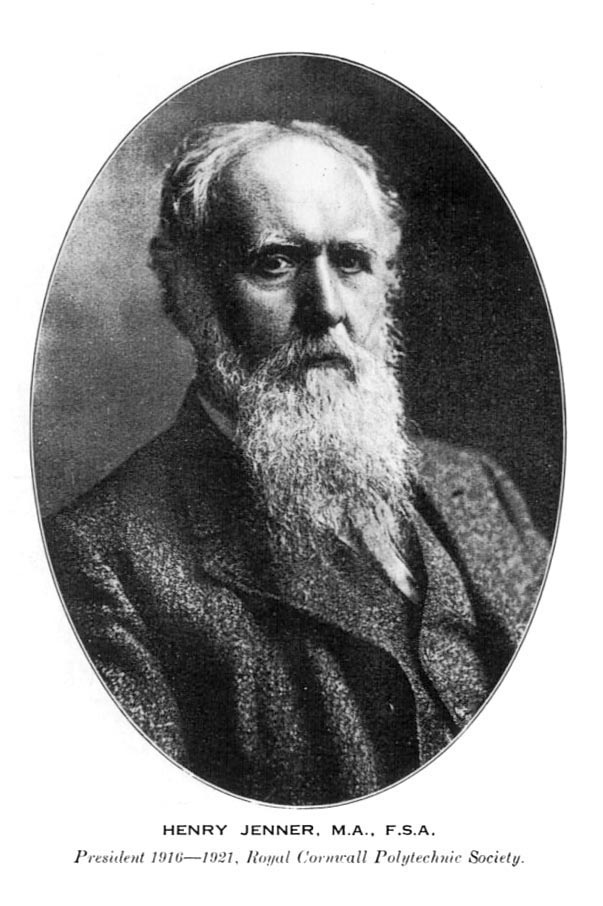|
Unified Cornish Revised
Unified Cornish (UC) (''Kernewek Uny '', ''KU'') is a variety of the Cornish language of the Cornish revival. Developed gradually by Robert Morton Nance during and before the 1930s, it derived its name from its standardisation of the variant spellings of traditional Cornish manuscripts. Nance's recommended spelling and grammar, based on Middle Cornish, soon supplanted Henry Jenner's system, which had been based largely on Late Cornish. Most of the older generation of Cornish users alive today would have started under this system. It was also the form originally used by Gorsedh Kernow, although they now use the new Standard Written Form The Standard Written Form or SWF ( kw, Furv Skrifys Savonek) of the Cornish language is an orthography standard that is designed to "provide public bodies and the educational system with a universally acceptable, inclusive, and neutral orthograph .... Criticism In the 1980s, Unified Cornish came under heavy criticism, leading to the creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornish Language
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or ) , is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. It is a List of revived languages, revived language, having become Extinct language, extinct as a living community language in Cornwall at the Last speaker of the Cornish language, end of the 18th century. However, knowledge of Cornish, including speaking ability to a certain extent, continued to be passed on within families and by individuals, and Cornish language revival, a revival began in the early 20th century. The language has a growing number of second language speakers, and a very small number of families now raise children to speak revived Cornish as a first language. Cornish is currently recognised under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, and the language is often described as an important part of Cornish identity, culture and heritage. Along with Welsh language, Welsh and Breton language, Breton, Cornish is descended from the Common Britto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornish Revival
The Cornish language revival ( kw, dasserghyans Kernowek, lit='resurrection of Cornish') is an ongoing process to revive the use of the Cornish language of Cornwall, England. The Cornish language's disappearance began to hasten during the 13th century, but its decline began with the spread of Anglo-Saxon in the 4th and 5th centuries. The last reported person to have full knowledge of a traditional form of Cornish, John Davey, died in 1891. The revival movement started in the late 19th century as a result of antiquarian and academic interest in the language, which was already extinct, and also as a result of the Celtic revival movement. In 2009, UNESCO changed its classification of Cornish from "extinct" to "critically endangered", seen as a milestone for the revival of the language. Revival During the 19th century the Cornish language was the subject of antiquarian interest and a number of lectures were given on the subject and pamphlets on it were published. In 1904, the Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Morton Nance
Robert Morton Nance (1873–1959) was a British writer and leading authority on the Cornish language, a nautical archaeologist, and joint founder of the Old Cornwall Society. Nance wrote many books and pamphlets on the Cornish language, including a Cornish dictionary, which is a standard work, and edited magazines and pamphlets about Cornwall, including ''Old Cornwall'', the journal of the Federation of Old Cornwall Societies. Nance was also a nautical archaeologist of distinction and was an originator of the Society for Nautical Research. His insight and learning were displayed in his book ''Sailing-ship Models'' which appeared in 1924. He studied art in Britain and France and was both a painter and a skilled craftsman. Work with the Cornish language In 1898, Robert Morton Nance wrote "The Merry Ballad of the Cornish Pasty".Hall, Stephen (2001) ''The Cornish Pasty''. Nettlecombe: Agre Books Nance began studying the Cornish language in 1904 from Henry Jenner's A H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Jenner
Henry Jenner (8 August 1848 – 8 May 1934) was a British scholar of the Celtic languages, a Cornish cultural activist, and the chief originator of the Cornish language revival. Jenner was born at St Columb Major on 8 August 1848. He was the son of Henry Lascelles Jenner, who was one of two curates to the Rector of St. Columb Major, and later consecrated though not enthroned as the first Bishop of Dunedin and the grandson of Herbert Jenner-Fust. In 1869 Jenner became a clerk in the Probate Division of the High Court and two years later was nominated by the Primate at Canterbury for a post in the Department of Ancient Manuscripts in the British Museum, his father then being the Rector of Wingham, a small village near Canterbury. In 1904, he successfully campaigned for Cornwall to join the Celtic Congress. He jointly founded the Old Cornwall Society at St Ives in 1920 and in 1928 he was a joint founder of the Cornish Gorsedh. Work with the Cornish language His earliest i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorsedh Kernow
Gorsedh Kernow (Cornish Gorsedd) is a non-political Cornish organisation, based in Cornwall, United Kingdom, which exists to maintain the national Celtic spirit of Cornwall. It is based on the Welsh-based Gorsedd, which was founded by Iolo Morganwg in 1792. History The Gorsedh Kernow (Gorsedd of Cornwall) was set up in 1928 at Boscawen-Un by Henry Jenner, one of the early proponents of Cornish language revival, who took the bardic name "Gwas Myghal", meaning "servant of Michael". He and twelve others (including Kitty Lee Jenner) were initiated by the Archdruid of Wales. It has been held every year since, except during World War II. 1,000 people have been Cornish bards, including Dame Alida Brittain, Ken George, R. Morton Nance, and Peter Berresford Ellis. After 1939 the Council of the Gorsedd of Cornwall approved additional regalia, and asked Francis Cargeeg to design and execute new regalia for the Grand Bard, the Deputy Grand Bard and the Secretary, and two headpiec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Written Form
The Standard Written Form or SWF ( kw, Furv Skrifys Savonek) of the Cornish language is an orthography standard that is designed to "provide public bodies and the educational system with a universally acceptable, inclusive, and neutral orthography". It was the outcome of a process initiated by the creation of the public body Cornish Language Partnership, which identified a need to agree on a single standard orthography in order to end previous orthographical disagreements, secure government funding, and increase the use of Cornish in Cornwall. The new form was agreed in May 2008 after two years of negotiations, and was influenced by all the previous orthographies. The negotiating teams comprised members of all the main Cornish language groups, Kesva an Taves Kernewek, Kowethas an Yeth Kernewek, Agan Tavas, and Cussel an Tavas Kernuak, and received input from experts and academics from Europe and the United States. The agreement meant that Cornish became officially accepted and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernewek Kemmyn
Kernewek Kemmyn (Common Cornish or "KK") is a variety of the revived Cornish language. Kernewek Kemmyn was developed, mainly by Ken George in 1986, based upon George's earlier doctoral thesis on the phonological history of Cornish. It takes much of its inspiration from medieval sources, particularly Cornish passion plays, as well as Breton and to a lesser extent Welsh. It was subsequently adopted by the Cornish Language Board as their preferred system. Like the earlier Unified Cornish, it retains a Middle Cornish base but aims to make the relationship between spelling and pronunciation more systematic by using an approximately morphophonemic orthography. In 2008, a survey indicated that KK users made up 55% of all Cornish speakers. The survey also showed that 21.5% of speakers continued to use the Unified system, and 14.8% were using Late Cornish. The orthography has drawn heavy criticism from several writers. In 1994, Charles Penglase berated the lack of authenticity in KK, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Williams (poet)
Nicholas Jonathan Anselm Williams (born October 1942 in Walthamstow, Essex), sometimes credited as N. J. A. Williams, is a leading expert and poet in the Cornish language. Life While a pupil at Chigwell School, Essex, Williams taught himself Cornish and became a bard of the Cornish Gorseth while still in his teens, taking the bardic name ''Golvan'' ('Sparrow'). He read classical languages, English language and Celtic in Oxford. After short periods in the universities of Belfast (where he received his PhD) and Liverpool, he was appointed lecturer in Irish in University College Dublin in 1977. In 2006 he was appointed Associate Professor in Celtic Languages there. He married Patricia Smyth from Portadown, County Armagh in 1976. Work Williams has written widely on the Celtic languages and their literatures. His works on Irish include the editions ''The Poems of Giolla Brighde Mac Con Midhe'' (1980) and ''Pairlement Chloinne Tomáis'' (1981); ''I bPrionta i Leabhar'' (1986), an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agan Tavas
Agan Tavas (''Our Language'') is a society which exists to promote the Cornish language and is represented on the Cornish Language Partnership. It was formed in 1987 to promote the use of Cornish as a spoken language in the Cornish revival ( kw, Dasserghyans Kernowek). At that time only those observed to be using the language fluently could become members by invitation. In 1990 Agan Tavas was reformed by its members into an open society with the aim of ensuring continued support for the Unified form of revived Cornish first put forward in 1929 by Robert Morton Nance. Orthographic Standards Agan Tavas recognises the validity of any form of Revived Cornish based on orthography used by Cornish people at any time in the history of the language. It opposes the use of what it sees as invented forms of the language which lack any historical authenticity. Agan Tavas received a boost in its membership after 1995 when Nicholas Williams of University College Dublin claimed in his book ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernowek Standard
Kernowek Standard (KS, ''Standard Cornish''), its initial version spelt Kernowak Standard, is a variety of the spelling of revived Cornish. It has two specifications, the first of which was published as a draft proposal in March 2007, and the second of which was published as a practical orthography in May 2012. Kernowak Standard (KS1) Its first iteration, then spelt Kernowak Standard and now designated KS1, was developed gradually by a group called ''UdnFormScrefys'' ('Single Written Form') as part of the Cornish language community's process of agreement on a Standard Written Form (SWF) for Cornish through the public body Cornish Language Partnership. It was published as a proposal in a series of revisions, Revision 11 of which was released to the Cornish Language Commission on 26 March 2007. Revision 15 was published on 22 June 2007. Revision 16 was published on 14 November 2007. Its principal authors were Michael Everson, Neil Kennedy and Nicholas Williams.The orthography was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cussel An Tavas Kernuak
Cussül an Tavas Kernôwek (formerly ''Cussel an Tavas Kernûak''; the Cornish Language Council) is an association founded in 1987 to teach, research and further the Cornish language in Cornwall (Cornish: Kernow), UK. Since the adoption of a Standard Written Form of Cornish (SWF) in 2008, it has worked closely with other bodies to achieve these aims. The Cussül encourages research into the Cornish of all periods but has a particular interest in developments after c.1600 and accordingly recommends a standard pronunciation based on c. 1600 to 1700. The Cussül largely draws its inspiration from those who attempted to save the language in the 18th century. The Cussül is run by volunteers and is a network of associates rather than a formal membership organization. See also * List of topics related to Cornwall The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Cornwall: Cornwall – ceremonial county and unitary authority area of England within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |