|
Umm Nidal
Maryam Mohammad Yousif Farhat ( ar, مريم محمد يوسف فرحات), or Mariam Farahat (24 December 1949 – 17 March 2013), popularly known as Umm Nidal ( ar, أم نضال), "the mother of Nidal", or "''Khansa of Palestine''" ( ar, خنساء فلسطين), was a Palestinian politician, member of parliament in the Palestinian Legislative Council, and one of Hamas' candidates elected in the 2006 Palestinian legislative election. The word "''Nidal''" in Arabic is a term, meaning "struggle", "effort" or "work". She was one of the prominent Islamist female leaders in Palestine. Early life She was born in Shuja'iyya neighborhood in Gaza City on 24 December 1949. Khansa of Palestine She became known as "''Khansa of Palestine''" ( ar, خنساء فلسطين), the nickname came from Al-Khansa (one of the companions of prophet Muhammad), all four of whose sons were killed in the Battle of Qadisiyah. ''Umm Nidal'' got this title because of her great sacrifices - as in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'right' bracket or, alternatively, an "opening bracket" or "closing bracket", respectively, depending on the Writing system#Directionality, directionality of the context. Specific forms of the mark include parentheses (also called "rounded brackets"), square brackets, curly brackets (also called 'braces'), and angle brackets (also called 'chevrons'), as well as various less common pairs of symbols. As well as signifying the overall class of punctuation, the word "bracket" is commonly used to refer to a specific form of bracket, which varies from region to region. In most English-speaking countries, an unqualified word "bracket" refers to the parenthesis (round bracket); in the United States, the square bracket. Glossary of mathematical sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kul Al-Arab
''Kul al-Arab'' ( ar, كل العرب, meaning ''All Arabs'') is an Israeli Arabic-language weekly newspaper, founded in 1987. Based in Nazareth, the paper is Israel's most influential and widely read Arabic-language periodical. It is also distributed in the West Bank. ''Kul al-Arab'' has 70 employees and a circulation of 38,000. According to the BBC the paper "is known primarily as a Christian paper" but "is trying to expand its Muslim audience." Most of the paper's revenue comes from advertising, and it is sometimes given away for free as a result. For some time the paper was edited by the poet Samih al-Qasim, who remains its honorary editor. In 2005, the BBC stated that the paper "is scathing of Israeli and US policies, but can be equally critical of the Palestinian Authority." It has referred to terrorists and suicide bombers as "Martyrs". The paper was founded by an advertising agency, al-Bustenai, then-managed by Mussa Hassadiya. As of 2008 Hassadiya owns 40% of the paper, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
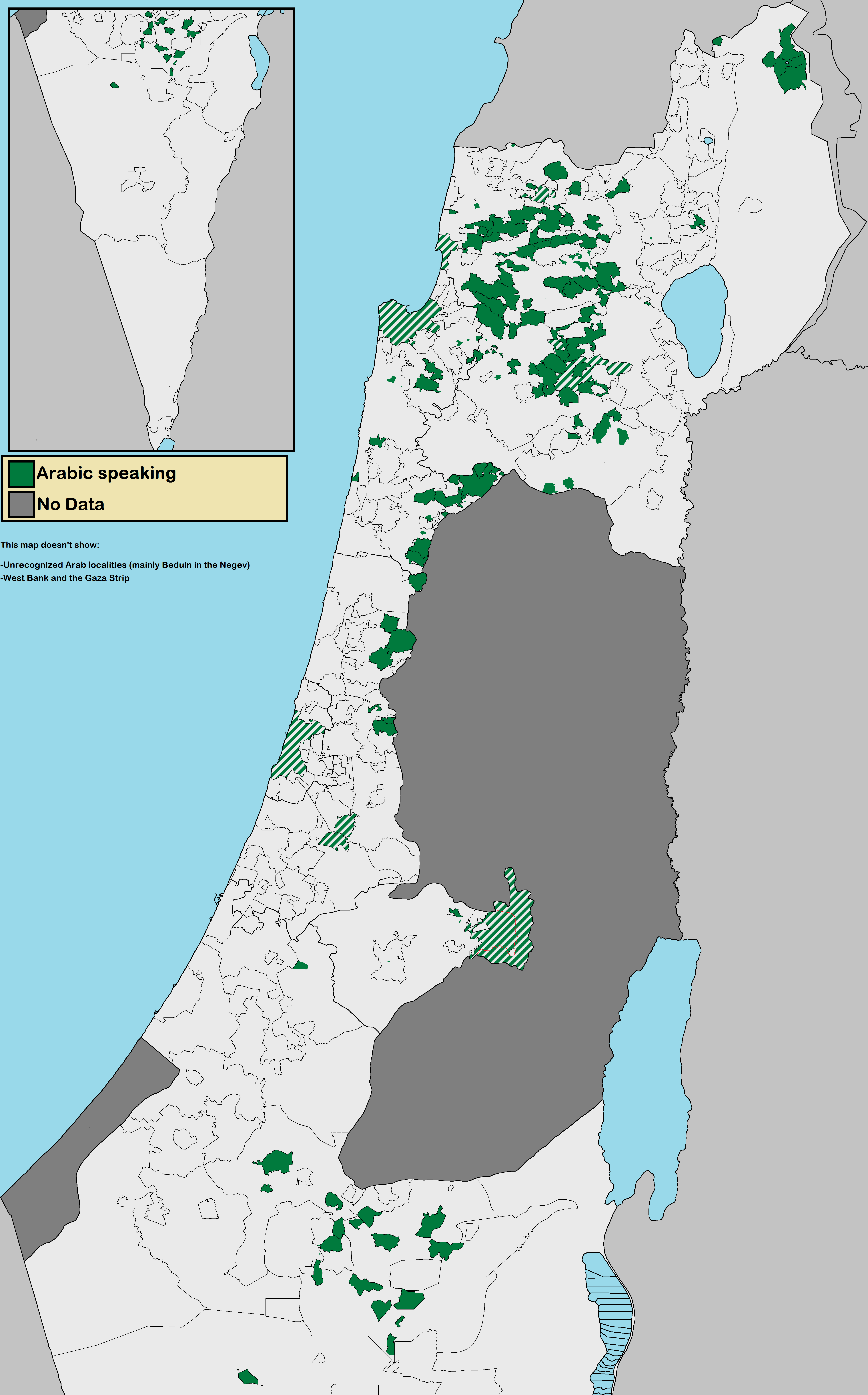
Israeli Arab
The Arab citizens of Israel are the largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic and Hebrew, and with varying social identities. Self-identification as Palestinian citizens of Israel has sharpened in recent years, alongside distinct identities including Galilee and Negev Bedouin, the Druze people, and Arab Christians and Arab Muslims who do not identify as Palestinians. In Arabic, commonly used terms to refer to Israel's Arab population include 48-Arab ( ar, عرب 48, Arab Thamaniya Wa-Arba'in, label=none) and 48-Palestinian (). Since the Nakba, the Palestinians that have remained within Israel's 1948 borders have been colloquially known as "48-Arabs". In Israel itself, Arab citizens are commonly referred to as Israeli-Arabs or simply as ''Arabs''; international media often uses the term Arab-Israeli to distinguish Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qassam Rocket
The Qassam rocket ( ar, صاروخ القسام ''Ṣārūkh al-Qassām''; also ''Kassam'') is a simple, steel artillery rocket developed and deployed by the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades, the military arm of Hamas. These rockets cannot be fired to target specific military objectives in or near civilian areas, and are "indiscriminate when used against targets in population centers". Three models have been produced and used, the first being introduced in 2001. More generally, all types of Palestinian rockets fired into southern Israel, for example the Palestinian Islamic Jihad Al Quds rockets, are called Qassams by the Israeli media, and often by foreign media. History of the Qassam Name Qassam rockets are named after the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades, the armed branch of Hamas, itself named for Izz ad-Din al-Qassam, a Syrian Muslim preacher whose death during a guerrilla raid against British Mandatory authorities in 1935 was one of the catalysts for the 1936–39 Arab revolt i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airstrike
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The official definition includes all sorts of targets, including enemy air targets, but in popular usage the term is usually narrowed to a tactical (small-scale) attack on a ground or naval objective as opposed to a larger, more general attack such as carpet bombing. Weapons used in an airstrike can range from direct-fire aircraft-mounted cannons and machine guns, rockets and air-to-surface missiles, to various types of aerial bombs, glide bombs, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, and even directed-energy weapons such as laser weapons. In close air support, air strikes are usually controlled by trained observers on the ground for coordination with ground troops and intelligence in a manner derived from artillery tactics. History Beginnings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nidal Fat'hi Rabah Farahat
''Nidal Fat’hi Rabah Farahat ( ar, نضال فتحي رباح فرحات, ) (8 April 197116 February 2003) created the Qassam rocket, a homemade weapon produced by the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades. After the Intifada, Farahat was arrested following the death of senior Hamas militant Imad Aqel. After spending three years in Israeli detention, he returned to Gaza. At the beginning of the Al-Aqsa Intifada, in 2000, Farahat officially joined the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades and soon became an active member in the organization, planning and carrying out numerous operations including mortar attacks on Jewish settlements in the Gaza strip. In 2001, Farahat, after several months of work, produced the first prototype for the Qassam rocket and presented it to Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades leaders Salah Shahade and Adnan al-Ghoul. Together with al-Ghoul, Farahat then worked on developing a better version of the Qassam, the "Qassam 2". Hamas militants used the Qassam 2 extensively afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEMRI
The Middle East Media Research Institute (MEMRI; officially the "Middle East Media and Research Institute") is a nonprofit press monitoring and analysis organization co-founded by former Israeli military intelligence officer Yigal Carmon and Israeli-American political scientist Meyrav Wurmser. Headquartered in Washington, D.C., MEMRI publishes and distributes free English-language translations of Arabic, Persian, Urdu, Pashto, and Turkish media reports. Critics describe MEMRI as a strongly pro-Israel advocacy group that, despite portraying itself as "independent" and "non-partisan",: "But what about using MEMRI, what about the various accusations? There is no monolithic answer. As a translation service it is of great value. As a research tool the evaluation is more complex as it demands good background information in order to contextualize the information obtained, due to the organization's lack of transparency and attempt to pose as something different than what they are. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civilization (19th-11th century BCE), and the majority of Mesoamerican people ─ including the Maya and Aztecs ─ made chocolate beverages. The seeds of the cacao tree have an intense bitter taste and must be fermented to develop the flavor. After fermentation, the seeds are dried, cleaned, and roasted. The shell is removed to produce cocoa nibs, which are then ground to cocoa mass, unadulterated chocolate in rough form. Once the cocoa mass is liquefied by heating, it is called chocolate liquor. The liquor may also be cooled and processed into its two components: cocoa solids and cocoa butter. Baking chocolate, also called bitter chocolate, contains cocoa solids and cocoa butter in varying proportions, without any added sugar. Powder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halva
Halva (also halvah, halwa, and other spellings, Persian : حلوا) is a type of confectionery originating from Persia and widely spread throughout the Middle East. The name is used for a broad variety of recipes, generally a thick paste made from flour, butter, liquid oil, saffron, rosewater, milk, cocoa powder, and sweetened with sugar. Halva is popular in Iran and the Middle East. Etymology The word ''halva'' entered the English language between 1840 and 1850 from Romanian, which came from the ota, حلوى, helva, itself ultimately derived from the ar, حلوى, ḥalwá, a sweet confection.Halvah , 2009 The root in ar, ح ل و, ''ḥ-l-w'', links=no, means "sweet". ...
|
Allahu Akbar
Allah (; ar, الله, translit=Allāh, ) is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from '' al- ilāh'', which means "the god", and is linguistically related to the Aramaic words Elah and Syriac (ʼAlāhā) and the Hebrew word '' El'' (''Elohim'') for God. The feminine form of Allah is thought to be the word Allat. The word ''Allah'' has been used by Arabic people of different religions since pre-Islamic times. The pre-Islamic Arabs worshipped a supreme deity whom they called Allah, alongside other lesser deities. Muhammad used the word ''Allah'' to indicate the Islamic conception of God. ''Allah'' has been used as a term for God by Muslims (both Arab and non-Arab) and even Arab Christians after the term " al- ilāh" and "Allah" were used interchangeably in Classical Arabic by the majority of Arabs who had become Muslims. It is also often, albeit not exclusivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |