|
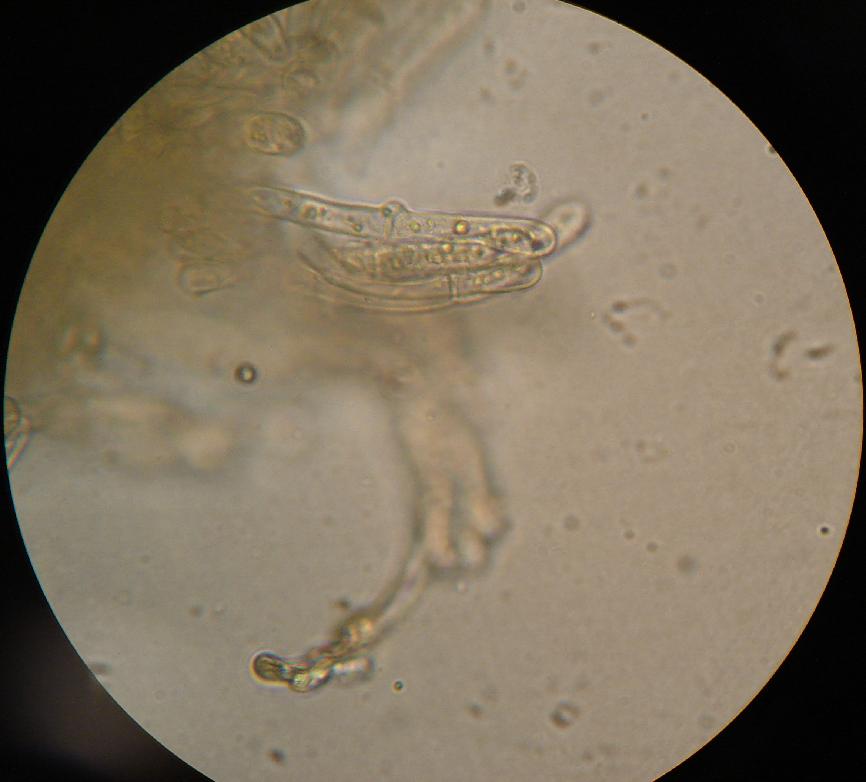
Unilacrymaceae
The Unilacrymaceae are a family of fungi in the order Dacrymycetales. The family currently contains the single genus '' Unilacryma'' with two known species from Europe, North Asia, and North America. The family was originally placed within its own order, the Unilacrymales, but subsequent research suggests it is better accommodated within the Dacrymycetales. As with other members of the Dacrymycetes, species within the ''Unilacrymaceae'' are saprotrophs, occur on dead wood, and have gelatinous basidiocarps. Microscopically all species have clamped hyphae, branched hyphidia, and muriform (multiseptate), subglobose to ellipsoid basidiospores. '' Unilacryma unispora'' is unique within the Dacrymycetes in having single-spored basidia A basidium () is a microscopic sporangium (a spore-producing structure) found on the hymenophore of fruiting bodies of basidiomycete fungi which are also called tertiary mycelium, developed from secondary mycelium. Tertiary mycelium is highly-c .... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacrymycetes
The Dacrymycetes are a class of fungi in the Basidiomycota. The class currently contains the single order Dacrymycetales, with a second proposed order Unilacrymales now treated at the family level. The order contains four families and has a cosmopolitan distribution. All fungi in the Dacrymycetes are wood-rotting saprotrophs. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are ceraceous to gelatinous, typically yellow to orange as a result of carotenoid pigments, and variously corticioid (effused and patch-forming), disc- or cushion-shaped, spathulate, or clavarioid (club or coral-like). Microscopically, nearly all species have distinctive Y-shaped holobasidia. Species were formerly placed in the Heterobasidiomycetes Heterobasidiomycetes, including jelly fungi, smuts and rusts, are basidiomycetes with Septum, septate Basidium, basidia. This contrasts them to homobasidiomycetes (alternatively called holobasidiomycetes), including most mushrooms and other Agari ... and are informally included in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacrymycetales
The Dacrymycetes are a class of fungi in the Basidiomycota. The class currently contains the single order Dacrymycetales, with a second proposed order Unilacrymales now treated at the family level. The order contains four families and has a cosmopolitan distribution. All fungi in the Dacrymycetes are wood-rotting saprotrophs. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are ceraceous to gelatinous, typically yellow to orange as a result of carotenoid pigments, and variously corticioid (effused and patch-forming), disc- or cushion-shaped, spathulate, or clavarioid (club or coral-like). Microscopically, nearly all species have distinctive Y-shaped holobasidia. Species were formerly placed in the Heterobasidiomycetes Heterobasidiomycetes, including jelly fungi, smuts and rusts, are basidiomycetes with Septum, septate Basidium, basidia. This contrasts them to homobasidiomycetes (alternatively called holobasidiomycetes), including most mushrooms and other Agari ... and are informally included in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprotrophs
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi (for example ''Mucor'') and soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes; saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes ( sapro- 'rotten material' + -phyte 'plant'), although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or other plants. The process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae. states the purpose of saprotrophs and their internal nutrition, as well as the main two types of fungi that are most often referred to, as well as describes, visually, the process of saprotrophic nutrition through a diagram of hypha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiocarps
In fungi, a basidiocarp, basidiome, or basidioma () is the sporocarp (fungi), sporocarp of a basidiomycota, basidiomycete, the Multicellular organism, multicellular structure on which the spore-producing hymenium is borne. Basidiocarps are characteristic of the hymenomycetes; Urediniomycetes, rusts and Ustilaginomycetes, smuts do not produce such structures. As with other sporocarps, epigeous (above-ground) basidiocarps that are visible to the naked eye (especially those with a more or less agaricoid morphology) are commonly referred to as mushrooms, while hypogeous (underground) basidiocarps are usually called false truffles. Structure All basidiocarps serve as the structure on which the hymenium is produced. Basidia are found on the surface of the hymenium, and the basidia ultimately produce spores. In its simplest form, a basidiocarp consists of an undifferentiated fruiting structure with a hymenium on the surface; such a structure is characteristic of many simple jelly fungi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamp Connections
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is a characteristic feature of Basidiomycetes fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell, or segment of hypha separated by septa (cross walls), receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating of hyphae of differing sexual types. It is used to maintain genetic variation within the hypha much like the mechanisms found in crozier (hook) during sexual reproduction. Formation Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes mitotic division to produce two daughter nuclei. As the clamp continues to develop it uptakes one of the daughter (green circle) nuclei and separates it from its sister nucleus. While this is occurring the remaining nuclei (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiospores
A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by Basidiomycete fungi, a grouping that includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, rusts, and smuts. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid nucleus that is the product of meiosis, and they are produced by specialized fungal cells called basidia. Typically, four basidiospores develop on appendages from each basidium, of which two are of one strain and the other two of its opposite strain. In gills under a cap of one common species, there exist millions of basidia. Some gilled mushrooms in the order Agaricales have the ability to release billions of spores. The puffball fungus ''Calvatia gigantea'' has been calculated to produce about five trillion basidiospores. Most basidiospores are forcibly discharged, and are thus considered ballistospores. These spores serve as the main air dispersal units for the fungi. The spores are released during periods of high humidity and generally have a night-time or pre-dawn peak concentration in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |