|
Unstated Assumption
An argument map or argument diagram is a visual representation of the structure of an argument. An argument map typically includes the key components of the argument, traditionally called the '' conclusion'' and the ''premises'', also called ''contention'' and ''reasons''. Argument maps can also show co-premises, objections, counterarguments, rebuttals, and lemmas. There are different styles of argument map but they are often functionally equivalent and represent an argument's individual claims and the relationships between them. Argument maps are commonly used in the context of teaching and applying critical thinking. The purpose of mapping is to uncover the logical structure of arguments, identify unstated assumptions, evaluate the support an argument offers for a conclusion, and aid understanding of debates. Argument maps are often designed to support deliberation of issues, ideas and arguments in wicked problems. An argument map is not to be confused with a concept map or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument Map
An argument map or argument diagram is a visual representation of the structure of an argument. An argument map typically includes the key components of the argument, traditionally called the '' conclusion'' and the ''premises'', also called ''contention'' and ''reasons''. Argument maps can also show co-premises, objections, counterarguments, rebuttals, and lemmas. There are different styles of argument map but they are often functionally equivalent and represent an argument's individual claims and the relationships between them. Argument maps are commonly used in the context of teaching and applying critical thinking. The purpose of mapping is to uncover the logical structure of arguments, identify unstated assumptions, evaluate the support an argument offers for a conclusion, and aid understanding of debates. Argument maps are often designed to support deliberation of issues, ideas and arguments in wicked problems. An argument map is not to be confused with a concept map or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependent Premises
A dependant is a person who relies on another as a primary source of income. A common-law spouse who is financially supported by their partner may also be included in this definition. In some jurisdictions, supporting a dependant may enable the provider to claim a tax deduction. In the United Kingdom, a full-time student in higher education who financially supports another adult may qualify for an Adult Dependant's Grant. Taxation In the US, a taxpayer may claim exemptions for their dependants. See also * Military dependent A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ... References {{reflist Interpersonal relationships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflective Equilibrium
Reflective equilibrium is a state of balance or coherence among a set of beliefs arrived at by a process of deliberative mutual adjustment among general principles and particular judgements. Although he did not use the term, philosopher Nelson Goodman introduced the method of reflective equilibrium as an approach to justifying the ''principles'' of inductive logic (this is now known as Goodman's method). The term ''reflective equilibrium'' was coined by John Rawls and popularized in his ''A Theory of Justice'' as a method for arriving at the content of the principles of justice. has pointed out that there are many interpretations of reflective equilibrium that deviate from Rawls' method in ways that reduce the cogency of the idea. Among these misinterpretations, according to Hübner, are definitions of reflective equilibrium as "(a) balancing theoretical accounts against intuitive convictions; (b) balancing general principles against particular judgements; (c) balancing opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherentism
In philosophical epistemology, there are two types of coherentism: the coherence theory of truth; and the coherence theory of justification (also known as epistemic coherentism). Coherent truth is divided between an anthropological approach, which applies only to localized networks ('true within a given sample of a population, given our understanding of the population'), and an approach that is judged on the basis of universals, such as categorical sets. The anthropological approach belongs more properly to the correspondence theory of truth, while the universal theories are a small development within analytic philosophy. The coherentist theory of justification, which may be interpreted as relating to either theory of coherent truth, characterizes epistemic justification as a property of a belief only if that belief is a member of a coherent set. What distinguishes coherentism from other theories of justification is that the set is the primary bearer of justification. As an epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Tree
A decision tree is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. It is one way to display an algorithm that only contains conditional control statements. Decision trees are commonly used in operations research, specifically in decision analysis, to help identify a strategy most likely to reach a goal, but are also a popular tool in machine learning. Overview A decision tree is a flowchart-like structure in which each internal node represents a "test" on an attribute (e.g. whether a coin flip comes up heads or tails), each branch represents the outcome of the test, and each leaf node represents a class label (decision taken after computing all attributes). The paths from root to leaf represent classification rules. In decision analysis, a decision tree and the closely related influence diagram are used as a visual and analytical decision support tool, where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composition Studies
Composition studies (also referred to as composition and rhetoric, rhetoric and composition, writing studies, or simply composition) is the professional field of writing, research, and instruction, focusing especially on writing at the college level in the United States. The flagship national organization for this field is the Conference on College Composition and Communication. In most US and some Canadian colleges and universities, undergraduates take freshman or higher-level composition courses. To support the effective administration of these courses, the development of basic and applied research on the acquisition of writing skills, and an understanding of the history of the uses and transformation of writing systems and writing technologies (among many other subareas of research), over 70 American universities offer doctoral study in rhetoric and composition. These programs of study usually include composition pedagogical theory, linguistics, professional and technical commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing Process
A writing process describes a sequence of physical and mental actions that people take as they produce any kind of text. These actions nearly universally involve tools for physical or digital inscription: e.g., chisels, pencils, brushes, chalk, dies, keyboards, touchscreens, etc.; these tools all have particular affordances that shape writers' processes. Writing processes are highly individuated and task-specific; they often involve other kinds of activities that are not usually thought of as writing ''per se'' (talking, drawing, reading, browsing, etc.). Historical and contemporary perspectives In 1972, Donald M. Murray published a brief manifesto titled "Teach Writing as a Process Not Product", in which he argued that English teachers' conventional training in literary criticism caused them to hold students' work to unhelpful standards of highly polished "finished writing".Donald M. Murray, "Teach Writing as a Process Not Product" ''The Leaflet'' (November 1972), rpt. in ''Cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Problem Structuring Methods
Problem structuring methods (PSMs) are a group of techniques used to model or to map the nature or structure of a situation or state of affairs that some people want to change. PSMs are usually used by a group of people in collaboration (rather than by a solitary individual) to create a consensus about, or at least to facilitate negotiations about, what needs to change. Some widely adopted PSMs include soft systems methodology, the strategic choice approach, and strategic options development and analysis (SODA). Unlike some problem solving methods that assume that all the relevant issues and constraints and goals that constitute the problem are defined in advance or are uncontroversial, PSMs assume that there is no single uncontested representation of what constitutes the problem. PSMs are mostly used with groups of people, but PSMs have also influenced the coaching and counseling of individuals. History The term "problem structuring methods" as a label for these techniques bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Using Harrell's Procedure
Use may refer to: * Use (law), an obligation on a person to whom property has been conveyed * Use (liturgy), a special form of Roman Catholic ritual adopted for use in a particular diocese * Use–mention distinction, the distinction between using a word and mentioning it * Consumption (economics) ** Resource depletion, use to the point of lack of supply ** Psychological manipulation, in a form that treats a person is as a means to an end * Rental utilization, quantification of the use of assets to be continuously let See also * Use case * User story * USE (other) * Used (other) Used may refer to: Common meanings *Used good, goods of any type that have been used before or pre-owned *Used to, English auxiliary verb Places *Used, Huesca, a village in Huesca, Aragon, Spain *Used, Zaragoza, a town in Zaragoza, Aragon, Spain ... * User (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
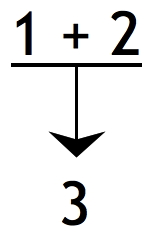
Diagram Using Beardsley's Procedure
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In science the term is used in both ways. For example, Anderson (1997) stated more generally: "diagrams are pictorial, yet abstract, representat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monroe Beardsley
Monroe Curtis Beardsley (; December 10, 1915 – September 18, 1985) was an American philosopher of art. Biography Beardsley was born and raised in Bridgeport, Connecticut, and educated at Yale University (B.A. 1936, Ph.D. 1939), where he received the John Addison Porter Prize. He taught at a number of colleges and universities, including Mount Holyoke College and Yale University, but most of his career was spent at Swarthmore College (22 years) and Temple University (16 years). His wife and occasional coauthor, Elizabeth Lane Beardsley, was also a philosopher at Temple. His work in aesthetics is best known for its championing of the instrumentalist theory of art and the concept of aesthetic experience. Beardsley was elected president of the American Society for Aesthetics in 1956. Among literary critics, Beardsley is known for two essays written with W.K. Wimsatt, "The Intentional Fallacy" and "The Affective Fallacy," both key texts of New Criticism. His books include: ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Sample Argument Using Objections
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''a'' (pronounced ), plural English alphabet#Letter names, ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Greek alphabet#History, Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The Letter case, uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, "English articles, a", and its variant "English articles#Indefinite article, an", are Article (grammar)#Indefinite article, indefinite arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |