|
Ukiyoburo
is a Japanese novel written by Shikitei Sanba between 1809 and 1813. It belongs to the kokkeibon genre, of which it is one of the masterpieces. Contents ''Ukiyoburo'' (Ukiyo Bath) depicts the humor of daily life and culture through the conversations of customers at the public bath. It contains illustrations from Utagawa Kuninao and Kitao Shigemasa (credited as Kitagawa Yoshimaru). Shikitei notes that his inspiration to base the story at a public bath was due to Santō Kyōden's (1802) and a rakugo performance by Sanshōtei Karaku. The text is composed of four parts contained within nine volumes: *Part 1: "Men's Bath", published in 1809 *Part 2: "Women's Bath", published in 1810 *Part 3: "Omissions from the Women's Bath", published in 1812 *Part 4: "Men's Bath Continued", published in 1813 There were advertisements for parts 5, 6, and 7, but they were never written. Linguistics Shikitei was particularly careful in noting a number of linguistic characteristics. In part two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikitei Sanba
, better known by his pen name , was a Japanese comic writer of the Edo period. Major works *''Ukiyoburo'' *''Ukiyodoko'' References 1776 births 1822 deaths Japanese writers of the Edo period {{Japan-writer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokkeibon
The was a genre and type of early modern Japanese novel. It came into being late in the Edo period during the 19th century. As a genre, it depicted the comical behavior occurring in commoners' daily lives. The ''kokkeibon'' genre is the successor of the ''dangibon'' genre. Jippensha Ikku's ''Tōkaidōchū Hizakurige'' (1802–1822) is identified as the first representative novel. A less strict definition includes the ''dangibon'' as an "early ''kokkeibon''". ''Kokkeibon'' generally consists of dialogue among the main characters and includes illustrations. The genre was most popular between 1804 and 1830, and is most representative by the works of Jippensha Ikku and Shikitei Sanba. See also *''Gesaku is an alternative style, genre, or school of Japanese literature. In the simplest contemporary sense, any literary work of a playful, mocking, joking, silly or frivolous nature may be called gesaku. Unlike predecessors in the literary field, gesak ...'' References * * E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
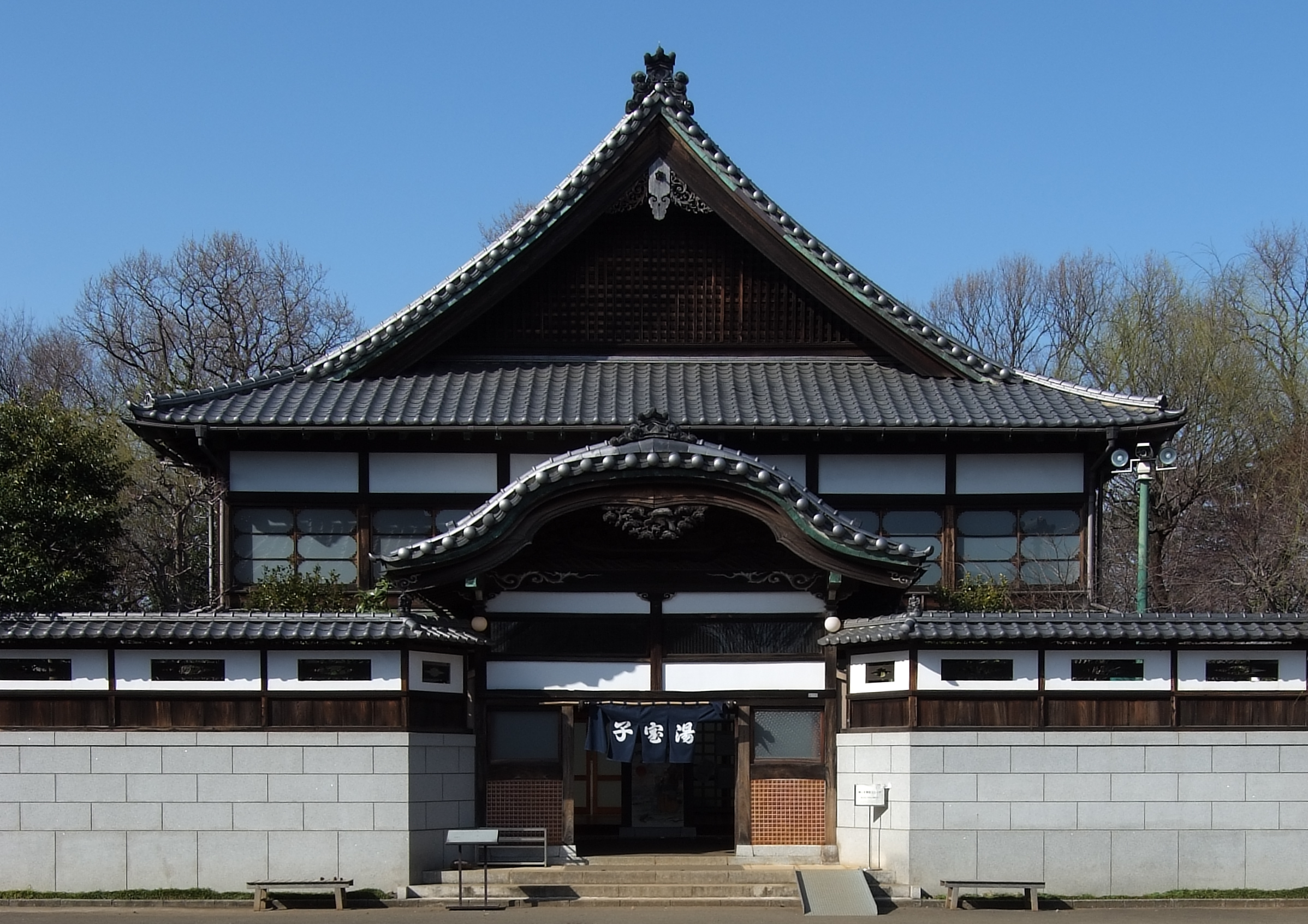
Sentō
is a type of Japanese communal bathhouse where customers pay for entrance. Traditionally these bathhouses have been quite utilitarian, with a tall barrier separating the sexes within one large room, a minimum of lined-up faucets on both sides, and a single large bath for the already washed bathers to sit in among others. Since the second half of the 20th century, these communal bathhouses have been decreasing in numbers as more and more Japanese residences now have baths. Some Japanese find social importance in going to public baths, out of the theory that physical proximity/intimacy brings emotional intimacy, which is termed '' skinship'' in pseudo-English Japanese. Others go to a ''sentō'' because they live in a small housing facility without a private bath or to enjoy bathing in a spacious room and to relax in saunas or jet baths that often accompany new or renovated sentōs. Another type of Japanese public bath is ''onsen'', which uses hot water from a natural hot spring. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utagawa Kuninao
The name Utagawa may refer to: *The Utagawa school The Utagawa school () was one of the main schools of ukiyo-e, founded by Utagawa Toyoharu. It was the largest ukiyo-e school of its period. The main styles were bijin-ga (beautiful women) and uki-e (perspective picture). His pupil, Toyokuni I, to ... of Japanese woodblock print artists *One of the artists of the Utagawa school, including: ** ** **, also known as Andō Hiroshige **, also known as Utagawa Toyokuni III ** ** ** ** *, Japanese ornithologist and academic *, Japanese scholar of Western Studies {{disambiguation, surname Japanese-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitao Shigemasa
was a Japanese ukiyo-e artist from Edo. He was one of the leading printmakers of his day, but his works have been slightly obscure. He is noted for images of beautiful women (''bijinga''). He was taught by Shigenaga and has been referred to as "a chameleon" who adopted to changing styles. He was less active after the rise of Torii Kiyonaga and produced relatively few works considering the length of his career. He is also noted for his haikai (poetry) and shodō (Japanese calligraphy). In his later years he used the studio name Kosuisai. Life and career Shigemasa was born the eldest son of bookseller Suharaya Mohei in 1739 in Nihonbashi area Edo (modern Tokyo). His family name was Kitabatake and his childhood name was Tarōkichi. Throughout his life he also used the personal names Kyūgorō and Sasuke. His work also appeared under the art names Hokuhō, Kōsuisai, Kōsuiken, Suihō Itsujin, and others, and he used the poetry name Karan. Shigemasa taught himself art before becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santō Kyōden
Santō Kyōden (山東 京伝, 13 September 1761 Edo – 27 October 1816) was a Japanese artist, writer, and the owner of a tobacco shop during the Edo period. His real name was Iwase Samuru (岩瀬 醒), and he was also known popularly as Kyōya Denzō (京屋伝蔵, ''kyōya denzō''). He began his professional career illustrating the works of others before writing his own Kibyōshi and Sharebon. Within his works, Kyōden often included references to his shop to increase sales. Kyōden's works were affected by the shifting publication laws of the Kansei Reforms which aimed to punish writers and their publishers for writings related to the Yoshiwara and other things that were deemed to be "harmful to society" at the time by the Tokugawa Bakufu. As a result of his punishment in 1791, Kyōden shifted his writings to the more didactic Yomihon. During the 1790s, Santō Kyōden became a household name and one of his works could sell as many as 10,000 copies, numbers that were previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rakugo
is a form of ''yose'', which is itself a form of Japanese verbal entertainment. The lone sits on a raised platform, a . Using only a and a as props, and without standing up from the seiza sitting position, the rakugo artist depicts a long and complicated comical (or sometimes sentimental) story. The story always involves the dialogue of two or more characters. The difference between the characters is depicted only through change in pitch, tone, and a slight turn of the head. Lexical background Rakugo was originally known as . The oldest appearance of the kanji which refers specifically to this type of performance dates back to 1787, but at the time the characters themselves (落とし噺) were normally read as ''otoshibanashi'' (falling discourse). In the middle of the Meiji period (1868–1912) the expression ''rakugo'' first started being used, and it came into common usage only in the Shōwa period (1926–1989). Description The speaker is in the middle of the audience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansai Dialect
The is a group of Japanese dialects in the Kansai region (Kinki region) of Japan. In Japanese, is the common name and it is called in technical terms. The dialects of Kyoto and Osaka are known as , and were particularly referred to as such in the Edo period. The Kansai dialect is typified by the speech of Osaka, the major city of Kansai, which is referred to specifically as . It is characterized as being both more melodic and harsher by speakers of the standard language.Omusubi: Japan's Regional Diversity retrieved January 23, 2007 Background Since Osaka is the largest city in the region and its speakers gained the most media exposure over the last century, non-Kansai-dialect speakers tend to associate the dialect of Osaka with the entire Kansai region. However, technically ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
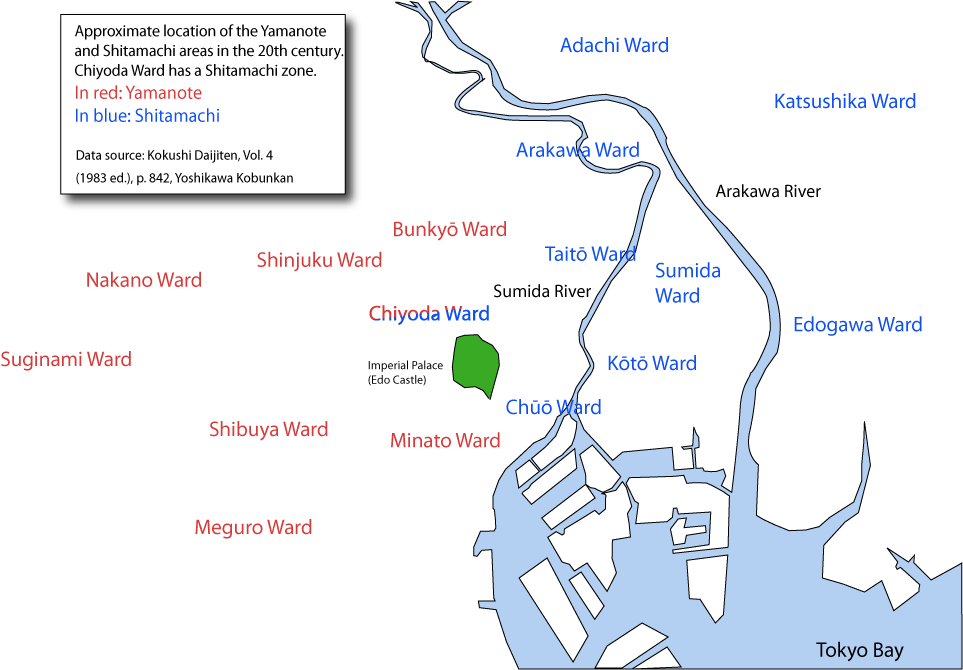
Tokyo Dialect
The Tokyo dialect () is a variety of Japanese language spoken in modern Tokyo. As a whole, it is generally considered to be Standard Japanese, though specific aspects of slang or pronunciation can vary by area and social class. Overview Traditional dialects in central Tokyo are generally classified in two groups: and . The Yamanote dialect is characteristic of the old upper class from the Yamanote area. Standard Japanese was based on the Yamanote dialect during the Meiji period. The Shitamachi dialect is a working-class dialect, and it preserves features of Edo Chōnin (Edokko) speech, so also called . Tokyo-style rakugo is typically played in the Shitamachi dialect. Tokyo dialect dates back to Tokugawa Ieyasu's establishment of Edo. Large groups of people, speaking a range of dialects migrated across the country. The Kyoto dialect was the prestige language of the time and strongly influenced the Edo dialect in the early Edo period; the dialect grew inside the largest c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labialisation
Labialization is a secondary articulatory feature of sounds in some languages. Labialized sounds involve the lips while the remainder of the oral cavity produces another sound. The term is normally restricted to consonants. When vowels involve the lips, they are called rounded. The most common labialized consonants are labialized velars. Most other labialized sounds also have simultaneous velarization, and the process may then be more precisely called labio-velarization. In phonology, labialization may also refer to a type of assimilation process. Occurrence Labialization is the most widespread secondary articulation in the world's languages. It is phonemically contrastive in Northwest Caucasian (e.g. Adyghe), Athabaskan, and Salishan language families, among others. This contrast is reconstructed also for Proto-Indo-European, the common ancestor of the Indo-European languages; and it survives in Latin and some Romance languages. It is also found in the Cushitic and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakuten
The , colloquially , is a diacritic most often used in the Japanese kana syllabaries to indicate that the consonant of a syllable should be pronounced voiced, for instance, on sounds that have undergone rendaku (sequential voicing). The , colloquially , is a diacritic used with the kana for syllables starting with ''h'' to indicate that they should instead be pronounced with . History The ''kun'yomi'' pronunciation of the character is ''nigori''; hence the ''daku-ten'' may also be called the ''nigori-ten''. This character, meaning ''muddy'' or ''turbid'', stems from historical Chinese phonology, where consonants were traditionally classified as ''clear'' ( "voiceless"), ''lesser-clear'' ( " aspirated") and ''muddy'' ( "voiced"). (See: Middle Chinese § Initials) ''Dakuten'' were used sporadically since the start of written Japanese; their use tended to become more common as time went on. The modern practice of using dakuten in all cases of voicing in all writing only came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |