|
Universal Service Obligation
Universal service is an economic, legal and business term used mostly in regulated industries, referring to the practice of providing a baseline level of services to every resident of a country. An example of this concept is found in the US Telecommunications Act of 1996, whose goals are: *to promote the availability of quality services at just, reasonable, and affordable rates *to increase access to advanced telecommunications services throughout the Nation *to advance the availability of such services to all consumers, including those in low income, rural, insular, and high cost areas at rates that are reasonably comparable to those charged in urban areas Universal service was widely adopted in legislation in Europe beginning in the 1980s and 1990s. For instance, under the EU Postal Services Directive (97/67/EC), the Electricity Market Directive (2003/54/EC) and the Telecommunications Directive (2002/22/EC). The language of "universal service" has also been used in proposals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Act Of 1996
The Telecommunications Act of 1996 is a United States federal law enacted by the 104th United States Congress on January 3, 1996, and signed into law on February 8, 1996, by President Bill Clinton. It primarily amended Chapter 5 of Title 47 of the United States Code, The act was the first significant overhaul of United States telecommunications law in more than sixty years, amending the Communications Act of 1934, and represented a major change in American telecommunication law, because it was the first time that the Internet was included in broadcasting and spectrum allotment.The Telecommunications Act of 1996. Title 3, sec. 301. Retrieved frofcc.gov (2011) The goal of the law was to "let anyone enter any communications business – to let any communications business compete in any market against any other." The legislation's primary goal was deregulation of the converging broadcasting and telecommunications markets. The law's regulatory policies have been criticized, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cato Institute
The Cato Institute is an American libertarian think tank headquartered in Washington, D.C. It was founded in 1977 by Ed Crane, Murray Rothbard, and Charles Koch, chairman of the board and chief executive officer of Koch Industries.Koch Industries is the second largest privately held company by revenue in the United States. Cato was established to have a focus on public advocacy, media exposure and societal influence. According to the ''2020 Global Go To Think Tank Index Report'' (Think Tanks and Civil Societies Program, University of Pennsylvania), Cato is number 27 in the "Top Think Tanks Worldwide" and number 13 in the "Top Think Tanks in the United States". The Cato Institute is libertarian in its political philosophy, and advocates a limited role for government in domestic and foreign affairs as well as a strong protection of civil liberties. This includes support for lowering or abolishing most taxes, opposition to the Federal Reserve system and the Affordable Care Act, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
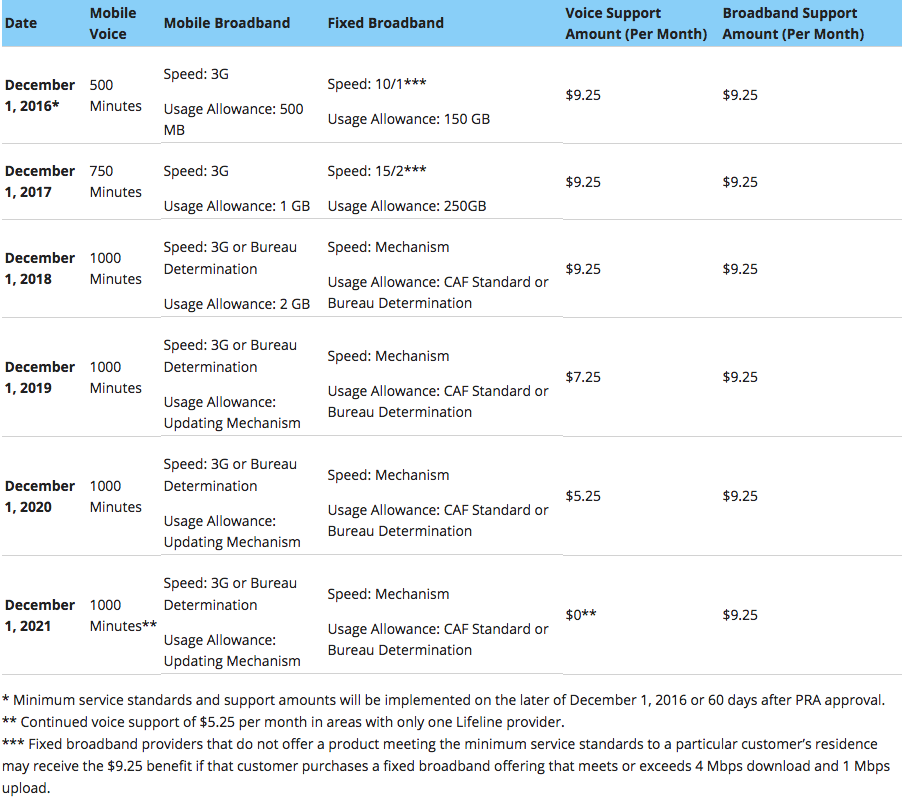
Universal Service Fund
The Universal Service Fund (USF) is a system of telecommunications subsidies and fees managed by the United States Federal Communications Commission (FCC) intended to promote universal access to telecommunications services in the United States. The FCC established the fund in 1997 in compliance with the Telecommunications Act of 1996. The FCC is a government agency that implements and enforces telecommunications regulations across the U.S. and its territories. The Universal Service Fund's budget ranges from $5–8 billion per year depending on the needs of the telecommunications providers. These needs include the cost to maintain the hardware needed for their services and the services themselves. The total 2019 proposed budget for the USF was $8.4 billion. The budget is revised quarterly allowing the service providers to accurately estimate their costs. As of 2019, roughly 60% of the USF budget was put towards “high-cost” areas, 19% went to libraries and schools, 13% was for low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baby Bell
The Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOC) are the result of '' United States v. AT&T'', the U.S. Department of Justice antitrust suit against the former American Telephone & Telegraph Company (later known as AT&T Corp.). On January 8, 1982, AT&T Corp. settled the suit and agreed to divest its local exchange service operating companies. Effective January 1, 1984, AT&T Corp.'s local operations were split into seven independent Regional Bell Operating Companies known as the Baby Bells. RBOCs were originally known as Regional Holding Companies (RHCs). Currently, three companies have the RBOCs as predecessors: AT&T, Verizon, and Lumen Technologies. Some other companies are holding onto smaller segments of the companies. Baby Bells A baby bell is local telephone company in the United States that was in existence at the time of the breakup of AT&T into the resulting Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs), also known as the "Baby Bells." Sometimes also referred to as an "IL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBC Communications
The history of AT&T dates back to the invention of the telephone. The Bell Telephone Company was established in 1877 by Alexander Graham Bell, who obtained the first US patent for the telephone, and his father-in-law, Gardiner Greene Hubbard. Bell and Hubbard also established AT&T Corporation, American Telephone and Telegraph Company in 1885, which acquired the Bell Telephone Company and became the primary telephone company in the United States. This company maintained an effective monopoly on local telephone service in the United States until anti-trust regulators agreed to allow AT&T to retain Western Electric and enter general trades computer manufacture and sales in return for its offer to Breakup of the Bell System, split the Bell System by divesting itself of ownership of the Bell Operating Companies in 1982. AT&T Corporation was eventually purchased by one of the Regional Bell Operating Companies, the former Southwestern Bell Company, in 2005, and the combined company became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell System Divestiture
The breakup of the Bell System was mandated on January 8, 1982, by an agreed consent decree providing that AT&T Corporation would, as had been initially proposed by AT&T, relinquish control of the Bell Operating Companies, which had provided local telephone service in the United States. This effectively took the monopoly that was the Bell System and split it into entirely separate companies that would continue to provide telephone service. AT&T would continue to be a provider of long-distance service, while the now-independent Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs), nicknamed the "Baby Bells", would provide local service, and would no longer be directly supplied with equipment from AT&T subsidiary Western Electric. This divestiture was initiated by the filing in 1974 by the United States Department of Justice of an antitrust lawsuit against AT&T. AT&T was, at the time, the sole provider of telephone service throughout most of the United States. Furthermore, most telephonic eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdiction over the areas of broadband access, fair competition, radio frequency use, media responsibility, public safety, and homeland security. The FCC was formed by the Communications Act of 1934 to replace the radio regulation functions of the Federal Radio Commission. The FCC took over wire communication regulation from the Interstate Commerce Commission. The FCC's mandated jurisdiction covers the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and the territories of the United States. The FCC also provides varied degrees of cooperation, oversight, and leadership for similar communications bodies in other countries of North America. The FCC is funded entirely by regulatory fees. It has an estimated fiscal-2022 budget of US $388 million. It has 1,482 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Radio Commission
The Federal Radio Commission (FRC) was a government agency that regulated United States radio communication from its creation in 1927 until 1934, when it was succeeded by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). The FRC was established by the Radio Act of 1927, which replaced the Radio Act of 1912 after the earlier law was found to lack sufficient oversight provisions, especially for regulating broadcasting stations. In addition to increased regulatory powers, the FRC introduced the standard that, in order to receive a license, a radio station had to be shown to be "in the public interest, convenience, or necessity". Previous regulation Radio Act of 1912 Although radio communication (originally known as "wireless telegraphy") was developed in the late 1890s, it was largely unregulated in the United States until the passage of the Radio Act of 1912. This law set up procedures for the Department of Commerce to license radio transmitters, which initially consisted primarily of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Act Of 1934
The Communications Act of 1934 is a United States federal law signed by President Franklin D. Roosevelt on June 19, 1934 and codified as Chapter 5 of Title 47 of the United States Code, et seq. The Act replaced the Federal Radio Commission with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). It also transferred regulation of interstate telephone services from the Interstate Commerce Commission to the FCC. The first section of the Act originally read as follows: "For the purpose of regulating interstate and foreign commerce in communication by wire and radio so as to make available, so far as possible to all the people of the United States a rapid, efficient, Nation-wide, and world-wide wire and radio communication service with adequate facilities at reasonable charges, for the purpose of the national defense, for the purpose of promoting safety of life and property through the use of wire and radio communication, and for the purpose of securing a more effective execution of this pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate Commerce Commission
The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) was a regulatory agency in the United States created by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887. The agency's original purpose was to regulate railroads (and later trucking) to ensure fair rates, to eliminate rate discrimination, and to regulate other aspects of common carriers, including interstate bus lines and telephone companies. Congress expanded ICC authority to regulate other modes of commerce beginning in 1906. Throughout the 20th century, several of ICC's authorities were transferred to other federal agencies. The ICC was abolished in 1995, and its remaining functions were transferred to the Surface Transportation Board. The Commission's five members were appointed by the President with the consent of the United States Senate. This was the first independent agency (or so-called ''Fourth Branch''). Creation The ICC was established by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887, which was signed into law by President Grover Cleveland. The cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antitrust
Competition law is the field of law that promotes or seeks to maintain market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies. Competition law is implemented through public and private enforcement. It is also known as antitrust law (or just antitrust), anti-monopoly law, and trade practices law. The history of competition law reaches back to the Roman Empire. The business practices of market traders, guilds and governments have always been subject to scrutiny, and sometimes severe sanctions. Since the 20th century, competition law has become global. The two largest and most influential systems of competition regulation are United States antitrust law and European Union competition law. National and regional competition authorities across the world have formed international support and enforcement networks. Modern competition law has historically evolved on a national level to promote and maintain fair competition in markets principally within the territorial boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

