|
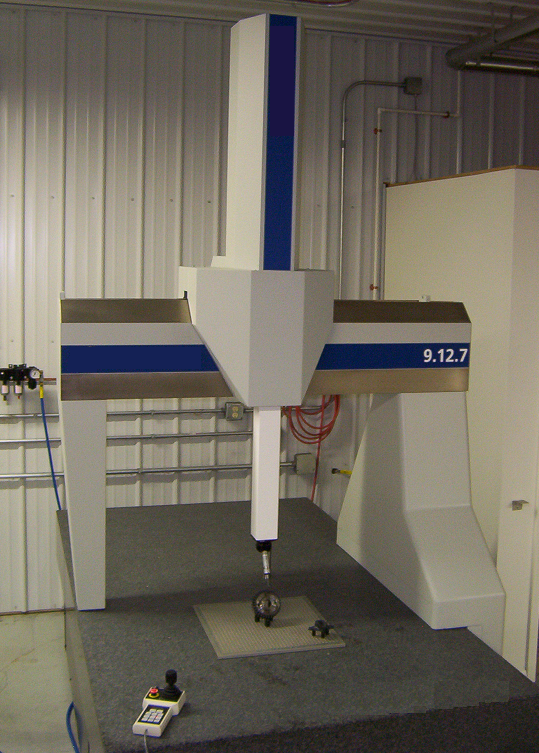
Universal Measuring Machine
Universal measuring machines (UMM) are measurement devices used for objects in which geometric relationships are the most critical element, with dimensions specified from geometric locations (see GD&T) rather than absolute coordinates. The very first uses for these machines was the inspection of gauges and parts produced by jig grinding. While bearing some resemblance to a coordinate-measuring machine (CMM) its usage and accuracy envelope differs significantly. While CMMs typically move in three dimensions and measure with a touch probe, a UMM aligns a spindle (4th axis) with a part geometry using a continuous scanning probe. Originally, universal measuring machines were created to fill a need to continuously measure geometric features in both an absolute and comparative capacity, rather than a point based coordinate measuring system. A CMM provides a rapid method for inspecting absolute points, but geometric relationships, such as runout, parallelism, perpendicularity, et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement Device
Instrumentation a collective term for measuring instruments that are used for indicating, measuring and recording physical quantities. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making. Instrumentation can refer to devices as simple as direct-reading thermometers, or as complex as multi-sensor components of industrial control systems. Today, instruments can be found in laboratories, refineries, factories and vehicles, as well as in everyday household use (e.g., smoke detectors and thermostats) History and development The history of instrumentation can be divided into several phases. Pre-industrial Elements of industrial instrumentation have long histories. Scales for comparing weights and simple pointers to indicate position are ancient technologies. Some of the earliest measurements were of time. One of the oldest water clocks was found in the tomb of the ancient Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep I, buried around 1500 BCE. Improvements were incorpora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Probe
A test probe is a physical device used to connect electronic test equipment to a device under test (DUT). Test probes range from very simple, robust devices to complex probes that are sophisticated, expensive, and fragile. Specific types include test prods, oscilloscope probes and current probes. A test probe is often supplied as a test lead, which includes the probe, cable and terminating connector. Voltage Voltage probes are used to measure voltages present on the DUT. To achieve high accuracy, the test instrument and its probe must not significantly affect the voltage being measured. This is accomplished by ensuring that the combination of instrument and probe exhibit a sufficiently high impedance that will not load the DUT. For AC measurements, the reactive component of impedance may be more important than the resistive. Simple test leads A typical voltmeter probe consists of a single wire ''test lead'' that has on one end a connector that fits the voltmeter and on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayne Moore (swimmer)
Wayne Richard Moore (November 20, 1931 – February 20, 2015) was an American competition swimmer, Olympic champion, and former world record-holder. Moore represented the United States at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki, Finland, where he won a gold medal in the men's 4×200-meter freestyle relay with U.S. teammates Bill Woolsey, Ford Konno and Jimmy McLane. Individually, Moore also competed in the men's 400-meter freestyle at the 1952 Olympics, finishing in sixth place in the event final. Moore was born in Bridgeport, Connecticut in 1931, the son of Richard F. and Mary S. Moore. He was a 1945 graduate of Warren Harding High School, and graduated from Yale University in 1953 with a degree in economics. Swimming for the Yale Bulldogs under coach Bob Kiphuth, Moore won NCAA titles in the 220-yard freestyle in 1952 and 440-yard freestyle in 1953. After college, Moore was drafted in the U.S. Army and served during the Korean War. Moore's father had founded the Moore Speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometric
