|
Ultra Low Velocity Zone
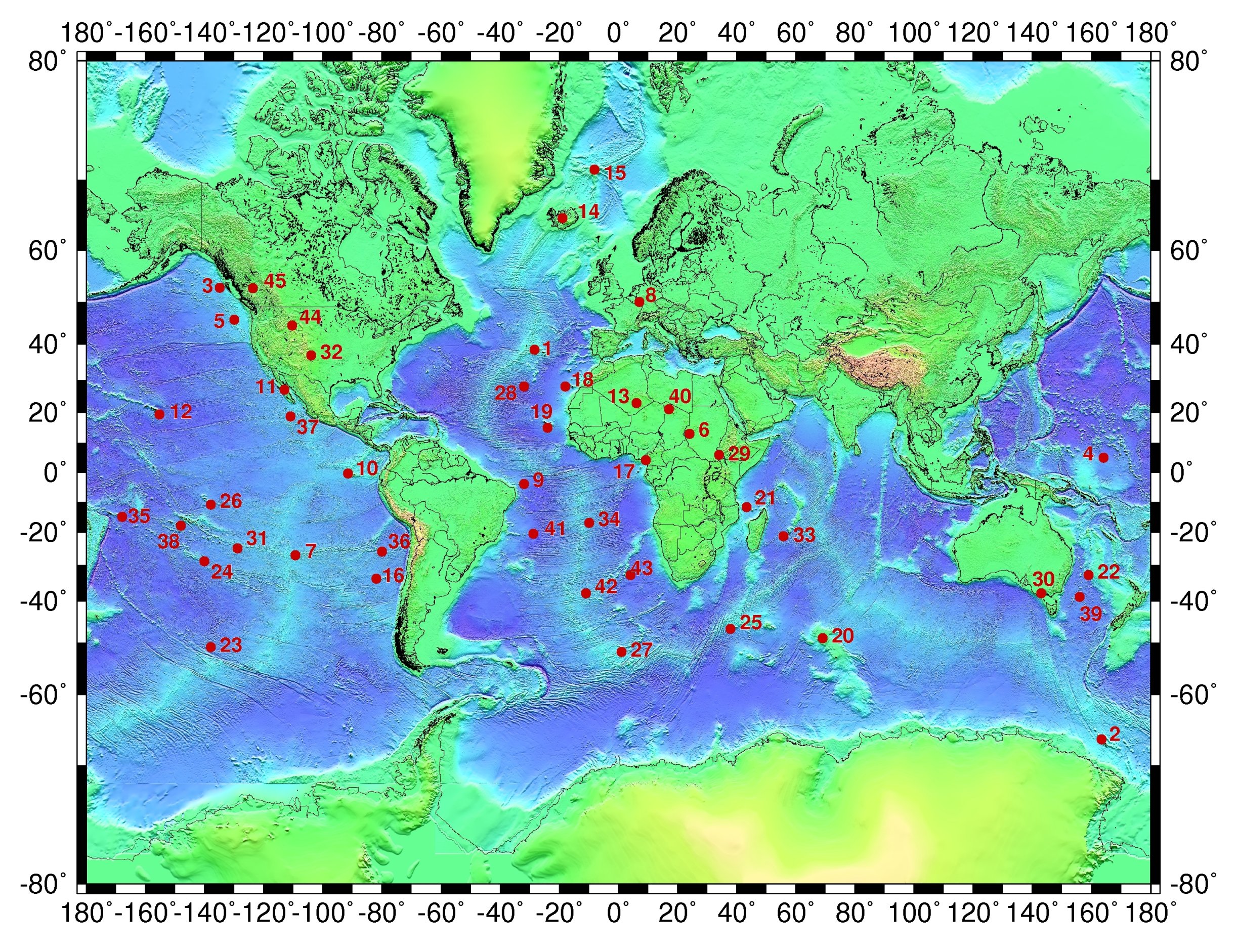
Ultra low velocity zones (ULVZs) are patches on the core-mantle boundary that have extremely low seismic velocities. The zones are mapped to be hundreds of kilometers in diameter and tens of kilometers thick. Their shear wave velocities can be up to 30% lower than surrounding material. The composition and origin of the zones remain uncertain. The zones appear to correlate with edges of the African and Pacific Large low-shear-velocity provinces (LLSVPs) as well as the location of hotspots. Discovery and constraints ULVZs are discovered by the delay and scattering of body waves that reflect and diffract on or are refracted by the core-mantle boundary. Different body waves types give different constraints on the dimensions or velocity contrasts of the ULVZ. Even though ULVZs are discovered in places, it remains difficult to map out their extent and constrain their density and velocity. Usually trade-offs between various parameters exist. In general though, ULVZs appear to be a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoa Hotspot
The Samoa hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located in the south Pacific Ocean. The hotspot model describes a hot upwelling plume of magma through the Earth's crust as an explanation of how volcanic islands are formed. The hotspot idea came from J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 based on the Hawaiian Islands volcanic chain. In theory, the Samoa hotspot is based on the Pacific Tectonic Plate traveling over a fixed hotspot located deep underneath the Samoan Islands. The Samoa hotspot includes the Samoan Islands (American Samoa and Samoa), and extends to the islands of Uvea or Wallis Island (Wallis and Futuna) and Niulakita (Tuvalu), as well as the submerged Pasco banks and Alexa Bank. As the Pacific Plate moves slowly over the hotspot, thermal activity builds up and is released in magma plume spewing through the Earth's crust, forming each island in a chain. The Samoa islands generally lie in a straight line, east to west, in the same direction of the tectonic plate 'drifting' over the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific ULVZs
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii Hotspot
The Hawaii hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located near the namesake Hawaiian Islands, in the northern Pacific Ocean. One of the best known and intensively studied hotspots in the world, the Hawaii plume is responsible for the creation of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, a mostly undersea volcanic mountain range. Four of these volcanoes are active, two are dormant; more than 123 are extinct, most now preserved as atolls or seamounts. The chain extends from south of the island of Hawaii to the edge of the Aleutian Trench, near the eastern coast of Russia. While most volcanoes are created by geological activity at tectonic plate boundaries, the Hawaii hotspot is located far from plate boundaries. The classic hotspot theory, first proposed in 1963 by John Tuzo Wilson, proposes that a single, fixed mantle plume builds volcanoes that then, cut off from their source by the movement of the Pacific Plate, become increasingly inactive and eventually erode below sea level over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Institute Of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasionally referred to as "CIT", most notably in its alma mater, but this is uncommon. is a private university, private research university in Pasadena, California. Caltech is ranked among the best and most selective academic institutions in the world, and with an enrollment of approximately 2400 students (acceptance rate of only 5.7%), it is one of the world's most selective universities. The university is known for its strength in science and engineering, and is among a small group of Institute of Technology (United States), institutes of technology in the United States which is primarily devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences. The institution was founded as a preparatory and vocational school by Amos G. Throop in 1891 and began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periclase
Periclase is a magnesium mineral that occurs naturally in contact metamorphic rocks and is a major component of most basic refractory bricks. It is a cubic form of magnesium oxide ( Mg O). In nature it usually forms a solid solution with wüstite (FeO) and is then referred to as ferropericlase or magnesiowüstite. It was first described in 1840 and named from the Greek περικλάω (to break around) in allusion to its cleavage. The type locality is Monte Somma, Somma-Vesuvius Complex, Naples Province, Campania, Italy. The old term for the mineral is ''magnesia''. Stones from the Magnesia region in ancient Anatolia contained both magnesium oxide and hydrated magnesium carbonate as well as iron oxides (such as magnetite). Thus these stones, called ''Stones from Magnesia'' in antiquity, with their unusual magnetic properties were the reason the terms ''magnet'' and ''magnetism'' were coined. Periclase is usually found in marble produced by metamorphism of dolomitic limest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite
Perovskite (pronunciation: ) is a calcium titanium oxide mineral composed of calcium titanate (chemical formula ). Its name is also applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure as (XIIA2+VIB4+X2−3), known as the perovskite structure. Many different cations can be embedded in this structure, allowing the development of diverse engineered materials. History The mineral was discovered in the Ural Mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and is named after Russian mineralogist Lev Perovski (1792–1856). Perovskite's notable crystal structure was first described by Victor Goldschmidt in 1926 in his work on tolerance factors. The crystal structure was later published in 1945 from X-ray diffraction data on barium titanate by Helen Dick Megaw. Occurrence Found in the Earth's mantle, perovskite's occurrence at Khibina Massif is restricted to the silica under-saturated ultramafic rocks and foidolites, due to the instability in a paragen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
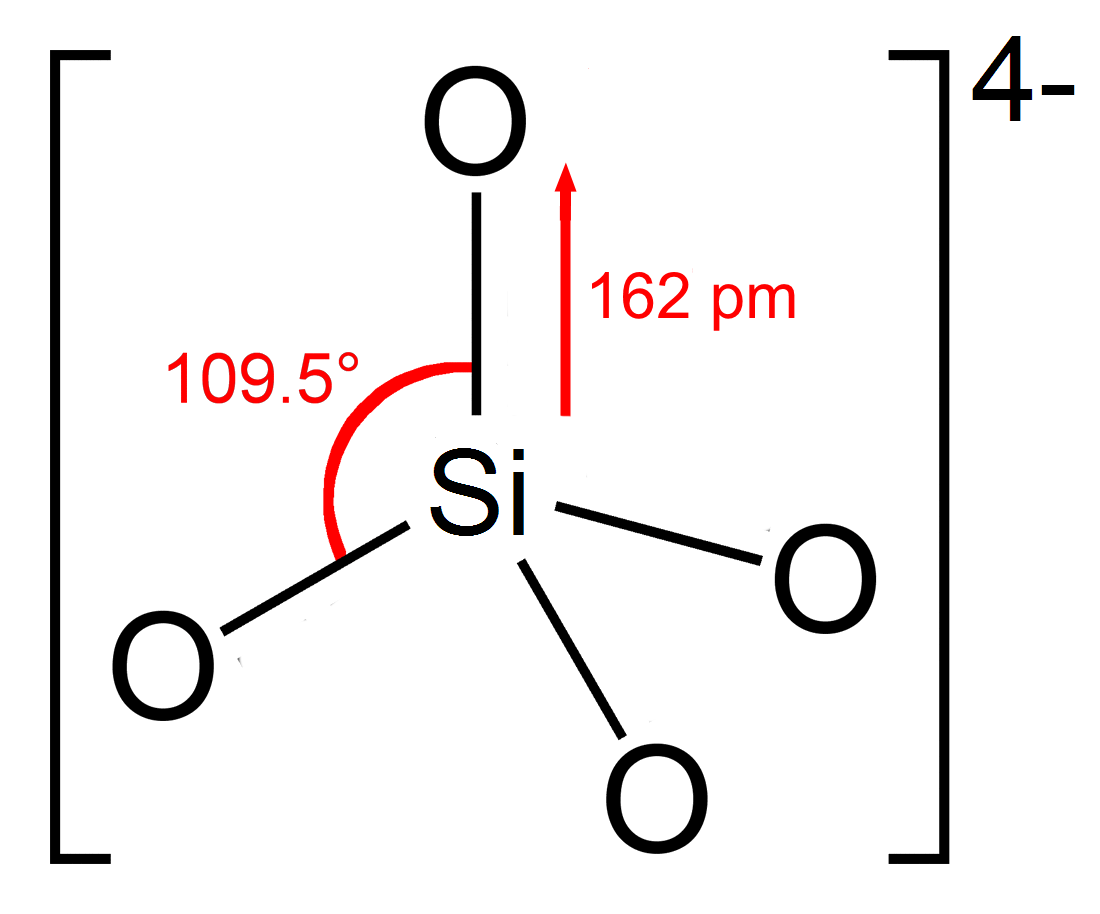
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma Ocean
Magma oceans exist during periods of Earth's or any planet's Accretion (astrophysics), accretion when the planet is completely or partly molten. In the early Solar System, magma oceans were formed by the melting of Planetesimal, planetesimals and planetary impacts. Small planetesimals are melted by the heat provided by the radioactive decay of aluminium-26. As planets grew larger, the energy was then supplied from large or giant impacts with other planetary bodies. Magma oceans are integral parts of planetary formation as they facilitate the formation of a core through metal segregation and an atmosphere and hydrosphere through degassing. Evidence exists to support the existence of magma oceans on both the Moon and the Earth. Magma oceans may survive for millions to tens of millions of years, interspersed by relatively mild conditions. Magma ocean heat sources The sources of the energy required for the formation of magma oceans in the early Solar System were the radioactive decay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Velocity
A seismic wave is a wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth. It can result from an earthquake, volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide, and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy. Seismic waves are studied by seismologists, who record the waves using seismometers, hydrophones (in water), or accelerometers. Seismic waves are distinguished from seismic noise (ambient vibration), which is persistent low-amplitude vibration arising from a variety of natural and anthropogenic sources. The propagation velocity of a seismic wave depends on density and elasticity of the medium as well as the type of wave. Velocity tends to increase with depth through Earth's crust and mantle, but drops sharply going from the mantle to Earth's outer core. Earthquakes create distinct types of waves with different velocities. When recorded by a seismic observatory, their different travel times help scientists locate the quake's hypoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)
_crystallographic_standard_alignment.png)