|
University Of Copenhagen Zoological Museum
The Copenhagen Zoological Museum (Danish: ''Zoologisk Museum'') is a part of the Natural History Museum of Denmark, which is affiliated with the University of Copenhagen. History The Zoological Museum It is among the world's oldest natural history museums, as its collection was started by Ole Worm more than 350 years ago, although it was officially founded in 1862. Collections The zoological collections contain some 10 million specimens representing an estimated 10 % of described multicellular animal species. The history of the collections reach back in time more than 200 years. Apart from rich collections of Danish animals, the museum has strong representation of: * The North Atlantic and Arctic (especially Greenland) * The former Danish colonies in the West Indies * East Africa (especially the Eastern Arc mountains) * South American insects (especially butterflies) * Philippines, Bismarck and Solomon Islands * Deep Sea faunas * Whale skeletons * Material from several expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan area has 2,057,142 people. Copenhagen is on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the Øresund strait. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. Beginning in the 17th century, it consolidated its position as a regional centre of power with its institutions, defences, and armed forces. During the Renaissance the city served as the de facto capital of the Kalmar Union, being the seat of monarchy, governing the majority of the present day Nordic region in a personal union with Sweden and Norway ruled by the Danis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Fossil
A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors. In 1859, when Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as "the most obvious and gravest objection which can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Museums In Denmark
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums In Copenhagen
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museums In Denmark
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Wilhelm Lund
Peter Wilhelm Lund (14 June 1801 – 25 May 1880) was a Danish paleontologist, zoologist, and archeologist. He spent most of his life working and living in Brazil. He is considered the father of Brazilian paleontology as well as archaeology. He was the first to describe dozens of species of pre-historic Pleistocene megafauna, including the fabled Saber-toothed cat ''Smilodon populator''. He also made the then ground-breaking discovery that humans co-existed with the long-extinct animal species, something which possibly prompted him to terminate his scientific work. His comprehensive collections are today found at the Danish Natural History Museum in Copenhagen. Early life and education Peter Wilhelm Lund was born into a wealthy family in Copenhagen. He showed an early interest in the natural science and was working towards a career in medicine but following the death of his father, his passion for natural history prompted him instead to opt for that study at the University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saber-toothed Cat
Machairodontinae is an extinct subfamily of carnivoran mammals of the family Felidae (true cats). They were found in Asia, Africa, North America, South America, and Europe from the Miocene to the Pleistocene, living from about 16 million until about 11,000 years ago. The Machairodontinae contain many of the extinct predators commonly known as "saber-toothed cats", including the famed genus ''Smilodon'', as well as other cats with only minor increases in the size and length of their maxillary canines. The name means "dagger-tooth", from Greek μάχαιρα (''machaira''), sword. Sometimes, other carnivorous mammals with elongated teeth are also called saber-toothed cats, although they do not belong to the felids. Besides the machairodonts, other saber-toothed predators also arose in the nimravids, barbourofelids, machaeroidines, hyaenodonts and even in two groups of metatherians (the thylacosmilid sparassodonts and the deltatheroideans). Evolution Family Felidae The Mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
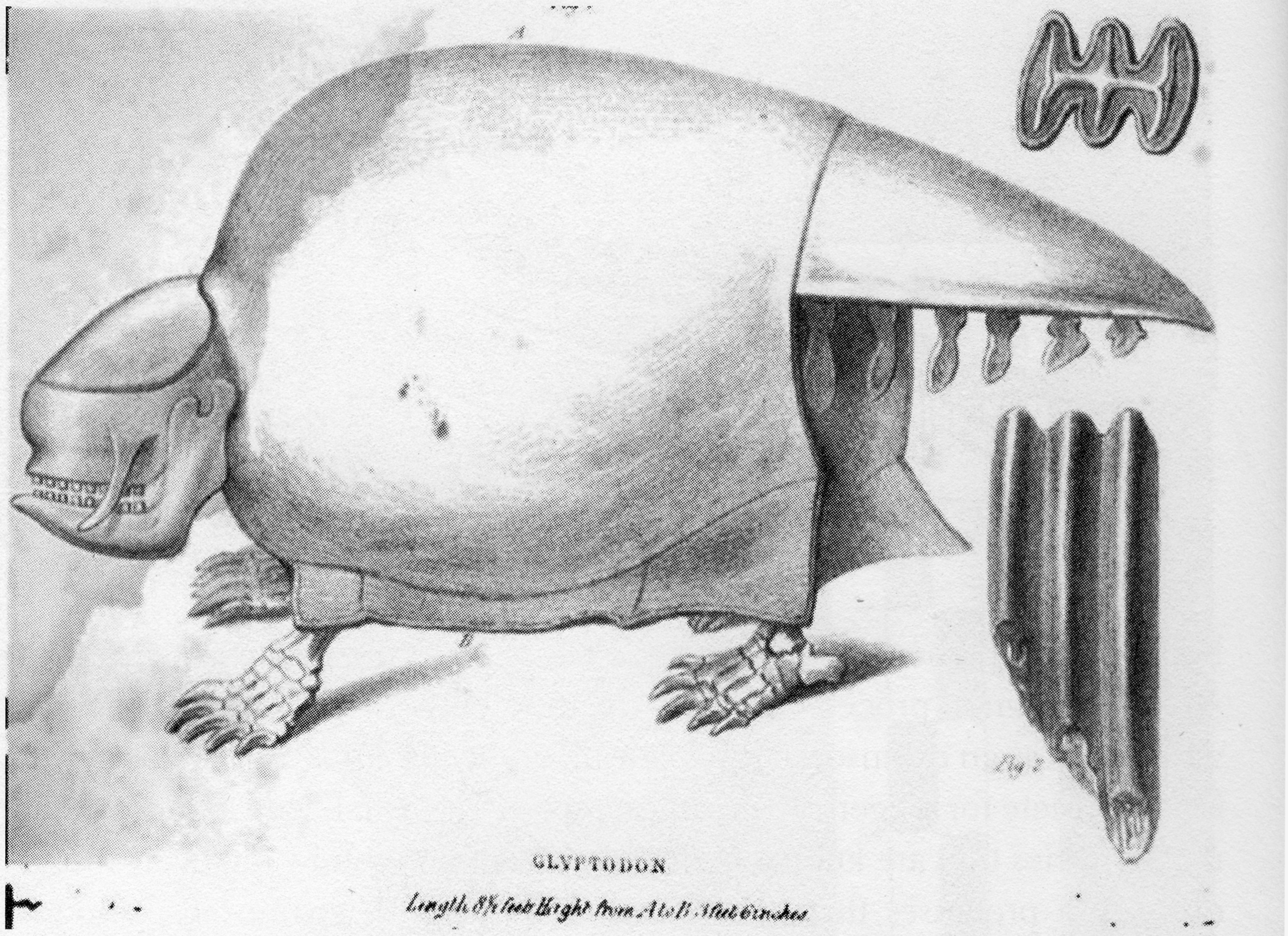
Glyptodon
''Glyptodon'' (from Greek for 'grooved or carved tooth': γλυπτός 'sculptured' and ὀδοντ-, ὀδούς 'tooth') is a genus of glyptodont (an extinct group of large, herbivorous armadillos) that lived from the Pleistocene, around 2.5 million years ago, to the Early Holocene, around 11,000 years ago, in Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, and Colombia. It was the first named extinct cingulate and is the type genus of Glyptodontinae, and, or, Glyptodontinae. Many species have been named for the genus, though few are considered valid, and it is one of, if not the, best known genus of glyptodont. Hundreds of specimens have been referred to the genus, but the holotype, or name specimen, of the type species, ''G. clavipes'', was described in 1839 by notable British paleontologist Sir Richard Owen. It was roughly the same size and weight as a Volkswagen Beetle, 800–840 kg (1,760–1,850 lb). With its rounded, bony shell and squat limbs, it superfic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plumage
Plumage ( "feather") is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, there can be different colour morphs. The placement of feathers on a bird is not haphazard, but rather emerge in organized, overlapping rows and groups, and these are known by standardized names. Most birds moult twice a year, resulting in a breeding or ''nuptial plumage'' and a ''basic plumage''. Many ducks and some other species such as the red junglefowl have males wearing a bright nuptial plumage while breeding and a drab ''eclipse plumage'' for some months afterward. The painted bunting's juveniles have two inserted moults in their first autumn, each yielding plumage like an adult female. The first starts a few days after fledging replacing the ''juvenile plumage'' with an ''auxiliary formative plumage''; the second a month or so l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
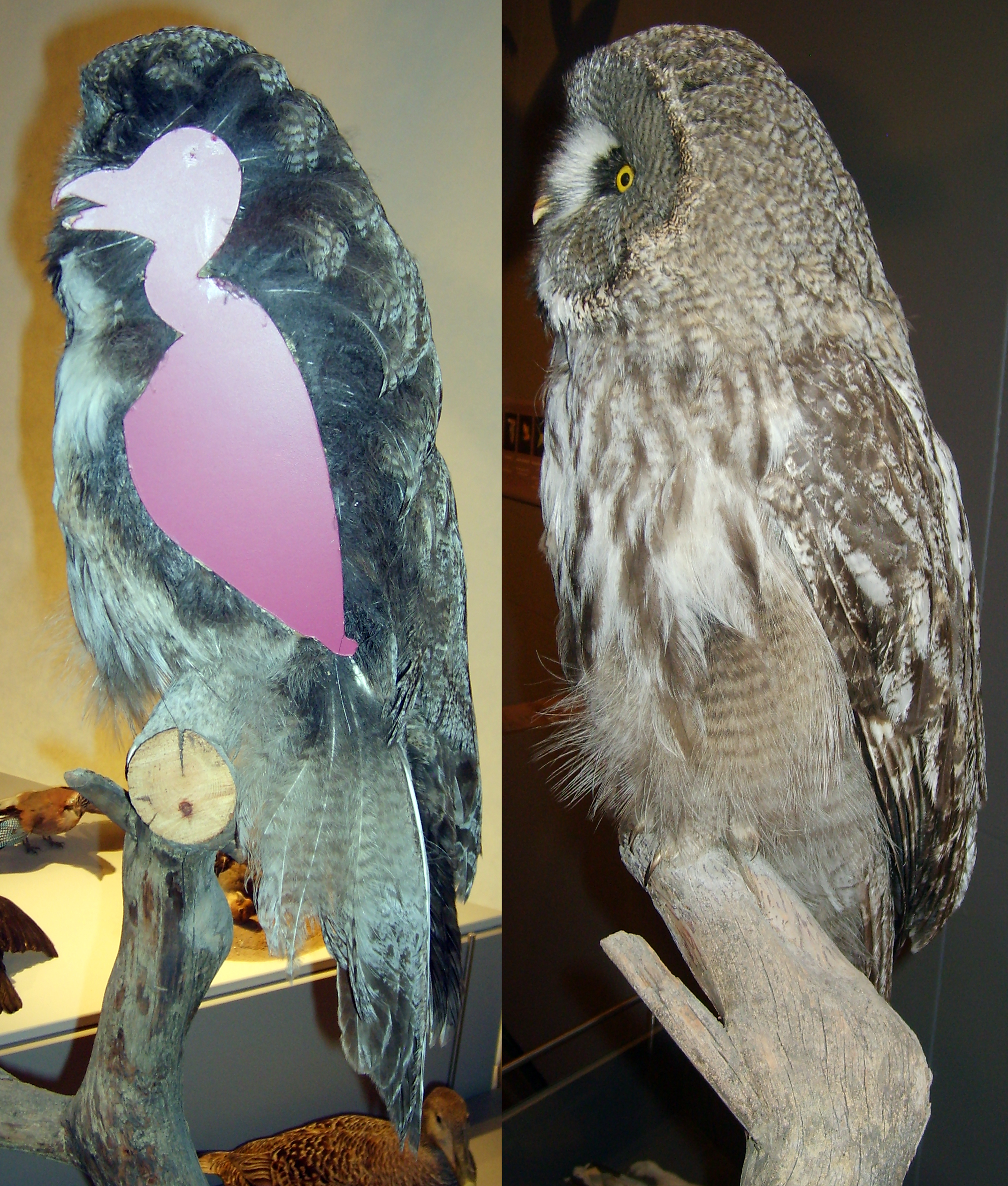
Great Grey Owl
The great grey owl (''Strix nebulosa'') (also great gray owl in American English) is a very large owl, documented as the world's largest species of owl by length. It is distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, and it is the only species in the genus ''Strix'' found in both Eastern and Western Hemispheres. In some areas it is also called Phantom of the North, cinereous owl, spectral owl, Lapland owl, spruce owl, bearded owl, and sooty owl. Description Adults have a large rounded head with a grey face and yellow eyes with darker circles around them. The underparts are light with dark streaks; the upper parts are grey with pale bars. This owl does not have ear tufts and has the largest facial disc of any raptor. There is a white collar or "bow tie" just below the beak. The long tail tapers to a rounded end. In terms of length, the great grey owl is believed to exceed the Eurasian eagle-owl and the Blakiston's fish owl as the world's largest owl. The great grey is outweighed by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Moa
The eastern moa (''Emeus crassus'') is an extinct species of moa. When the first specimens were originally described by Richard Owen, they were placed within the genus ''Dinornis'' as three different species, but, was later split off into their own genus, ''Emeus''. ''E. crassus'' is currently the only species of ''Emeus'', as the other two species, ''E. casuarinus'' and ''E. huttonii'' are now regarded as synonyms of ''E. crassus''. It has been long suspected that the "species" described as ''Emeus huttonii'' and ''E. crassus'' were males and females, respectively, of a single species. This has been confirmed by analysis for sex-specific genetic markers of DNA extracted from bone material; the females of ''E. crassus'' were 15-25% larger than males.Huynen, L. J., ''et al.'' (2003) This phenomenon — reverse size dimorphism — is not uncommon amongst ratites, being also very pronounced in kiwis. Description ''Emeus'' was of average size, standing tall. Like other moa, it h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnacle
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in erosive settings. They are sessile (nonmobile) and most are suspension feeders, but those in infraclass Rhizocephala are highly specialized parasites on crustaceans. They have four nektonic (active swimming) larval stages. Around 1,000 barnacle species are currently known. The name is Latin, meaning "curl-footed". The study of barnacles is called cirripedology. Description Barnacles are encrusters, attaching themselves temporarily to a hard substrate or a symbiont such as a whale ( whale barnacles), a sea snake ('' Platylepas ophiophila''), or another crustacean, like a crab or a lobster (Rhizocephala). The most common among them, "acorn barnacles" ( Sessilia), are sessile where they grow their shells directly onto the substrate. Peduncul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)