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that travel in different optical paths, which are then combined again to produce i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1960. Metrology is divided into three basic overlapping activities: * The definition of units of measurement * The realisation of these units of measurement in practice * Traceabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
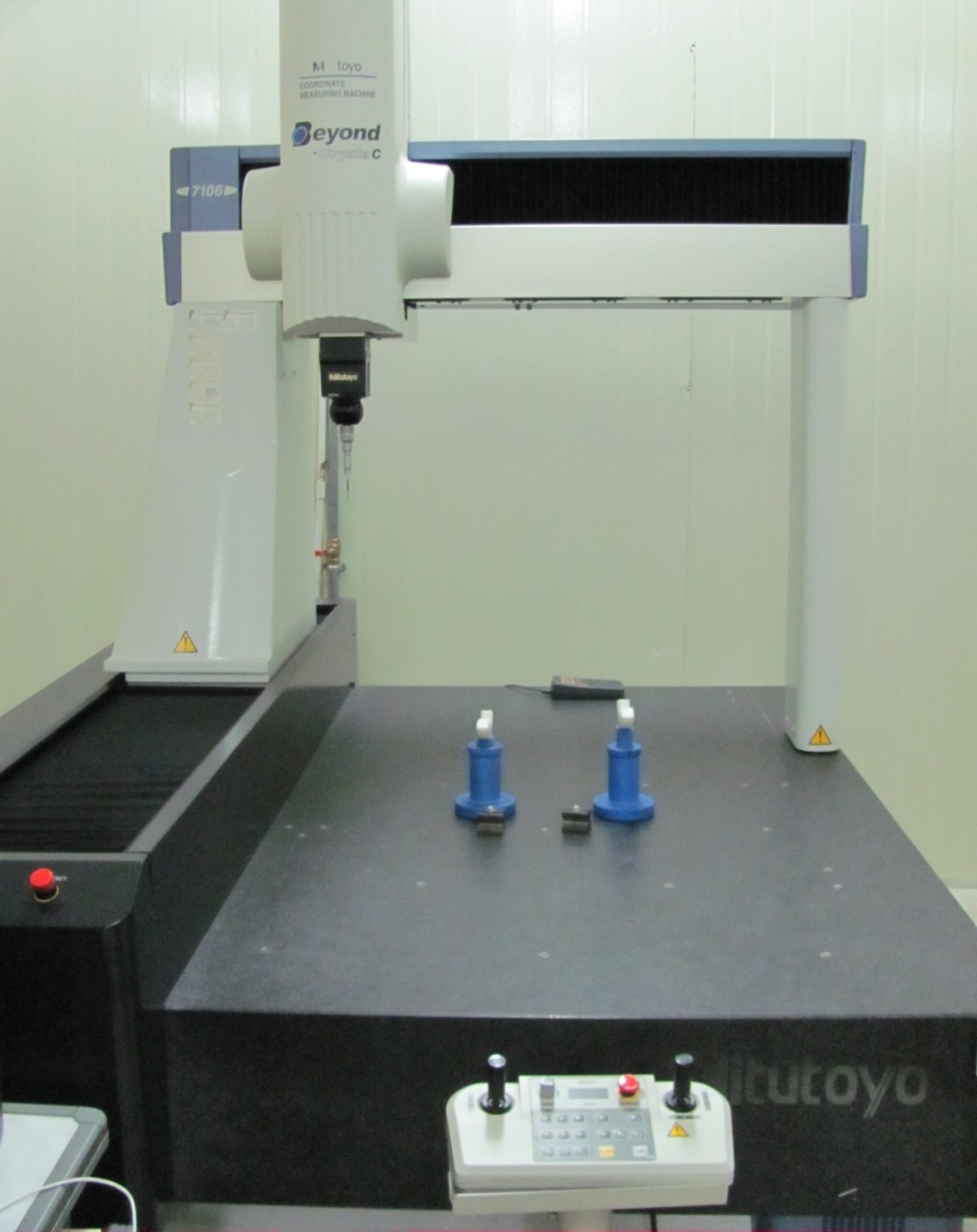
Coordinate-measuring Machine
A coordinate measuring machine (CMM) is a device that measures the geometry of physical objects by sensing discrete points on the surface of the object with a probe. Various types of probes are used in CMMs, the most common being mechanical and laser sensors, though optical and white light sensor do exist. Depending on the machine, the probe position may be manually controlled by an operator or it may be computer controlled. CMMs typically specify a probe's position in terms of its displacement from a reference position in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system (i.e., with XYZ axes). In addition to moving the probe along the X, Y, and Z axes, many machines also allow the probe angle to be controlled to allow measurement of surfaces that would otherwise be unreachable. Description The typical 3D "bridge" CMM allows probe movement along three axes, X, Y and Z, which are orthogonal to each other in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. Each axis has a sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profile (engineering)
In standardization, a profile is a subset internal to a specification. Aspects of a complex technical specification may necessarily have more than one interpretation, and there are probably many optional features. These aspects constitute a profile of the standard. Two implementations engineered from the same description may not interoperate due to having a different profile of the standard. Vendors can even ignore features that they view as unimportant, yet prevail in the long run. The use of profiles in these ways can force one interpretation, or create de facto standards from official standards. Engineers can design or procure by using a profile to ensure interoperability. For example, the International Standard Profile, ISP, is used by the ISO in their ISO ISP series of standards; in the context of OSI networking, Britain uses the UK-GOSIP profile and the US uses US-GOSIP; there are also various mobile profiles adopted by the W3C for web standards. In particular, implemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Of Rotation
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation along a number of stationary axes at the same time is impossible; if two rotations are forced at the same time, a new axis of rotation will appear. This article assumes that the rotation is also stable, such that no torque is required to keep it going. The kinematics and dynamics of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body are mathematically much simpler than those for free rotation of a rigid body; they are entirely analogous to those of linear motion along a single fixed direction, which is not true for ''free rotation of a rigid body''. The expressions for the kinetic energy of the object, and for the forces on the parts of the object, are also simpler for rotation around a fixed axis, than for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicator (distance Amplifying Instrument)
In various contexts of science, technology, and manufacturing (such as machining, fabricating, and additive manufacturing), an indicator is any of various instruments used to accurately measure small distances and angles, and amplify them to make them more obvious. The name comes from the concept of '' indicating'' to the user that which their naked eye cannot discern; such as the presence, or exact quantity, of some small distance (for example, a small height difference between two flat surfaces, a slight lack of concentricity between two cylinders, or other small physical deviations). The classic mechanical version, called a dial indicator, provides a dial display similar to a clock face with clock hands; the hands point to graduations in a circular scales on the dial which represent the distance of the probe tip from a zero setting. The internal works of a mechanical dial indicator are similar to the precision clockworks of a mechanical wristwatch, employing a rack and pinio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Dimensioning And Tolerancing
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) is a system for defining and communicating engineering tolerances and relationships. It uses a symbolic language on engineering drawings and computer-generated three-dimensional solid models that explicitly describe nominal geometry and its allowable variation. It tells the manufacturing staff and machines what degree of accuracy and precision is needed on each controlled feature of the part. GD&T is used to define the nominal (theoretically perfect) geometry of parts and assemblies, to define the allowable variation in form and possible size of individual features, and to define the allowable variation between features. *Dimensioning specifications define the nominal, as-modeled or as-intended geometry. One example is a basic dimension. *Tolerancing specifications define the allowable variation for the form and possibly the size of individual features, and the allowable variation in orientation and location between features. Two exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle (tool)
In machine tools, a spindle is a rotating axis of the machine, which often has a shaft at its heart. The shaft itself is called a spindle, but also, in shop-floor practice, the word often is used metonymically to refer to the entire rotary unit, including not only the shaft itself, but its bearings and anything attached to it (chuck, etc.). A machine tool may have several spindles, such as the headstock and tailstock spindles on a bench lathe. The main spindle is usually the biggest one. References to "the spindle" without further qualification imply the main spindle. Some machine tools that specialize in high-volume mass production have a group of 4, 6, or even more main spindles. These are called multispindle machines. For example, gang drills and many screw machines are multispindle machines. Although a bench lathe has more than one spindle (counting the tailstock), it is not called a multispindle machine; it has one main spindle. Examples of spindles include * On a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate-measuring Machine
A coordinate measuring machine (CMM) is a device that measures the geometry of physical objects by sensing discrete points on the surface of the object with a probe. Various types of probes are used in CMMs, the most common being mechanical and laser sensors, though optical and white light sensor do exist. Depending on the machine, the probe position may be manually controlled by an operator or it may be computer controlled. CMMs typically specify a probe's position in terms of its displacement from a reference position in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system (i.e., with XYZ axes). In addition to moving the probe along the X, Y, and Z axes, many machines also allow the probe angle to be controlled to allow measurement of surfaces that would otherwise be unreachable. Description The typical 3D "bridge" CMM allows probe movement along three axes, X, Y and Z, which are orthogonal to each other in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. Each axis has a sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |