|
Under Class
The underclass is the segment of the population that occupies the lowest possible position in a class hierarchy, below the core body of the working class. The general idea that a class system includes a population ''under'' the working class has a long tradition in the social sciences (for example, lumpenproletariat). However, the specific term, ''underclass'', was popularized during the last half of the 20th century, first by social scientists of American poverty, and then by American journalists. The underclass concept has been a point of controversy among social scientists. Definitions and explanations of the underclass, as well as proposed solutions for managing or fixing the ''underclass problem'' have been highly debated. History Gunnar Myrdal is generally credited as the first proponent of the term ''underclass.'' Writing in the early 1960s on economic inequality in the U.S., Myrdal's underclass refers to a "class of unemployed, unemployables, and underemployed, who are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the Upper class, upper, Middle class, middle and Working class, lower classes. Membership in a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, income, and belonging to a particular subculture or social network. "Class" is a subject of analysis for List of sociologists, sociologists, political scientists, anthropologists and Social history, social historians. The term has a wide range of sometimes conflicting meanings, and there is no broad consensus on a definition of "class". Some people argue that due to social mobility, class boundaries do not exist. In common parlance, the term "social class" is usually synonymous with "Socioeconomic status, socio-economic class", defined as "people having the same social, economic, cultural, political or educational status", e.g., "the working class"; "an emerging professional class". H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elijah Anderson (sociologist)
Elijah Anderson (born 1943 in Hermondale, Missouri) is an American sociologist. He is the Sterling Professor of Sociology and of African American Studies at Yale University,"Elijah Anderson" at . where he teaches and directs the Urban Ethnography Project. Anderson is one of the nation’s leading urban s and s. Anderson is known most notably for his book, ''Code of the Street: Decency, Violence, and the Moral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deindustrialization
Deindustrialization is a process of social and economic change caused by the removal or reduction of industrial capacity or activity in a country or region, especially of heavy industry or manufacturing industry. There are different interpretations of what deindustrialization is. Many associate American deindustrialization with the mass closing of automaker plants in the now so-called "Rust Belt" between 1980 and 1990. The US Federal Reserve raised interest and exchange rates beginning in 1979, and continuing until 1984, which automatically caused import prices to fall. Japan was rapidly expanding productivity during this time, and this decimated the US machine tool sector. A second wave of deindustrialization occurred between 2001 and 2009, culminating in the automaker bailout of GM and Chrysler. Research has pointed to investment in patents rather than in new capital equipment as a contributing factor.Kerwin Kofi Charles et al (201The Transformation of Manufacturing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Massey
Douglas Steven Massey (born October 5, 1952 in Olympia, Washington, United States) is an American sociologist. Massey is currently a professor of Sociology at the Princeton School of Public and International Affairs at Princeton University and is an adjunct professor of Sociology at the University of Pennsylvania. Massey specializes in the sociology of immigration, and has written on the effect of residential segregation on the black underclass in the United States. He has been president of the Population Association of America, the American Sociological Association and the American Academy of Political and Social Science. He is a co-editor of the ''Annual Review of Sociology''. Academia Massey received his Bachelor of Arts in Sociology, Psychology, and Spanish, from Western Washington University in 1974, and in 1977 he received a Master of Arts in Sociology from Princeton University. Massey continued at Princeton University and received his PhD in 1978. He was a Guggenheim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Poverty
The culture of poverty is a concept in social theory that asserts that the values of people experiencing poverty play a significant role in perpetuating their impoverished condition, sustaining a cycle of poverty across generations. It attracted policy attention in the 1970s, and received academic criticism (; ; ), and made a comeback at the beginning of the 21st century. It offers one way to explain why poverty exists despite anti-poverty programs. Early formations suggest that poor people lack resources and acquire a poverty-perpetuating value system. Critics of the early culture of poverty arguments insist that explanations of poverty must analyze how structural factors interact with and condition individual characteristics (; ; ). As put by , "since human action is both constrained and enabled by the meaning people give to their actions, these dynamics should become central to our understanding of the production and reproduction of poverty and social inequality." Further disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentrated Poverty
Concentrated poverty concerns the spatial distribution of socio-economic deprivation, specifically focusing on the density of poor populations. Within the United States, common usage of the term concentrated poverty is observed in the fields of policy and scholarship referencing areas of " extreme" or "high-poverty." These are defined by the US census as areas where "40 percent of the tract population ivesbelow the federal poverty threshold." A large body of literature argues that areas of concentrated poverty place additional burdens on poor families residing within them, burdens beyond what these families' individual circumstances would dictate. Research also indicates that areas of concentrated poverty can have effects beyond the neighborhood in question, affecting surrounding neighborhoods not classified as "high-poverty" and subsequently limiting their overall economic potential and social cohesion. Concentrated poverty is a global phenomenon, with prominent examples world-wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
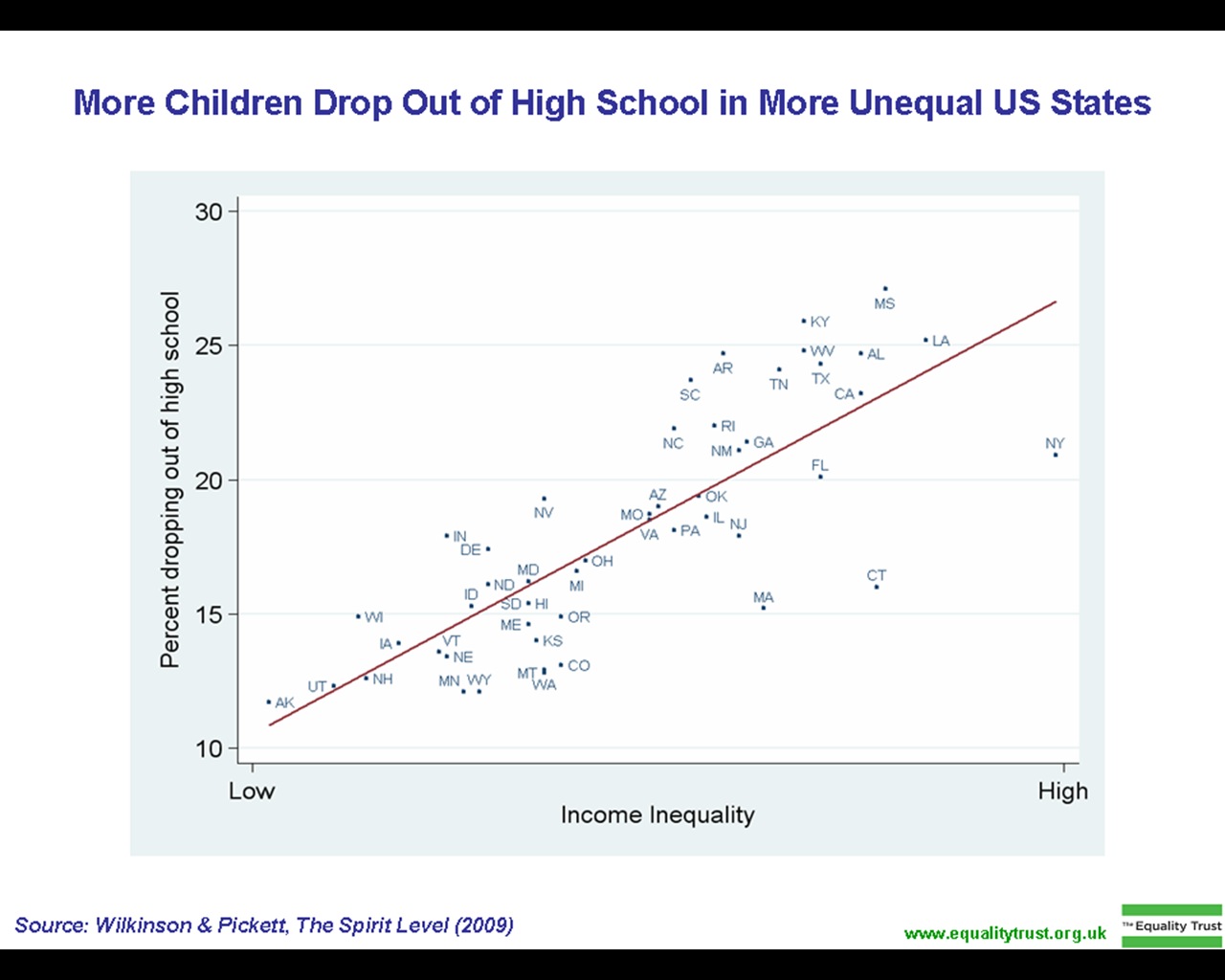
Dropping Out
Dropping out refers to leaving high school, college, university or another group for practical reasons, necessities, inability, apathy, or disillusionment with the system from which the individual in question leaves. Canada In Canada, most individuals graduate from grade 12 by the age of 18, according to Jason Gilmore who collects data on employment and education using the Labour Force Survey. The LFS is the official survey used to collect unemployment data in Canada (2010). Using this tool, assessing educational attainment and school attendance can calculate a dropout rate (Gilmore, 2010). It was found by the LFS that by 2009, one in twelve 20- to 24-year-old adults did not have a high school diploma (Gilmore, 2010). The study also found that men still have higher dropout rates than women, and that students outside of major cities and in the northern territories also have a higher risk of dropping out. Although