, water, or another uranyl oxygen. Reactions The aquo ligands can be replaced by a variety of donors, e.g. THF. Industri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Homogeneous Reactor
Aqueous homogeneous reactors (AHR) are a type of nuclear reactor in which soluble nuclear salts (usually uranium sulfate or uranium nitrate) are dissolved in water. The fuel is mixed with the coolant and the moderator, thus the name "homogeneous" ("of the same physical state"). The water can be either heavy water or ordinary (light) water, both of which need to be very pure. Their self-controlling features and ability to handle very large increases in reactivity make them unique among reactors, and possibly safest. At Santa Susana, California, Atomics International performed a series of tests titled The Kinetic Energy Experiments. In the late 1940s, control rods were loaded on springs and then flung out of the reactor in milliseconds. Reactor power shot up from ~100 watts to over ~1,000,000 watts with no problems observed. Aqueous homogeneous reactors were sometimes called "water boilers" (not to be confused with boiling water reactors), as the water inside appears to boil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranyl Compounds
The uranyl ion is an oxycation In chemistry, an oxycation is a polyatomic ion with a positive charge that contains oxygen. Examples * Dioxygenyl ion, * Nitrosonium ion, * Nitronium ion, * Vanadyl ion, VO2+, a very stable oxycation * Uranyl ion, , all natural U6+ occurs in t ... of uranium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula . It has a linear structure with short U–O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen. Four or more ligands may be bound to the uranyl ion in an equatorial plane around the uranium atom. The uranyl ion forms many complex (chemistry), complexes, particularly with ligands that have oxygen donor atoms. Complexes of the uranyl ion are important in the extraction of uranium from its ores and in nuclear fuel reprocessing. Structure and bonding The uranyl ion is linear and symmetrical, with both U–O bond lengths of about 180 pm. The bond lengths are indicative of the presence of multiple bonding between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Becquerel
Antoine Henri Becquerel (; 15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French engineer, physicist, Nobel laureate, and the first person to discover evidence of radioactivity. For work in this field he, along with Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre Curie, received the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics. The SI unit for radioactivity, the becquerel (Bq), is named after him. Biography Early life Becquerel was born in Paris, France, into a wealthy family which produced four generations of physicists: Becquerel's grandfather (Antoine César Becquerel), father ( Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel), and son (Jean Becquerel). Henri started off his education by attending the Lycée Louis-le-Grand school, a prep school in Paris. He studied engineering at the École Polytechnique and the École des Ponts et Chaussées. In 1874, Henri married Lucie Zoé Marie Jamin, who would die while giving birth to their son, Jean. In 1890 he married Louise Désirée Lorieux. Career In Becquerel's early career, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowcake
Yellowcake (also called urania) is a type of uranium concentrate powder obtained from leach solutions, in an intermediate step in the processing of uranium ores. It is a step in the processing of uranium after it has been mined but before fuel fabrication or uranium enrichment. Yellowcake concentrates are prepared by various extraction and refining methods, depending on the types of ores. Typically, yellowcakes are obtained through the milling and chemical processing of uranium ore, forming a coarse powder that has a pungent odor, is insoluble in water, and contains about 80% uranium oxide, which melts at approximately 2880 °C. Overview Originally raw uranium ore was extracted by traditional mining and this is still the case in many mines. It is first crushed to a fine powder by passing it through crushers and grinders to produce "pulped" ore. This is further processed with concentrated acid, alkaline, or peroxide solutions to leach out the uranium. However, nearly ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaching (chemical Science)
Leaching is the process of a solute becoming detached or extracted from its carrier substance by way of a solvent. Leaching is a naturally occurring process which scientists have adapted for a variety of applications with a variety of methods. Specific extraction methods depend on the soluble characteristics relative to the sorbent material such as concentration, distribution, nature, and size. Leaching can occur naturally seen from plant substances (inorganic and organic), solute leaching in soil, and in the decomposition of organic materials. Leaching can also be applied affectedly to enhance water quality and contaminant removal, as well as for disposal of hazardous waste products such as fly ash, or rare earth elements (REEs). Understanding leaching characteristics is important in preventing or encouraging the leaching process and preparing for it in the case where it is inevitable. In an ideal leaching equilibrium stage, all the solute is dissolved by the solvent, leaving th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enriched Uranium
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (238U with 99.2739–99.2752% natural abundance), uranium-235 (235U, 0.7198–0.7202%), and uranium-234 (234U, 0.0050–0.0059%). 235U is the only nuclide existing in nature (in any appreciable amount) that is fissile with thermal neutrons. Enriched uranium is a critical component for both civil nuclear power generation and military nuclear weapons. The International Atomic Energy Agency attempts to monitor and control enriched uranium supplies and processes in its efforts to ensure nuclear power generation safety and curb nuclear weapons proliferation. There are about 2,000 tonnes of highly enriched uranium in the world, produced mostly for nuclear power, nuclear weapons, naval propulsion, and smaller quantities for research reactors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium-235
Uranium-235 (235U or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists in nature as a primordial nuclide. Uranium-235 has a half-life of 703.8 million years. It was discovered in 1935 by Arthur Jeffrey Dempster. Its fission cross section for slow thermal neutrons is about 584.3±1 barns. For fast neutrons it is on the order of 1 barn. Most but not all neutron absorptions result in fission; a minority result in neutron capture forming uranium-236. Natural decay chain :\begin \ce \begin \ce \\ \ce \end \ce \\ \ce \begin \ce \\ \ce \end \ce \end Fission properties The fission of one atom of uranium-235 releases () inside the reactor. That corresponds to 19.54 TJ/ mol, or 83.14 TJ/kg. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
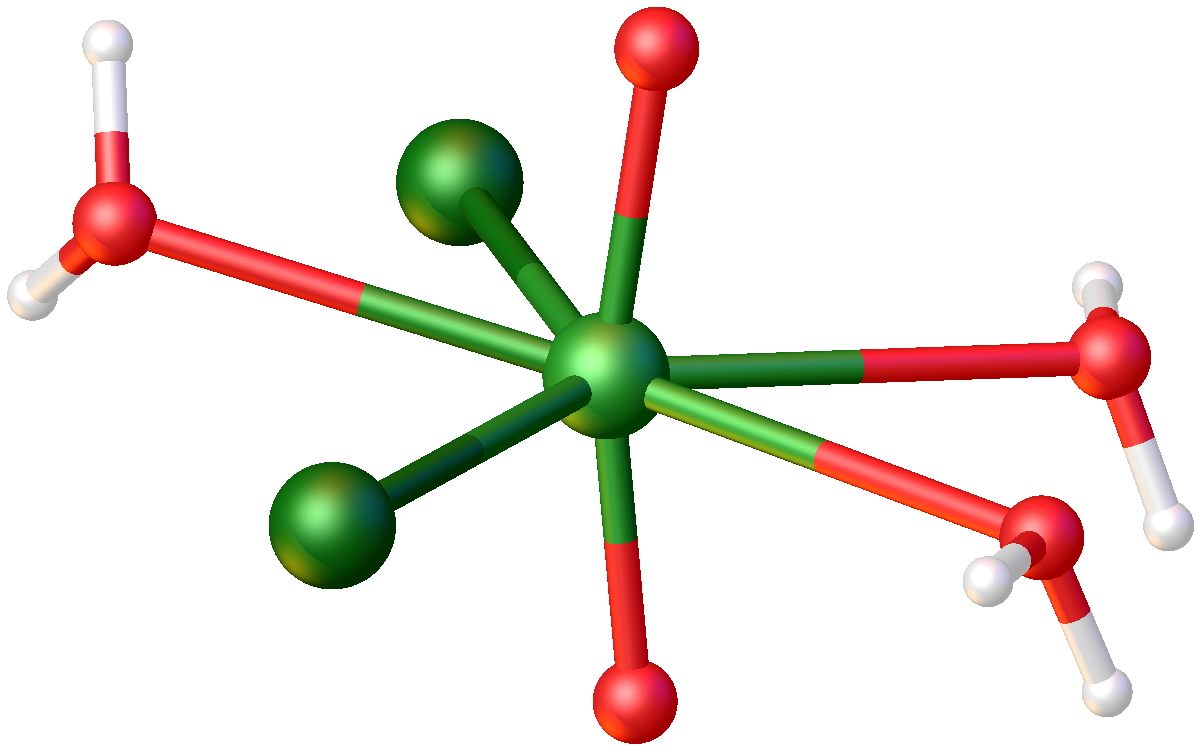
Uranyl Nitrate
Uranyl nitrate is a water-soluble yellow uranium salt with the formula . The hexa-, tri-, and dihydrates are known. The compound is mainly of interest because it is an intermediate in the preparation of nuclear fuels. Uranyl nitrate can be prepared by reaction of uranium salts with nitric acid. It is soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone. As determined by neutron diffraction, the uranyl center is characteristically linear with short U=O distances. In the equatorial plane of the complex are six U-O bonds to bidentate nitrate and two water ligands. At 245 pm, these U-O bonds are much longer than the U=O bonds of the uranyl center. Uses Processing of nuclear fuels Uranyl nitrate is important for nuclear reprocessing. It is the compound of uranium that results from dissolving the decladded spent nuclear fuel rods or yellowcake in nitric acid, for further separation and preparation of uranium hexafluoride for isotope separation for preparing of enriched uranium. A special feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


