|
Uncinaria
''Uncinaria'' is a genus of nematode. The genus was circumscribed by Josef Aloys Frölich in 1789. Species include: * '' Uncinaria criniformis'' * '' Uncinaria lucasi'' * ''Uncinaria sanguinis'' * ''Uncinaria stenocephala ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is a nematode that Parasitism, parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such ...'' * '' Uncinaria yukonensis'' References Further reading * * Strongylida Rhabditida genera {{parasitic animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinaria Criniformis
''Uncinaria'' is a genus of nematode. The genus was circumscribed by Josef Aloys Frölich in 1789. Species include: * '' Uncinaria criniformis'' * '' Uncinaria lucasi'' * ''Uncinaria sanguinis'' * ''Uncinaria stenocephala ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is a nematode that Parasitism, parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such ...'' * '' Uncinaria yukonensis'' References Further reading * * Strongylida Rhabditida genera {{parasitic animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinaria Lucasi
''Uncinaria'' is a genus of nematode. The genus was circumscribed by Josef Aloys Frölich in 1789. Species include: * ''Uncinaria criniformis'' * '' Uncinaria lucasi'' * ''Uncinaria sanguinis'' * ''Uncinaria stenocephala ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is a nematode that Parasitism, parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such ...'' * '' Uncinaria yukonensis'' References Further reading * * Strongylida Rhabditida genera {{parasitic animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinaria Yukonensis
''Uncinaria'' is a genus of nematode. The genus was circumscribed by Josef Aloys Frölich in 1789. Species include: * ''Uncinaria criniformis'' * ''Uncinaria lucasi'' * ''Uncinaria sanguinis'' * ''Uncinaria stenocephala ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is a nematode that Parasitism, parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such ...'' * '' Uncinaria yukonensis'' References Further reading * * Strongylida Rhabditida genera {{parasitic animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
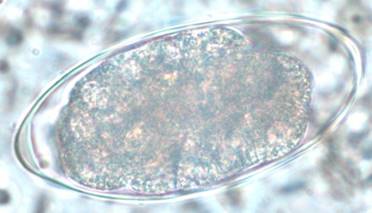
Uncinaria Stenocephala
''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is a nematode that Parasitism, parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such as Canada and the northern regions of the US, where it can be found primarily in foxes (40%). ''U. stenocephala'' is also one of the most common hookworms in the UK, called the northern hookworm, however it has a rather low prevalence. ''U. stenocephala is'' also considered to be zoonotic hookworms because they live in animals but can be transmitted to humans. Life cycle The host ingests an infective third stage larva. The larva matures to the adult in the small intestine. Eggs are laid in the small intestine and pass out with the feces. The prepatent period is about 15 to 17 days. The eggs hatch in the soil and the larvae molt twice to reach the infective third-stage. Infections worsen and amplify when dogs who are regularly kept outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinaria Sanguinis
''Uncinaria sanguinis'' is a species of nematode. It is a parasite of the Australian sea lion, found in South Australia South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories .... References Strongylida Invertebrates of Australia Parasites of carnivores Nematodes described in 2014 {{parasitic animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongylida
The Strongylida suborder includes many of the important nematodes found in the gastrointestinal tracts of ruminants, horses, and swine, as well as the lungworms of ruminants and the hookworms of dogs and cats. Taxonomy This suborder includes (superfamily - included families): *Ancylostomatoidea ** Ancylostomatidae * Diaphanocephaloidea **Diaphanocephalidae * Heligmosomoidea ** Heligmosomidae * Metastrongyloidea **Angiostrongylidae **Crenosomatidae **Filaroididae **Metastrongylidae **Protostrongylidae **Pseudaliidae ** Syngamidae * Molineoidea ** Molineidae * Strongyloidea **Chabertiidae **Cloacinidae ** Deletrocephalidae ** Stephanuridae **Strongylidae *Trichostrongyloidea ** Amidostomatidae **Cooperiidae ** Dictyocaulidae ** Dromaeostrongylidae ** Haemonchidae ** Heligmonellidae **Heligmosomatidae ** Herpetostrongylidae ** Mackerrasrtongylidae ** Nicollinidae **Trichostrongylidae Major superfamilies Diaphanocephaloidea These are parasites of the digestive tracts of terrestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Aloys Frölich
Josef Aloys Frölich or Alois von Frölich (10 March 1766, Marktoberdorf – 11 March 1841) was a German Physician, doctor, botanist and entomologist. He is not to be confused with Franz Anton Gottfried Frölich (1805–1878), his son, also an entomologist but specialising in Lepidoptera. In the field of botany he described many species within the genus ''Hieracium''. The genus ''Froelichia'' (family Amaranthaceae) is named in his honor. Froelichia Moench, Methodus. 50. 1794. Works * ''De Gentiana libellus sistens specierum cognitarum descriptiones cum observationibus. Accedit tabula aenea'' Erlangen: Walther, 1796 [Titel auch: ''De Gentiana'', Erlangen: Kunstmann; ''De gentiana dissertatio''; ''Dissertatio inauguralis de Gentiana''], zugleich: Erlangen, Med. Diss., January 1 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with Arthropod, arthropods, Tardigrade, tardigrades and other moulting animalia, animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike platyhelminthe, flatworms, have tubular digestion, digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscription (taxonomy)
In biological taxonomy, circumscription is the content of a taxon, that is, the delimitation of which subordinate taxa are parts of that taxon. If we determine that species X, Y, and Z belong in Genus A, and species T, U, V, and W belong in Genus B, those are our circumscriptions of those two genera. Another systematist might determine that T, U, V, W, X, Y, and Z all belong in genus A. Agreement on circumscriptions is not governed by the Codes of Zoological or Botanical Nomenclature, and must be reached by scientific consensus. A goal of biological taxonomy is to achieve a stable circumscription for every taxon. This goal conflicts, at times, with the goal of achieving a natural classification that reflects the evolutionary history of divergence of groups of organisms. Balancing these two goals is a work in progress, and the circumscriptions of many taxa that had been regarded as stable for decades are in upheaval in the light of rapid developments in molecular phylogenetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |