|
United Nations Conference On Trade And Development
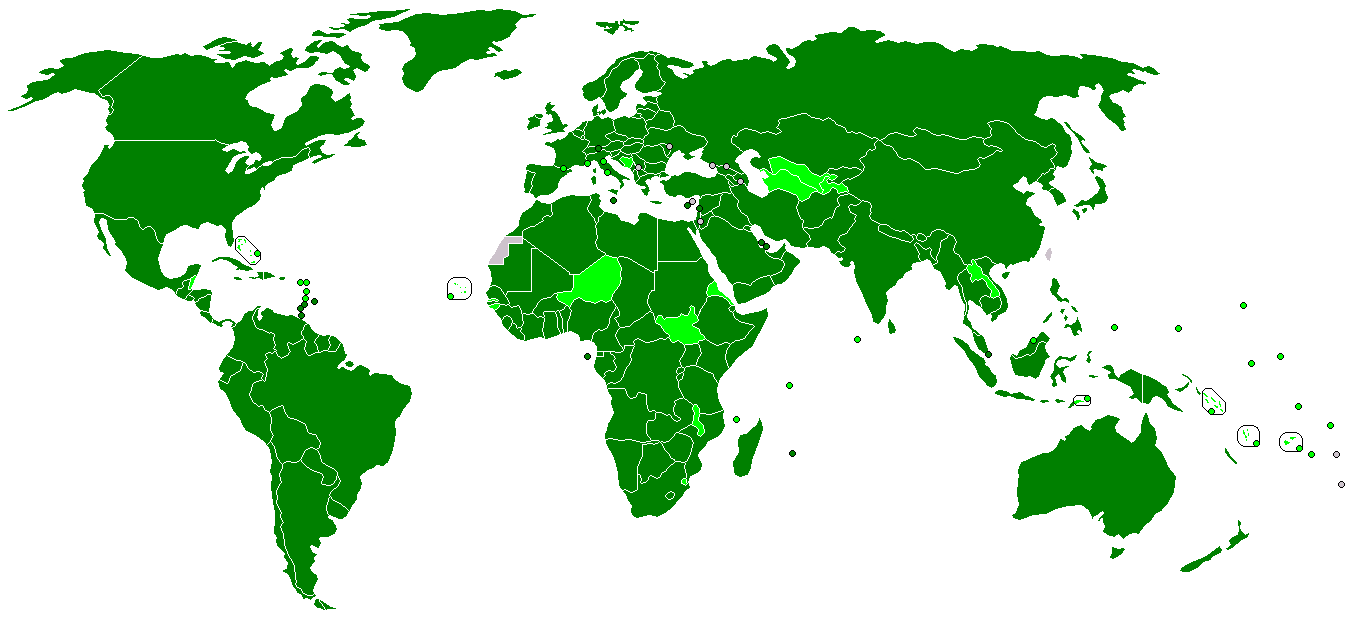
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) and reports to that body and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). UNCTAD is composed of 195 member states and works with nongovernmental organizations worldwide; its permanent secretariat is in Geneva, Switzerland. The primary objective of UNCTAD is to formulate policies relating to all aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance and technology. It was created in response to concerns among developing countries that existing international institutions like GATT (now replaced by the World Trade Organization), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank were not properly organized to handle the particular problems of developing countries; UNCTAD w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebeca Grynspan
Rebeca Grynspan Mayufis (born 14 December 1955) is a Costa Rican economist who has been serving as Secretary General of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) since 13 September 2021. Grynspan previously served as Ibero-American Secretary General (2014–2021) and as UN Under-Secretary-General and the Associate Administrator of the United Nations Development Programme (2010–2014). She previously served as Director of UNDP's Regional Bureau for Latin America and the Caribbean, appointed to the position by United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan in December 2005. She was the Vice President of Costa Rica from 1994 to 1998. Early life and education Grynspan is the daughter of Manuel Grynspan Burstin and Sara Mayufis Schapiro, immigrants from Poland of Jewish ancestry. Grynspan obtained a Bachelor of Science degree with a major in economics from the University of Costa Rica and later on a Master of Arts in Economics from Sussex University. Early career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgetown
Bridgetown (UN/LOCODE: BB BGI) is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The City", but the most common reference is simply "Town". As of 2014, its metropolitan population stands at roughly 110,000. The ''Bridgetown'' port, found along Carlisle Bay (at ) lies on the southwestern coast of the island. Parts of the Greater Bridgetown area (as roughly defined by the Ring Road Bypass or more commonly known as the ABC Highway), sit close to the borders of the neighbouring parishes Christ Church and St. James. The Grantley Adams International Airport for Barbados, is located southeast of Bridgetown city centre, and has daily flights to major cities in the United Kingdom, United States, Canada and the Caribbean. There is no longer a local municipal government, but it is a constituency of the national Parliament. During t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Industrial Development Organization
The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) (French: Organisation des Nations unies pour le développement industriel; French/Spanish acronym: ONUDI) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that assists countries in economic and industrial development. It is headquartered at the UN Office in Vienna, Austria, with a permanent presence in over 60 countries. As of April 2019, UNIDO comprises 170 member states, which together set the organization's policies, programs, and principles through the biannual General Conference. UNIDO was established in 1966 by the UN General Assembly to promote and accelerate the industrialization of developing countries, which were emerging from decolonization in record numbers and with little to no industrial base. In 1979 it became one of the 15 specialized agencies of the UN, with its new constitution coming into force in 1985. Since its founding, the organization has restructured and reformed several times; the 2013 Lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
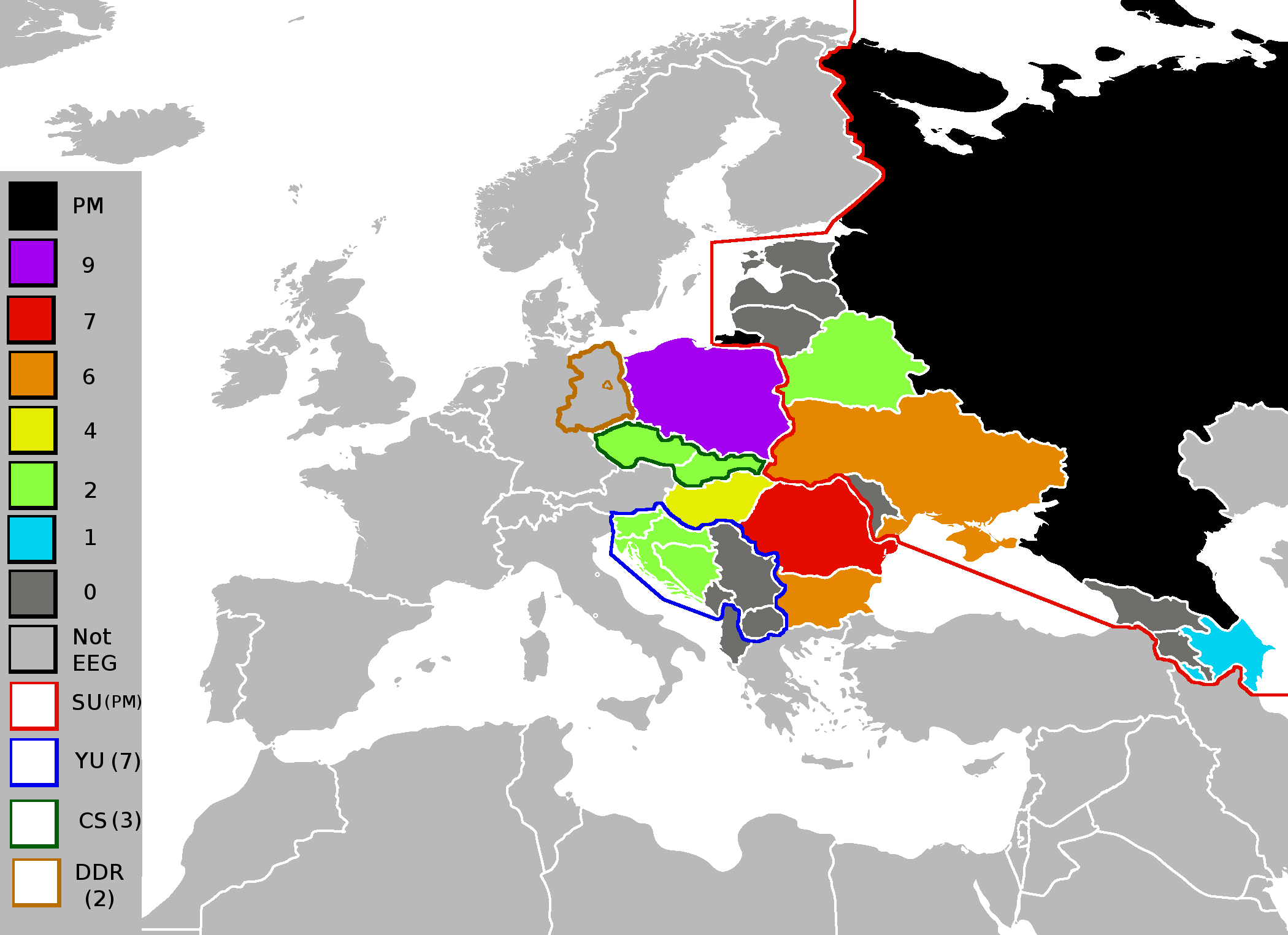
Eastern European Group
The Group of Eastern European States (EEG) is one of the five United Nations regional groups and is composed of 23 Member States from Eastern, Central and Southern Europe. The Group, as with all the regional groups, is a non-binding dialogue group where subjects concerning regional and international matters are discussed. Additionally, the Group works to help allocate seats on United Nations bodies by nominating candidates from the region. History Prior to the creation of the Regional Groups in 1964, the United Nations Security Council had an Eastern European and Asian Seat, that was occupied between 1946 and 1964 by countries from Eastern Europe (including Greece and Turkey), as well as by members of the modern Western European and Others and Asia-Pacific Groups. Since its creation, the Group has changed significantly due to the dissolution of various members: the Soviet Union in 1991, Yugoslavia between 1991-2006 and Czechoslovakia in 1993. Additionally, through the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European And Others Group
The Group of Western European and Other States, also known as the Western European and Other States Group or WEOG, is one of the five United Nations regional groups and is composed of 28 Member States mainly from Western Europe, but also from Oceania, Northern America, and Western Asia. The Group is a non-binding dialogue group where subjects concerning regional and international matters are discussed. Additionally, the Group works to help allocate seats on United Nations bodies by nominating candidates from the region. Unlike most other Regional Groups, WEOG is unusual in that geography is not the sole defining factor of its membership. Instead, its membership is based on geopolitical breakdown, namely its member states share a Western-Democratic common denominator. For example, Canada, Australia and New Zealand are WEOG members even though they are not geographically close to Western Europe, but are culturally and politically descended from Western European states, in par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Regional Groups
The United Nations Regional Groups are the geopolitical regional groups of member states of the United Nations. Originally, the UN member states were unofficially organized into five groups as an informal means of sharing the distribution of posts for General Assembly committees. Now this grouping has taken on a much more expansive and official role. Many UN bodies are allocated on the basis of geographical representation. Top leadership positions, including Secretary-General and President of the General Assembly, are rotated among the regional groups. The groups also coordinate substantive policy and form common fronts for negotiations and bloc voting. History League of Nations The precedent of the geographic distribution of seats was set by the United Nations' predecessor, the League of Nations. Under the League's system, a Nominations Committee was created in order to create election slates for distribution of seats in the Council of the League. This proved a difficult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rome, which has ecclesiastical jurisdiction over the Catholic Church and the sovereign city-state known as the Vatican City. According to Catholic tradition it was founded in the first century by Saints Peter and Paul and, by virtue of Petrine and papal primacy, is the focal point of full communion for Catholic Christians around the world. As a sovereign entity, the Holy See is headquartered in, operates from, and exercises "exclusive dominion" over the independent Vatican City State enclave in Rome, of which the pope is sovereign. The Holy See is administered by the Roman Curia (Latin for "Roman Court"), which is the central government of the Catholic Church. The Roman Curia includes various dicasteries, comparable to ministries and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Palestine
Palestine ( ar, فلسطين, Filasṭīn), officially the State of Palestine ( ar, دولة فلسطين, Dawlat Filasṭīn, label=none), is a state located in Western Asia. Officially governed by the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), it claims the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip as its territory, though the entirety of that territory has been occupied by Israel since the 1967 Six-Day War. As a result of the Oslo Accords of 1993–1995, the West Bank is currently divided into 165 Palestinian enclaves that are under partial Palestinian National Authority (PNA) rule; the remainder, including 200 Israeli settlements, is under full Israeli control. The Gaza Strip has been ruled by the militant Islamic group Hamas and has been subject to a long-term blockade by Egypt and Israel since 2007. After World War II, in 1947, the United Nations (UN) adopted a Partition Plan for Mandatory Palestine, which recommended the creation of independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member States Of The United Nations
The United Nations member states are the sovereign states that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the United Nations General Assembly, UN General Assembly. The UN is the world's largest international organization, intergovernmental organization. The criteria for admission of new members to the UN are set out in Chapter II of the United Nations Charter, Chapter II, Article 4 of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter: # Membership in the United Nations is open to all peace-loving states which accept the obligations contained in the present Charter and, in the judgement of the Organization, are able and willing to carry out these obligations. # The admission of any such state to membership in the United Nations will be effected by a decision of the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the United Nations Security Council, Security Council. A recommendation for admission from the Security Council requires affirmative votes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNCTAD List ABCD Map 2021
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) and reports to that body and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). UNCTAD is composed of 195 member states and works with nongovernmental organizations worldwide; its permanent secretariat is in Geneva, Switzerland. The primary objective of UNCTAD is to formulate policies relating to all aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance and technology. It was created in response to concerns among developing countries that existing international institutions like GATT (now replaced by the World Trade Organization), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank were not properly organized to handle the particular problems of developing countries; UNCTAD woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)