|
United Express Flight 2415
United Express Flight 2415 was a regularly scheduled flight in the northwest United States from Seattle to Pasco, Washington, operated using a BAe Jetstream 31. Late on Tuesday, December 26, 1989, Flight 2415 crashed while attempting to land at Pasco's Tri-Cities Airport, killing both pilots and all four passengers aboard. Aircraft, crew, and flight information North Pacific Airlines, operating as United Express, operated Flight 2415 as a regularly scheduled flight from Seattle to Pasco, with an intermediate stop in Yakima. On the night of the accident, Flight 2415 was operated using a BAe Jetstream 31 twin-turboprop airliner, registration number ''N410UE''. The aircraft was manufactured two years earlier in October 1987, and had accumulated approximately 4,972 flight hours at the time of the accident. The aircraft was not equipped with a ground proximity warning system and did not have a cockpit voice recorder or flight data recorder. The captain was 38-year-old Barry W. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot Error
Pilot error generally refers to an Aviation accidents and incidents, accident in which an action or decision made by the Aircraft pilot#Airline, pilot was the cause or a contributing factor that led to the accident, but also includes the pilot's failure to make a correct decision or take proper action. Errors are intentional actions that fail to achieve their intended outcomes. Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation, Chicago Convention defines accident as "An occurrence associated with the operation of an aircraft [...] in which [...] a person is fatally or seriously injured [...] ''except when the injuries are [...] inflicted by other persons."'' Hence the definition of the "pilot error" does not include deliberate crash (and such crash is not an accident). The causes of pilot error include psychological and physiological human limitations. Various forms of threat and error management have been implemented into pilot training programs to teach crew members how t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockpit Voice Recorder
A flight recorder is an electronic recording device placed in an aircraft for the purpose of facilitating the investigation of aviation accidents and incidents. The device may often be referred to as a "black box", an outdated name which has become a misnomer—they are now required to be painted bright orange, to aid in their recovery after accidents. There are two types of flight recording devices: the flight data recorder (FDR) preserves the recent history of the flight through the recording of dozens of parameters collected several times per second; the cockpit voice recorder (CVR) preserves the recent history of the sounds in the cockpit, including the conversation of the pilots. The two devices may be combined into a single unit. Together, the FDR and CVR objectively document the aircraft's flight history, which may assist in any later investigation. The two flight recorders are required by international regulation, overseen by the International Civil Aviation Organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airliner Accidents And Incidents Caused By Ice
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an airplane intended for carrying multiple passengers or cargo in commercial service. The largest of them are wide-body jets which are also called twin-aisle because they generally have two separate aisles running from the front to the back of the passenger cabin. These are usually used for long-haul flights between airline hubs and major cities. A smaller, more common class of airliners is the narrow-body or single-aisle. These are generally used for short to medium-distance flights with fewer passengers than their wide-body counterparts. Regional airliners typically seat fewer than 100 passengers and may be powered by turbofans or turboprops. These airliners are the non- mainline counterparts to the larger aircraft operated by the major carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Accidents And Incidents Caused By Air Traffic Controller Error
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. Etymology The word ''aviation'' was coined by the French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863. He derived the term from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airliner Accidents And Incidents Caused By Pilot Error
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an airplane intended for carrying multiple passengers or cargo in commercial service. The largest of them are wide-body aircraft, wide-body jets which are also called twin-aisle because they generally have two separate aisles running from the front to the back of the passenger cabin. These are usually used for Flight length#long-haul, long-haul flights between airline hubs and major cities. A smaller, more common class of airliners is the narrow-body aircraft, narrow-body or single-aisle. These are generally used for short to medium-distance flights with fewer passengers than their wide-body counterparts. Regional airliners typically seat fewer than 100 passengers and may be powered by turbofans or turboprops. These airliners are the non-mainli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accidents And Incidents Involving The British Aerospace Jetstream
An accident is an unintended, normally unwanted event that was not directly caused by humans. The term ''accident'' implies that nobody should be blamed, but the event may have been caused by unrecognized or unaddressed risks. Most researchers who study unintentional injury avoid using the term ''accident'' and focus on factors that increase risk of severe injury and that reduce injury incidence and severity. For example, when a tree falls down during a wind storm, its fall may not have been caused by humans, but the tree's type, size, health, location, or improper maintenance may have contributed to the result. Most car wrecks are not true accidents; however English speakers started using that word in the mid-20th century as a result of media manipulation by the US automobile industry. Types Physical and non-physical Physical examples of accidents include unintended motor vehicle collisions, falls, being injured by touching something sharp or hot, or bumping into some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Accidents And Incidents In The United States In 1989
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. Etymology The word ''aviation'' was coined by the French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863. He derived the term from the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stall (fluid Mechanics)
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack increases.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 486. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. This occurs when the critical angle of attack of the foil is exceeded. The critical angle of attack is typically about 15°, but it may vary significantly depending on the fluid, foil, and Reynolds number. Stalls in fixed-wing flight are often experienced as a sudden reduction in lift as the pilot increases the wing's angle of attack and exceeds its critical angle of attack (which may be due to slowing down below stall speed in level flight). A stall does not mean that the engine(s) have stopped working, or that the aircraft has stopped moving—the effect is the same even in an unpowered glider aircraft. Vectored thrust in aircraft is used to maintain altitude or controlled flight with wings stalled by replacing lost wing lift with engine or propeller thru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. newspapers and broadcasters. The AP has earned 56 Pulitzer Prizes, including 34 for photography, since the award was established in 1917. It is also known for publishing the widely used '' AP Stylebook''. By 2016, news collected by the AP was published and republished by more than 1,300 newspapers and broadcasters, English, Spanish, and Arabic. The AP operates 248 news bureaus in 99 countries. It also operates the AP Radio Network, which provides newscasts twice hourly for broadcast and satellite radio and television stations. Many newspapers and broadcasters outside the United States are AP subscribers, paying a fee to use AP material without being contributing members of the cooperative. As part of their cooperative agreement with the AP, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
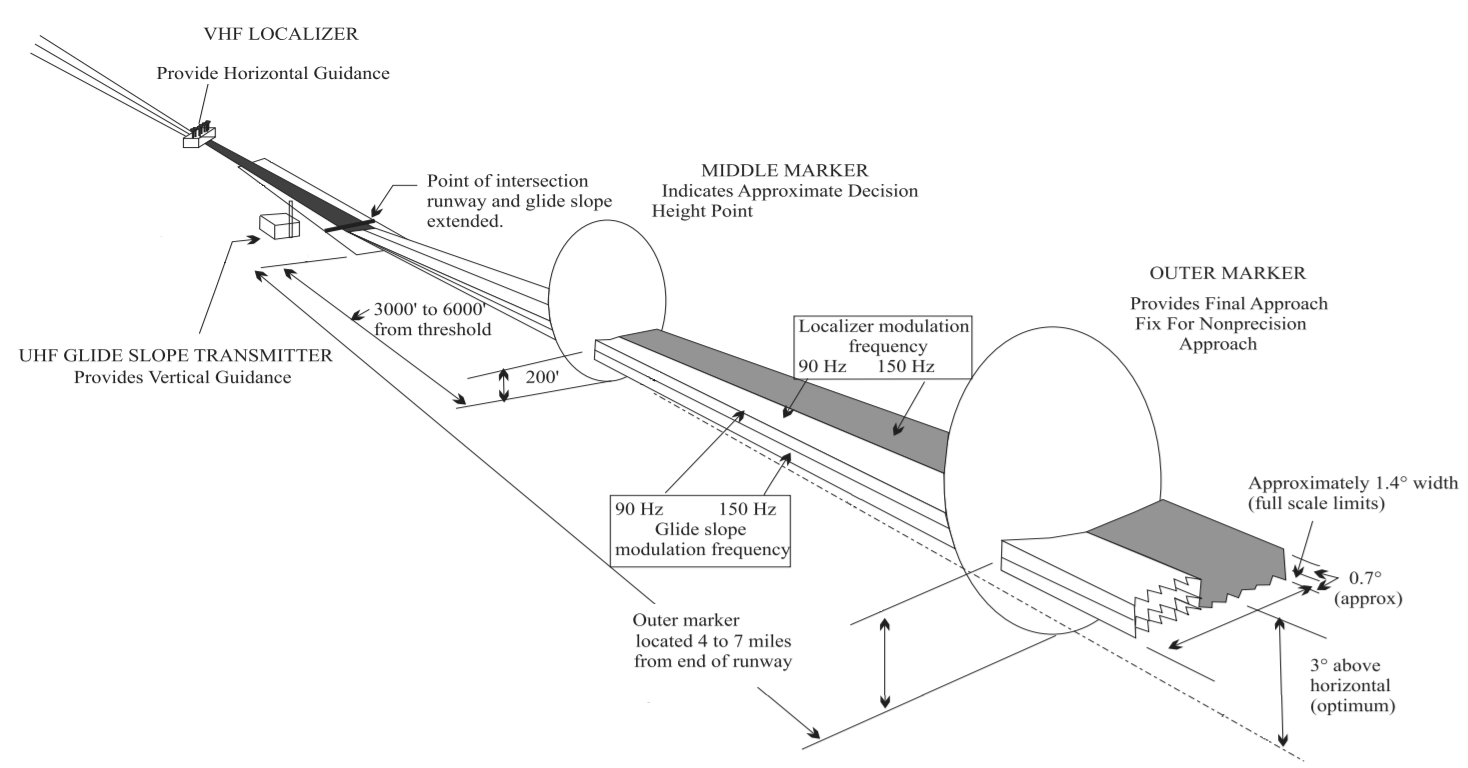
Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Traffic Controller
Air traffic control specialists, abbreviated ATCS, are personnel responsible for the safe, orderly, and expeditious flow of air traffic in the global air traffic control system. Usually stationed in air traffic control centers and control towers on the ground, they monitor the position, speed, and altitude of aircraft in their assigned airspace visually and by radar, and give directions to the pilots by radio. The position of air traffic controller is one that requires highly specialized knowledge, skills, and abilities. Controllers apply separation rules to keep aircraft at a safe distance from each other in their area of responsibility and move all aircraft safely and efficiently through their assigned sector of airspace, as well as on the ground. Because controllers have an incredibly large responsibility while on duty (often in aviation, "on position") and make countless real-time decisions on a daily basis, the ATC profession is consistently regarded around the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying (magazine)
''Flying'', sometimes styled ''FLYING'', is an aviation magazine published since 1927 and called ''Popular Aviation'' prior to 1942, as well as ''Aeronautics'' for a brief period. It is read by pilots, aircraft owners, aviation enthusiasts and aviation-oriented executives in business, commercial and general aviation markets worldwide. It has the largest paid subscription, newsstand, and international circulation of any U.S.-based aviation magazine, according to its former publisher the Bonnier Corporation, and is promoted as "the world's most widely read aviation magazine". It is owned by digital media entrepreneur Craig Fuller. History The magazine first began publishing in 1927 as ''Popular Aviation'' soon after Charles Lindbergh's historic transatlantic flight. It was given the name ''Aeronautics'' briefly from 1929–1930 and was changed back to ''Popular Aviation'' until 1942, when it became ''Flying''. In June 2009, ''Flying'' owner, Hachette Filipacchi Media U.S., so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.jpg)