since 1990 dropout rates have gone down from 20% to a low of 9% in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behaviour occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.. Drugs most often associated with this term include: alcohol, amphetamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens (although there is no known ''psychedelic'', one of the three categories of hallucinogens, that has been found to have any addictive potential), methaqualone, and opioids. The exact cause of substance abu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violence
Violence is the use of physical force so as to injure, abuse, damage, or destroy. Other definitions are also used, such as the World Health Organization's definition of violence as "the intentional use of physical force or Power (social and political), power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation."Krug et al."World report on violence and health", World Health Organization, 2002. Internationally, violence resulted in deaths of an estimated 1.28 million people in 2013 up from 1.13 million in 1990. However, global population grew by roughly 1.9 billion during those years, showing a dramatic reduction in violence per capita. Of the deaths in 2013, roughly 842,000 were attributed to self-harm (suicide), 405,000 to interpersonal violence, and 31,000 to collective violence (war) and legal intervention. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crime
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a State (polity), state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Cane and Conoghan (editors), ''The New Oxford Companion to Law'', Oxford University Press, 2008 (), p. 263Google Books). though statutory definitions have been provided for certain purposes. The most popular view is that crime is a Category of being, category created by law; in other words, something is a crime if declared as such by the relevant and applicable law. One proposed definition is that a crime or offence (or criminal offence) is an act harmful not only to some individual but also to a community, society, or the state ("a public wrong"). Such acts are forbidden and punishable by law. The notion that acts such as murder, rape, and theft are to be prohibited exists worldwide. What precisely is a criminal offence is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joblessness
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * new technologies and inventions * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * policies of the government * regulation and market Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, can influence the availability and cost for money through its monetary p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Auletta
Kenneth B. Auletta (born April 23, 1942) is an American author, a political columnist for the New York Daily News, and media critic for ''The New Yorker''. Early life and education The son of an Italian American father and a Jewish American mother, Auletta grew up in the Coney Island section of Brooklyn, New York, where he attended Abraham Lincoln High School. He graduated from the State University of New York at Oswego and received his M.A. in political science from the Maxwell School of Citizenship and Public Affairs at Syracuse University. Writing career While in graduate school, Auletta taught and trained Peace Corps volunteers. He "got bored in a Ph.D political science program and left to be a gofer and write speeches in politics; then on to serve in government", then working for then-Senator Robert F. Kennedy's 1968 presidential campaign before serving as campaign manager for former Administrator of the Small Business Administration Howard J. Samuels's failed 1974 gub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)