|
Uranium City
Uranium City is a northern settlement in Saskatchewan, Canada. Located on the northern shores of Lake Athabasca near the border of the Northwest Territories, it is above sea level. The settlement is northwest of Prince Albert, northeast of Edmonton and south of the Northwest Territories-Saskatchewan boundary. For census purposes, it is located within the province's Division No. 18 territory. History In 1949, athabascaite was discovered by S. Kaiman while he was researching radioactive materials around Lake Athabasca near Uranium City. In 1952, the provincial government decided to establish a community to service the mines in the Beaverlodge uranium area developed by Eldorado Mining and Refining, a federal crown corporation. In 1954, the local newspaper, ''The Uranium Times'', noted that 52 mines were operating and 12 open-pit mines were next to Beaverlodge Lake. Initially, most of the residences in Uranium City were simply tents. Some of the mines operating in the are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Settlement
Communities in the Province of Saskatchewan, Canada include incorporated municipalities, unincorporated communities and First Nations communities. Types of incorporated municipalities include urban municipalities, rural municipalities and northern municipalities. Urban municipalities are further classified into four sub-types – cities, towns, villages and resort villages. Northern municipalities, which are located in the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District (NSAD), are further classified into three sub-types – northern towns, northern villages and northern hamlets. Rural municipalities are not classified into sub-types. Types of unincorporated communities include hamlets and organized hamlets within rural municipalities and northern settlements within the NSAD. The administration of rural municipalities, towns, villages, resort villages, organized hamlets and hamlets is regulated by ''The Municipalities Act'', while the administration of cities is regulated by ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaverlodge Lake
Beaverlodge Lake is a remote lake in northern Saskatchewan, Canada, located east of Uranium City. Road access is provided by Highway 962. The former Eldorado town site is on the lake and there has been extensive uranium exploration in the surrounding area. Islands A number of islands are located in the lake, including: * Hofer Island * Lenz Island * Todd Island * Umisk Island See also *List of lakes of Saskatchewan This is a list of lakes of Saskatchewan, a province of Canada. The largest and most notable lakes are listed at the start, followed by an alphabetical listing of other lakes of the province. Larger lake statistics "The total area of a lak ... References Lakes of Saskatchewan {{Saskatchewan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
First Nations (french: Premières Nations) is a term used to identify those Indigenous Canadian peoples who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group," along with women, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Some of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Written records began with the arrival of European explorers and colonists during the Age of Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis People (Canada)
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives from specific mixed European (primarily French) and Indigenous ancestry which became a distinct culture through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three major groups of Indigenous peoples that were legally recognized in the Constitution Act of 1982, the other two groups being the First Nations and Inuit. Smaller communities who self-identify as Métis exist in Canada and the United States, such as the Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana. The United States recognizes the Little Shell Tribe as an Ojibwe Native American tribe. Alberta is the only Canadian province with a recognized Métis Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Development Research Centre
The International Development Research Centre (IDRC; french: Centre de recherches pour le développement international, ''CRDI'') is a Canadian federal Crown corporation that funds research and innovation within and alongside developing regions as part of Canada’s foreign affairs and development efforts. Activities According to its ''2030 Strategy'', IDRC’s work currently focuses on the following five areas, aimed at contributing to the achievement of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals: climate-resilient food systems; global health; education and science; democratic and inclusive governance; and sustainable inclusive economies. History IDRC was established by the Parliament of Canada in 1970 under the ''International Development Research Centre Act'', which directs IDRC "to initiate, encourage, support and conduct research into the problems of the developing regions of the world and into the means for applying and adapting scientific, technical, and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arvida, Quebec
Arvida ( ) is a settlement of 12,000 people (2010)Peritz, Ingrid, "Saguenay 'utopia' dreaming big again", ''The Globe and Mail'', 13 November 2010, p. A31 in Quebec, Canada, that is part of the City of Saguenay. Its name is derived from the name of its founder, Arthur Vining Davis, president of the Alcoa aluminum company. Arvida was founded as an industrial city by Alcoa in 1927, when the first aluminum smelter was constructed. Located north of Quebec City, south of the Saguenay River between Chicoutimi and Jonquière, the town was planned from the first day and was developed as a company town, to have a population of about 14,000 inhabitants, four Catholic parishes, and many other denominations, parishes and schools. It was known as "the City Built in 135 Days" and described by ''The New York Times'' as a "model town for working families" on "a North Canada steppe". History In 1912 James B. Duke purchased the rights to the power on the Saguenay River, and in 1925 the Isle Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Province of the Canadian Shield, a vast rocky plateau located mainly north of Lake Huron (including Georgian Bay), the French River, Lake Nipissing, and the Mattawa River. The statistical region extends south of the Mattawa River to include all of the District of Nipissing. The southern section of this district lies on part of the Grenville Geological Province of the Shield which occupies the transitional area between Northern and Southern Ontario. The extended federal and provincial quasi-administrative regions of Northern Ontario have their own boundaries even further south in the transitional area that vary according to their respective government policies and requirements. Ontario government departments and agencies such as the Growth Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
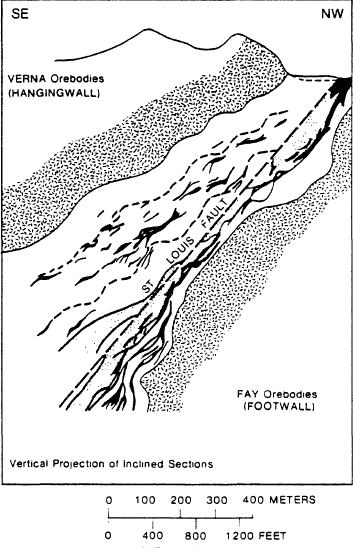
Eldorado, Saskatchewan
Eldorado is a former mining community turned ghost town located on Beaverlodge Lake in northern Saskatchewan, Canada. Its original name was Beaverlodge. Eldorado and nearby Uranium City are along Saskatchewan Highway 962, an isolated stretch of highway. History After uranium was discovered in the Beaverlodge District in 1946, Eldorado Mining and Refining established Eldorado as a community to house its miners, their families, and related workers. By 1951, the community of Eldorado had a population of 184. Eldorado Mining and Refining opened the Beaverlodge Mine in 1953. The Eldorado Company's major production came from the Fay-Ace-Verna mine shafts, mostly from uranium deposits located in the Archaen Tazin Group. The deposits are found within the footwall and hanging wall of the St. Louis fault. Eldorado had a one-room school that taught students through to grade six, after which they were transported to Uranium City. The first post office was established in 1953 with Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorado Mine
__NOTOC__ The Lorado Mine was a uranium mine in northern Saskatchewan, Canada located around south of the community of Uranium City, Saskatchewan in the Beaverlodge Uranium District. See also * Gunnar Mine *Eldorado, Saskatchewan *Uranium ore deposits Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within the Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the more common elements in the Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It ... References External links * * *{{cite web , url=http://www.saskcleans.ca/html/mine_sites/Lorado/index.cfm , publisher=Cleanup of Abandoned Northern Sites (CLEANS) , title= Lorado , accessdate=2009-10-25 Uranium mines in Canada Mines in Saskatchewan Underground mines in Canada Uranium City, Saskatchewan Division No. 18, Saskatchewan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunnar Mine
__NOTOC__ The Gunnar Mine was a uranium mine in northern Saskatchewan, Canada located around southwest of the community of Uranium City, and approximately 600 km north of Saskatoon. The mine was situated on the Crackingstone Peninsula on the north shore of Lake Athabasca in the Beaverlodge Uranium District. The Gunnar deposit was discovered in July 1952, and the mine operated as both an open pit (1955–1961) and underground (1957–1963). The mine ceased production in 1963. The Gunnar Mine headframe was demolished on August 4, 2011 but not decommissioning in any meaningful way. As of 2020, the mine was being decommissioned by the Saskatchewan Research Council who have a license to operate the site until 2024. In 2019 the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission inspection found overall good performance, but some errors with regards to controlling radioactive zones and labeling radioactive materials. These non-compliant acts were descried as having "low safety significance," bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Mining In Canada
For many years, North America was the largest exporter of uranium ore in the world and has been a major world producer since demand for uranium developed. In 2009 Kazakhstan took over top spot, relegating Canada to second. 20% of the world's primary uranium production came from mines in Canada in 2009. 14.5% of the world production came from one mine, McArthur River. Currently the only producing area in Canada is northern Saskatchewan, although other areas have had active mines in the past. History Discovery of uranium Canada's first recorded discovery of uranium came in the 1930s 3 when prospector Gilbert LaBine discovered pitchblende, a major uranium bearing mineral, on the shores of the Great Bear Lake in the Northwest Territories. This discovery led Labine's company, Eldorado Gold Mines Limited, to develop the Eldorado Mine at Port Radium, Northwest Territories in 1932 and a refinery to extract Radium from the ore in Port Hope, Ontario, the following year. Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
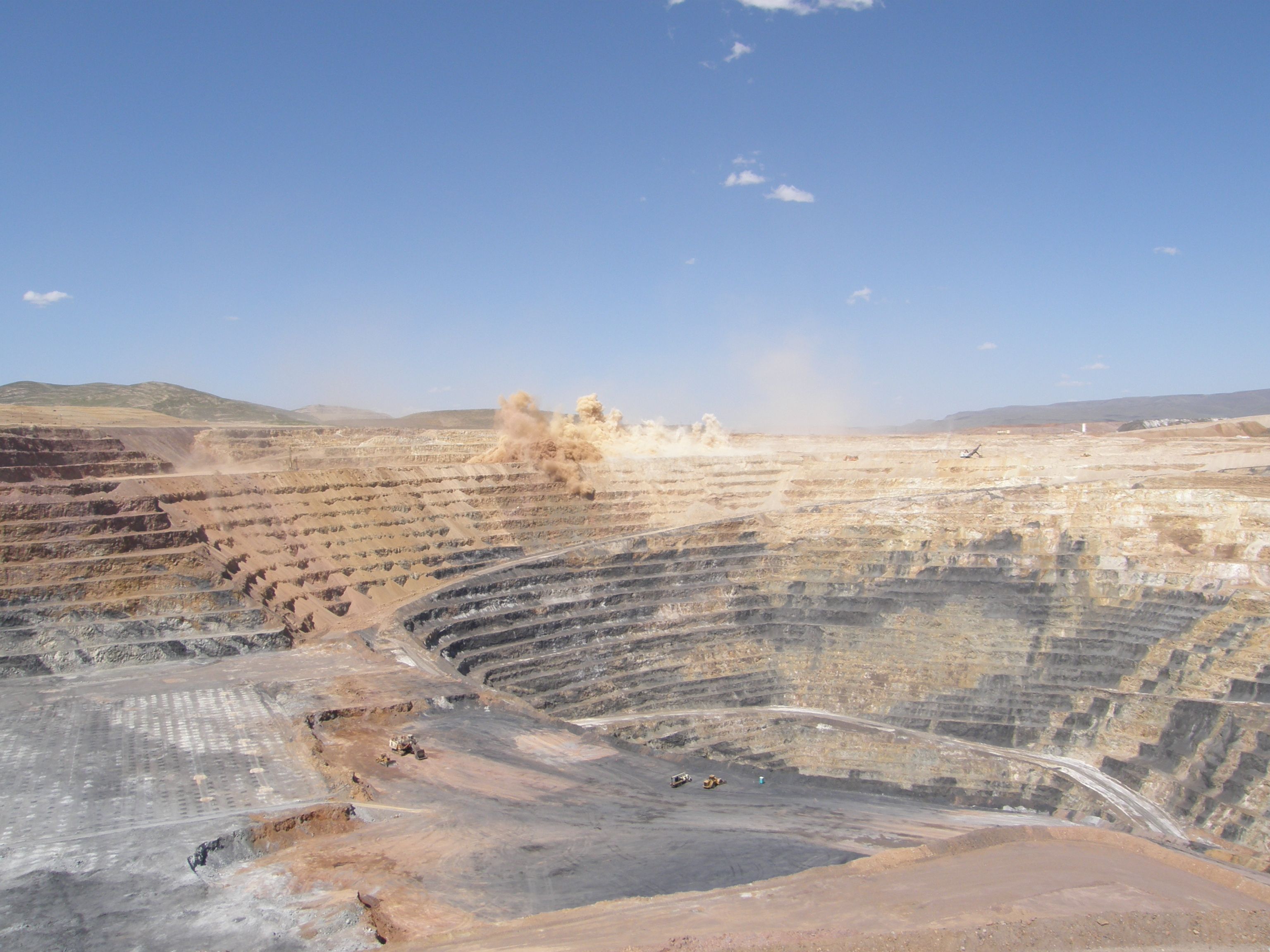
Open-pit Mine
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow. This form of mining differs from extractive methods that require tunnelling into the earth, such as long wall mining. Open-pit mines are used when deposits of commercially useful ore or rocks are found near the surface. It is applied to ore or rocks found at the surface because the overburden is relatively thin or the material of interest is structurally unsuitable for tunnelling (as would be the case for cinder, sand, and gravel). In contrast, minerals that have been found underground but are difficult to retrieve due to hard rock, can be reached using a form of underground mining. To create an open-pit mine, the miners must determine the information of the ore that is underground. This is done through drilling of probe holes in the ground, then plotting eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |