|
Ugyuligmiut
The Ugyuligmiut were a geographically defined Copper Inuit band in the Canadian Arctic's Northwest Territories. They were located on Victoria Island north of Minto Inlet, and on Banks Island in the Aulavik National Park region. The Minto Inlet Ugyuligmiut were noted during the Arctic voyages of both Sir Richard Collinson and Sir Robert McClure in the mid 19th century. However, at the time of Vilhjalmur Stefansson Vilhjalmur Stefansson (November 3, 1879 – August 26, 1962) was an Arctic explorer and ethnologist. He was born in Manitoba, Canada. Early life Stefansson, born William Stephenson, was born at Arnes, Manitoba, Canada, in 1879. His parents had ...'s explorations in 1914, the Victoria Island Inuit told him of the Ugyuligmiut, a "numerous population", but that they were now extinct, either from famine or from being shot. References Copper Inuit Inuvialuit groups {{NorthwestTerritories-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Inuit
Copper Inuit, also known as Kitlinermiut and Inuinnait, are a Canadian Inuit group who live north of the tree line, in what is now the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut and in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Most of them historically lived in the area around Coronation Gulf, on Victoria Island, and southern Banks Island. Their western boundary was Wise Point, near Dolphin and Union Strait. Their northwest territory was the southeast coast of Banks Island. Their southern boundary was the eastern shore of Great Bear Lake, Contwoyto Lake and Lake Beechey on the Back River. To the east, the Copper Inuit and the Netsilingmiut were separated by Perry River in Queen Maud Gulf. While Copper Inuit travelled throughout Victoria Island, to the west, they concentrated south of Walker Bay, while to the east, they were concentrated south of Denmark Bay. As the people have no collective name for themselves, they have adopted the English term "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three Provinces_and_territories_of_Canada#Territories, territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 1 per cent of demographics of Canada, Canada's population. The terms "northern Canada" or "the North" may be used in contrast with ''the far north'', which may refer to the Canadian Arctic, the portion of Canada that lies north of the Arctic Circle, east of Alaska and west of Greenland. However, in many other uses the two areas are treated as a single unit. __TOC__ Definitions Subdivisions As a social rather than political region, the Canadian North is often subdivided into two distinct regions based on climate, the ''near north'' and the ''far north''. The different climates of these two regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2022 is 45,605. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. Since then, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current borders date from April 1, 1999, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Island (Canada)
Victoria Island ( ikt, Kitlineq, italic=yes) is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain () but smaller than Honshu (). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The island is named after Queen Victoria, the Canadian sovereign from 1867 to 1901 (though she first became Queen in 1837). The features bearing the name "Prince Albert" are named after her consort, Albert. History In 1826 John Richardson saw the southwest coast and called it " Wollaston Land". In 1839 Peter Warren Dease and Thomas Simpson followed its southeast coast and called it "Victoria Land". A map published by John Barro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
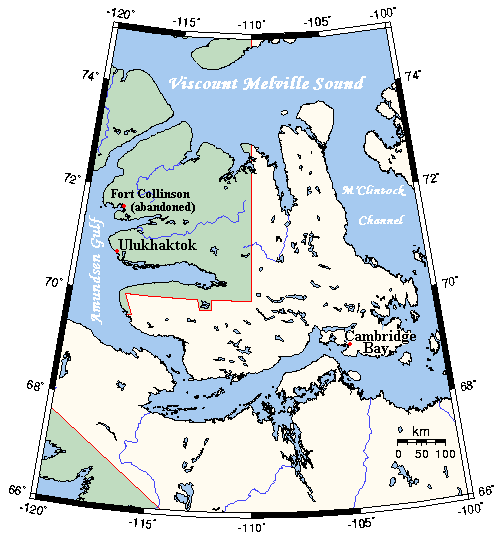
Minto Inlet
Minto Inlet is located east of Amundsen Gulf in western Victoria Island, at the southern end of Prince of Wales Strait in the Northwest Territories. It is long and between wide. The inlet is part of the historical territory of the Copper Inuit. It continues to be notable for the Minto Inlet caribou herd calving grounds. Richard Collinson Admiral Sir Richard Collinson (7 November 1811 – 13 September 1883) was an English naval officer and explorer of the Northwest Passage. Early life He was born in Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, England, then part of County Durham. He joined the R ... wintered here in 1851/52. References Further reading Minto Inlet and the "Blond Eskimos" Inlets of the Northwest Territories Inlets of the Arctic Ocean Victoria Island (Canada) {{NorthwestTerritories-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banks Island
Banks Island is one of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago. Situated in the Inuvik Region, and part of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, of the Northwest Territories, it is separated from Victoria Island to its east by the Prince of Wales Strait and from the mainland by Amundsen Gulf to its south. The Beaufort Sea lies to its west, and to its northeast M'Clure Strait separates the island from Prince Patrick Island and Melville Island. It is home to at least fourteen mammal species including the Peary caribou, barren-ground caribou, and polar bears. At one time over 68,000 muskoxen lived on the island, the majority of the world's population. However, the bacterium ''Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae'' has led to a sharp decline in their numbers. The island is the summer home to hundreds of thousands of migratory birds who nest at Banks Island Migratory Bird Sanctuary No. 1 and Banks Island Migratory Bird Sanctuary No. 2. As of the 2016 census it had a human population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulavik National Park
Aulavik National Park ( ); from the Inuvialuktun for "place where people travel") is a national park located on Banks Island in the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is known for its access to the Thomsen River, one of the most northerly navigable rivers in North America. The park is a fly-in park, and protects approximately of Arctic Lowlands at the northern end of the island. The most practical way to visit the park is to charter a plane, and currently the park has four landing sites. Aulavik is considered a polar desert and often experiences high winds. Precipitation for the park is approximately per year. In the southern regions of the park a sparsely vegetated upland plateau reaches a height of above sea level. The park has the highest concentration of muskoxen on earth, with estimates of 68,000 to 80,000 animals on the island, approximately 20% of which are thought to reside in the park. It is also home to the endangered Peary caribou as well as the more common barr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), Sweden and the United States (Alaska). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and sea ice, ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost (permanently frozen underground ice) containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold and extreme conditions. Life in the Arctic includes zooplankton and phytoplankton, fish and marine mammals, birds, land animals, plants and human societies. Arctic land is bordered by the subarctic. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Collinson
Admiral Sir Richard Collinson (7 November 1811 – 13 September 1883) was an English naval officer and explorer of the Northwest Passage. Early life He was born in Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, England, then part of County Durham. He joined the Royal Navy in 1823 at age twelve and rose in the ranks, becoming a lieutenant in 1835, commander in 1841, and captain in 1842. China Collinson was in command of the ''Lady Bentinck'', a vessel of 1800 tons burden and 520 horsepower, when it appeared with the ''Phlegethon'' off Chapoo in eastern China, causing a "sensation". On 1 April 1842, the British Plenipotentiary of Trade Henry Pottinger reported that Collinson, as commander of the ''Nemesis'' based in Chusan, had contributed to a successful skirmish with Chinese troops on the island of Taisam near Ningbo in February of that year. As commander of HMS ''Plover'', and with the aid of Lt Henry Kellett in HMS ''Starling'', he surveyed the China coast from 1842 to 1846, producing charts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert McClure
Vice-Admiral Sir Robert John Le Mesurier McClure (28 January 1807 – 17 October 1873) was an Irish explorer of Scots descent who explored the Arctic. In 1854 he traversed the Northwest Passage by boat and sledge, and was the first to circumnavigate the Americas. Early life and career McClure was born in Wexford in the south-east of Ireland. His father was Captain Robert McClure from County Londonderry in Ulster, who was serving with the 89th Foot. McClure's mother (the daughter of Archdeacon John Elgee) and father had met and married while his father was stationed in Wexford in 1807; but, his father had died by the time of McClure's birth. He was a first cousin of Jane Wilde, the mother of Oscar Wilde, and spent his childhood under the care of his godfather, John Le Mesurier, governor of Alderney, by whom he was educated for the army. It is said that this branch of the McClures, who settled in County Londonderry in the 1650s, during the Plantation of Ulster, were actu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilhjalmur Stefansson
Vilhjalmur Stefansson (November 3, 1879 – August 26, 1962) was an Arctic explorer and ethnologist. He was born in Manitoba, Canada. Early life Stefansson, born William Stephenson, was born at Arnes, Manitoba, Canada, in 1879. His parents had emigrated from Iceland to Manitoba two years earlier. After losing two children during a period of devastating flooding, the family moved to Dakota Territory in 1880 and homesteaded a mile southwest of the village of Mountain in Thingvalla Township of Pembina County. He was educated at the universities of North Dakota and of Iowa (A.B., 1903). During his college years, in 1899, he changed his name, for unknown reasons, to Vilhjalmur Stefansson. He studied anthropology at the graduate school of Harvard University, where for two years he was an instructor. Early explorations In 1904 and 1905, Stefansson did archaeological research in Iceland. Recruited by Ejnar Mikkelsen and Ernest de Koven Leffingwell for their Anglo-American Polar Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(20511445502).jpg)


