|
Union Hall, County Cork
Union Hall (), also Unionhall, is a small fishing village located in County Cork, Ireland, located on the west side of Glandore Harbour. Its nearest neighbour to the west is Castletownshend; to the east, Glandore village. It is approximately 10 kilometres south-east of Skibbereen. As of the 2016 census, 270 people were living in Union Hall. A key source of employment in the area is fishing, and the pier has its own ice plant and fish processing factory run by Glenmar Shellfish Ltd. Tourism is also an economic driver, and among the area's attractions are boat trips to view whales, dolphins and seals. Location and access The coastal village lies on a hill, and has a small harbour for small fishing boats and other small craft. By road it is accessible over the narrow Poulgorm Bridge on the R597 regional road to Glandore, Rosscarbery and Leap. The bridge is only one lane wide, so traffic must wait for the bridge to be clear before crossing. The bridge was built c.1890, and feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. Around 2.1 million of the country's population of 5.13 million people resides in the Greater Dublin Area. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the , consists of a lower house, ; an upper house, ; and an elected President () who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the (Prime Minister, literally 'Chief', a title not used in English), who is elected by the Dáil and appointed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the brackish dolphins), and the extinct Lipotidae (baiji or Chinese river dolphin). There are 40 extant species named as dolphins. Dolphins range in size from the and Maui's dolphin to the and orca. Various species of dolphins exhibit sexual dimorphism where the males are larger than females. They have streamlined bodies and two limbs that are modified into flippers. Though not quite as flexible as seals, some dolphins can briefly travel at speeds of per hour or leap about . Dolphins use their conical teeth to capture fast-moving prey. They have well-developed hearing which is adapted for both air and water. It is so well developed that some can survive even if they are blind. Some species are well adapted for diving to great depths. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sept
A sept is a division of a family, especially of a Scottish or Irish family. The term is used in both Scotland and Ireland, where it may be translated as ''sliocht'', meaning "progeny" or "seed", which may indicate the descendants of a person (for example, ''Sliocht Bhriain Mhic Dhiarmada'', "the descendant of Brian MacDermott"). The word may derive from the Latin ''saeptum'', meaning "enclosure" or "fold", or via an alteration of "sect". Family branches ''Síol'' is a Gaelic word meaning "progeny" or "seed" that is used in the context of a family or clan with members who bear the same surname and inhabited the same territory,"Septs of Ireland" Irish Septs Association. as a manner of distinguishing one group from another; a family called ''Mac an Bháird'' ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
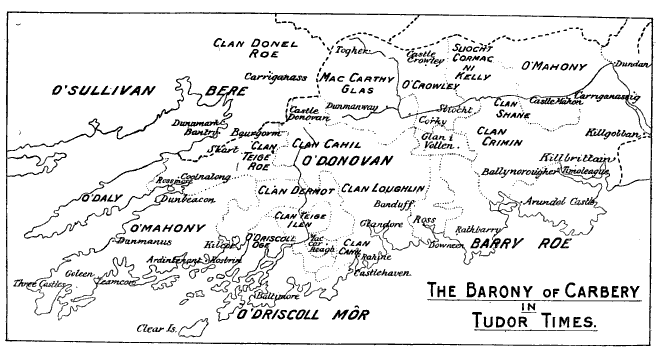
O'Donovan Family
The O'Donovans are an Irish family. Their patronymic surname derives from Irish ''Ó Donnabháin'', meaning the grandsons or descendants of Donnubán, referring to the 10th century ruler of the Uí Fidgenti, Donnubán mac Cathail. During the 12th and 13th century, O'Donovan relations relocated from the Bruree/Croom area south to the Kingdom of Desmond and to Carbery, where they were a ruling family for centuries and played a role in the establishment of a feudal society under the MacCarthys. Other septs retreated into the southeast corner of the Ui Fidgheinte territory, reaching from Broadford/Feenagh to the Doneraile area. The northern septs of the O'Donovans did not use a White Rod as the family's position in their original territory was vastly eroded, while several septs of O'Donovans in the southwest territories were semi-autonomous flatha under the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty in Carbery, with the most notable being local petty kings. The family were counted among the leading G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townland
A townland ( ga, baile fearainn; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a small geographical division of land, historically and currently used in Ireland and in the Western Isles in Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of Gaelic origin, pre-dating the Norman invasion, and most have names of Irish origin. However, some townland names and boundaries come from Norman manors, plantation divisions, or later creations of the Ordnance Survey.Connolly, S. J., ''The Oxford Companion to Irish History, page 577. Oxford University Press, 2002. ''Maxwell, Ian, ''How to Trace Your Irish Ancestors'', page 16. howtobooks, 2009. The total number of inhabited townlands in Ireland was 60,679 in 1911. The total number recognised by the Irish Place Names database as of 2014 was 61,098, including uninhabited townlands, mainly small islands. Background In Ireland a townland is generally the smallest administrative division of land, though a few large townlands are further divided into h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lime Kiln
A lime kiln is a kiln used for the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce the form of lime (material), lime called quicklime (calcium oxide). The chemical equation for this chemical reaction, reaction is :Calcium carbonate, CaCO3 + heat → Calcium oxide, CaO + Carbon dioxide, CO2 This reaction can take place at anywhere above 840 °C (1544 °F), but is generally considered to occur at 900 °C(1655 °F) (at which temperature the partial pressure of CO2 is 1 atmosphere (unit), atmosphere), but a temperature around 1000 °C (1832 °F) (at which temperature the partial pressure of CO2 is 3.8 atmospheres) is usually used to make the reaction proceed quickly.Parkes, G.D. and Mellor, J.W. (1939). ''Mellor's Modern Inorganic Chemistry'' London: Longmans, Green and Co. Excessive temperature is avoided because it produces unreactive, "dead-burned" lime. Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) can be formed by mixing quicklime with water. Early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Souterrain
''Souterrain'' (from French ''sous terrain'', meaning "under ground") is a name given by archaeologists to a type of underground structure associated mainly with the European Atlantic Iron Age. These structures appear to have been brought northwards from Gaul during the late Iron Age. Regional names include earth houses, fogous and Pictish houses. The term ''souterrain'' has been used as a distinct term from ''fogou'' meaning 'cave'. In Cornwall the regional name of ''fogou'' ( Cornish for 'cave') is applied to souterrain structures. The design of underground structures has been shown to differ among regions; for example, in western Cornwall the design and function of the fogou appears to correlate with a larder use. Etymology The name ''souterrain'' comes from the French language (''sous-terrain'' or ''souterrain''), in which it means "underground passageway" or refers to subterranea in general. In languages other than English, it is sometimes used to mean " basement", especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringfort
Ringforts, ring forts or ring fortresses are circular fortified settlements that were mostly built during the Bronze Age up to about the year 1000. They are found in Northern Europe, especially in Ireland. There are also many in South Wales and in Cornwall, where they are called rounds. Ringforts come in many sizes and may be made of stone or earth. Earthen ringforts would have been marked by a circular rampart (a bank and ditch), often with a stakewall. Both stone and earthen ringforts would generally have had at least one building inside. Distribution Ireland In Irish language sources they are known by a number of names: ' (anglicised ''rath'', also Welsh ''rath''), ' (anglicised ''lis''; cognate with Cornish '), ' (anglicised ''cashel''), ' (anglicised ''caher'' or ''cahir''; cognate with Welsh ', Cornish and Breton ') and ' (anglicised ''dun'' or ''doon''; cognate with Welsh and Cornish ').Edwards, Nancy. ''The Archaeology of Early Medieval Ireland''. Routledge, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Buttons (1994 Film)
''War of the Buttons'' is a 1994 comedy-drama adventure film directed by John Roberts. It was written by Colin Welland and based on the French novel '' La Guerre des boutons'', by Louis Pergaud. The story, about two rival boys' gangs in Ireland, the Ballys (working class) and the Carricks (middle class), is set in County Cork, where it was filmed on location. The film has been classified as a drama and comedy, and the tone is frequently light and humorous. It examines issues of conflict and war, the actions and consequences of violence, and how it can divide and oppose people who can be friends as easily as they can be enemies. Plot In the Republic of Ireland in the 1960s, more precisely the centre of the bridge over the river that separates the Irish villages of Carrickdowse and Ballydowse, there is a white line that few young people dare cross. The boys of each village spend most of their time trying to upstage the other, whether over the sale of hospital raffle tickets, or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Puttnam
David Terence Puttnam, Baron Puttnam, CBE, HonFRSA, HonFRPS, MRIA (born 25 February 1941) is a British film producer, educator, environmentalist and former member of the House of Lords. His productions include ''Chariots of Fire'', which won the Academy Award for Best Picture, '' The Mission'', ''The Killing Fields'', '' Local Hero'', '' Midnight Express'' and '' Memphis Belle''. In 1982, he received the BAFTA for Outstanding British Contribution to Cinema, and in 2006 he was awarded the BAFTA Fellowship for lifetime achievement from the British Academy of Film and Television Arts. Puttnam sat on the Labour benches in the House of Lords, although he was not principally a politician. In 2019 he was appointed chair to thselect committee on democracy and digital technologies The committee published its findings in its ' report in June 2020. Early life Puttnam was born in Southgate, London, England, the son of Marie Beatrix, a housewife of Jewish origin, and Leonard Arthur Put ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leap, County Cork
Leap (; or ''An Léim'') is a village in County Cork, Ireland, situated at the north end of Glandore Harbour, several miles inland from the seacoast. Leap is located on the N71 national secondary road which runs through West Cork from Cork city. It is in the parish of Kilmacabea which also includes Glandore village. Name and history The Irish name of the village, ''Léim Uí Dhonnabháin'', means "O'Donovan's Leap" and is reputedly derived from the story of a chieftain called O'Donovan, who was pursued by English English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national ide ... soldiers, but escaped them by jumping across a ravine on the western side of the village. In 1684, Jeremiah O'Donovan (MP Baltimore), Lord of Clan Loughlin, obtained letters patent from Charles II of England. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosscarbery
Rosscarbery () is a village and census town in County Cork, Ireland. The village is on a shallow estuary, which opens onto Rosscarbery Bay. Rosscarbery is in the Cork South-West (Dáil Éireann) constituency, which has three seats. History The area has been occupied since at least the Neolithic period, as evidenced by several Neolithic sites such as portal dolmens. The area is also home to a number of Bronze Age remains, including a number of stone circles and ring forts. There are two inscribed stones in Burgatia, and several (later) holy wells nearby. Rosscarbery was home to the School of Ross, a major centre of learning, at one time being a university town, and one of the major cities in Europe, around the 6th century. Due to its popularity as a centre of pilgrimage it was also known as ''Ros Ailithir ("Wood of the Pilgrims")''. The hereditary chieftains of the area, or tuath, were the O'Learys, known as Uí Laoghaire Ruis Ó gCairbre, until it passed to Norman control in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_Co_Roscommon%2C_Ireland.jpg)