|
Udaipur Solar Observatory
The Udaipur Solar Observatory (USO) is in Udaipur, Rajasthan in India on an island in the Fateh Sagar Lake. The sky conditions at Udaipur are quite favourable for solar observations. Since the observatory is situated amidst a large mass of water, air turbulence which occurs due to ground heating by sun's rays is decreased. This improves the image quality and accuracy (average between 1-2 arc seconds). History The observatory was built in 1976 by Dr. Arvind Bhatnagar following the model of the Solar Observatory at Big Bear lake in Southern California. Later, he was joined by Dr. Ashok Ambastha in 1983 and subsequently by many others at different stages who have continued further contributing to the growth of this observatory. Telescopes Utilizing a variety of telescopes, USO is known for its solar observations, which include high-resolution solar chromospheric, magnetic field, velocity, and spectral observations, for studies pertaining to solar flares, mass ejections, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udaipur Observatory
Udaipur () ( ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of the kingdom of Mewar in the former Rajputana Agency. It was founded in 1559 by Udai Singh II of the Sisodia clan of Rajput, when he shifted his capital from the city of Chittorgarh to Udaipur after Chittorgarh was besieged by Akbar. It remained as the capital city till 1818 when it became a British princely state, and thereafter the Mewar province became a part of Rajasthan when India gained independence in 1947. The city is located in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, near the Gujarat border. It is surrounded by the Aravali Range, which separates it from the Thar Desert. It is placed almost in the middle of two major Indian metro cities, around 660 km from Delhi and 800 km from Mumbai. Besides, connectivity with Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Ejections
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attractions In Udaipur
Udaipur city, also known as the 'City of Lakes' and 'Venice of East', is a very popular tourist destination in Rajasthan, India. The capital of the former princely state of Mewar, and considered as one amongst the most romantic cities of India, Udaipur is a land around the azure water lakes, hemmed in by the lush hills of the Aravalis. The city is a blend of sights, sounds and experiences. With its kaleidoscope of fairy-tale palaces, lakes, temples, gardens and narrow lanes, the city carries the flavor of heroic past, epitomizing valor and chivalry. Voted the Best City in the World in 2009 by ''Travel + Leisure'' magazine, Udaipur is now amongst the favourite wedding destinations for Indian as well as foreign nationals. Some of the key tourist destinations are: Ahar Cenotaphs The Ahar Cenotaphs are a group of royal cenotaphs of the Maharanas of Mewar, located about 2 km east of Udaipur. It has about nineteen cenotaphs of various Maharanas cremated, including one of Maha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Udaipur
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatories In India
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, professional a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatories In Rajasthan
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Solar Telescopes
This is a list of solar telescopes built in various countries around the world. A solar telescope is a specialized telescope that is used to observe the Sun. This list contains ground-based professional observatory telescopes at optical wavelengths in chronological order. Solar telescopes often have multiple focal lengths, and use a various combination of mirrors such as coelostats, lenses, and tubes for instruments including spectrographs, cameras, or coronagraphs. There are many types of instruments that have been designed to observe Earth's Sun, for example, in the 20th century solar towers were common. Ground telescopes Optical telescopes Telescopes for the Sun have existed for hundreds of years, this list is not complete and only goes back to 1900. Potential future optical telescopes Radio telescopes Other types of solar telescopes There are much smaller commercial and/or amateur telescopes such as ''Coronado Filters'' from founder and designer David Lunt, bought by Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Oscillations Network Group
The Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) is a worldwide network of six identical telescopes, designed to have 24/7 observations of the Sun. The network serves multiple purposes, including the provision of operation data for use in space weather prediction, and the study of solar internal structure and dynamics using helioseismology. Deployed in 1995, GONG is a set of six observing systems geographically distributed around the Earth so that the Sun can be observed as continuously as possible. The six observatories are the Teide Observatory ( Canary Islands), thLearmonth Solar Observatory(Western Australia), the Big Bear Solar Observatory (California), the Mauna Loa Solar Observatory (Hawaii), the Udaipur Solar Observatory (India) and the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (Chile). With these sites, GONG typically can observe the Sun 91% of the time, 24/7. GONG was constructed to provide observations for helioseismology, which aims to understand the solar interior by analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
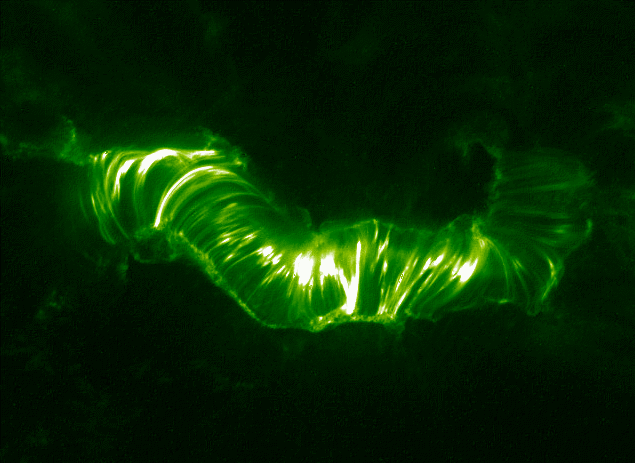
Solar Active Regions
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from '' Mesmer'', 2017 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * Solar, Erode, India * Solar, Iran, Iran Companies * Solar Entertainment Corporation, a Philippines television and radio media company * Solar TV, a former TV channel * Solar Television Network, Inc., a former name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. High-energy electromagnetic radiation from solar flares is absorbed by the daylight side of Earth's upper atmosphere, in particular the ionosphere, and does not reach the surface. This absorption can temporarily increase the ionization of the ionosphere which may interfere with short-wave radio communication. The prediction of solar flares is an active area of research. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term ''stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of the kingdom of Mewar in the former Rajputana Agency. It was founded in 1559 by Udai Singh II of the Sisodia clan of Rajput, when he shifted his capital from the city of Chittorgarh to Udaipur after Chittorgarh was besieged by Akbar. It remained as the capital city till 1818 when it became a British princely state, and thereafter the Mewar province became a part of Rajasthan when India gained independence in 1947. The city is located in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, near the Gujarat border. It is surrounded by the Aravali Range, which separates it from the Thar Desert. It is placed almost in the middle of two major Indian metro cities, around 660 km from Delhi and 800 km from Mumbai. Besides, connectivity with Gujar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |