|
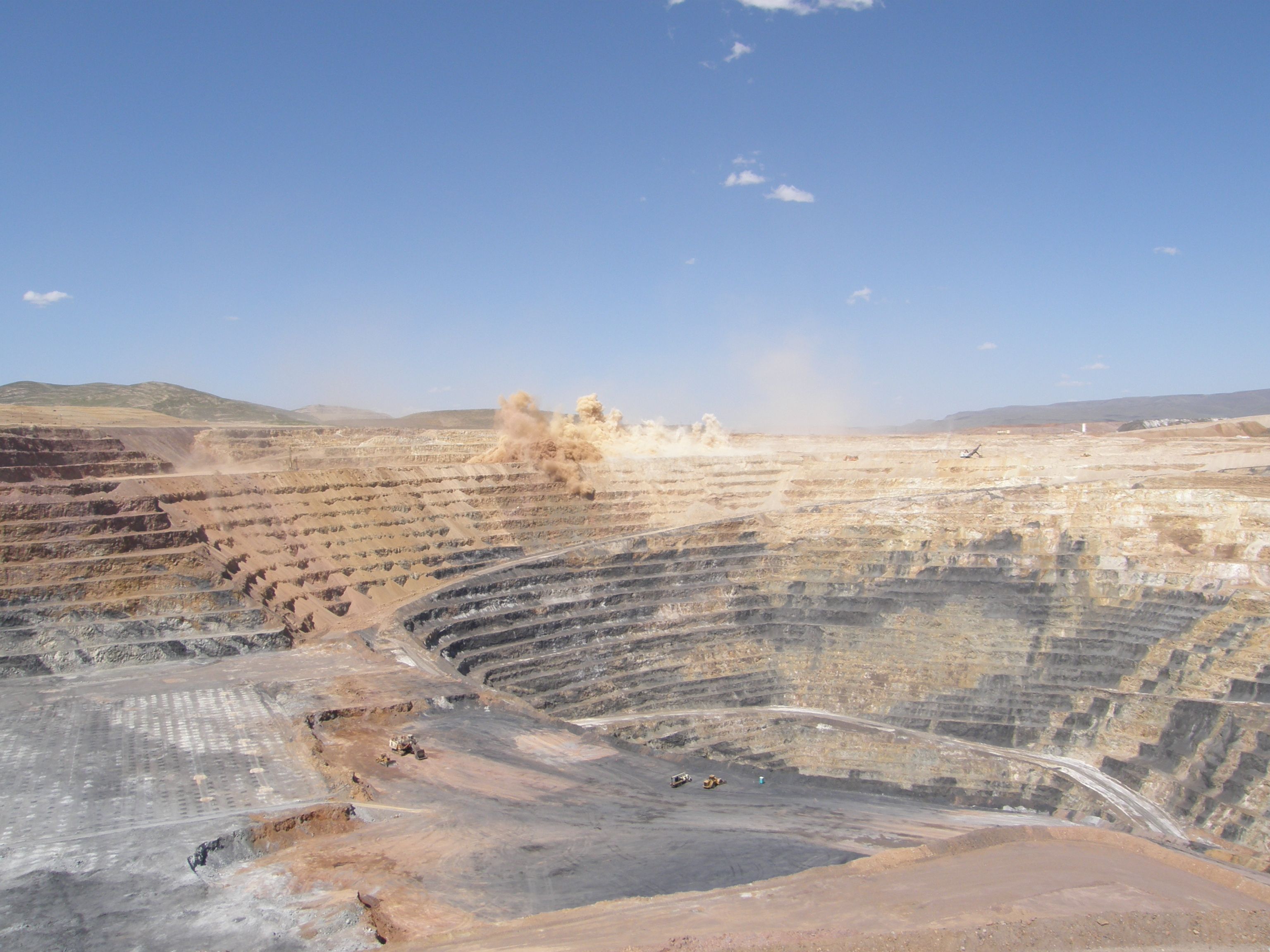
Udachnaya Pipe
The Udachnaya pipe (russian: тру́бка Уда́чная, literally ''lucky pipe'') is a diamond deposit in the Daldyn- Alakit kimberlite field in Sakha Republic, Russia. It is an open-pit mine, and is located just outside the Arctic circle at . History Udachnaya was discovered on 15 June 1955, just two days after the discovery of the diamond pipe Mir by Soviet geologist Vladimir Shchukin and his team. It is about deep, making it the third deepest open-pit mine in the world (after Bingham Canyon Mine and Chuquicamata). The nearby settlement of Udachny is named for the deposit. , Udachnaya pipe is controlled by Russian diamond company Alrosa, which planned to halt open-pit mining in favor of underground mining in 2010. The mine has estimated reserves of of diamonds and an annual production capacity of . See also * Mir mine * Volcanic pipe Volcanic pipes or volcanic conduits are subterranean geological structures formed by the violent, supersonic eruption of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirninsky District
Mirninsky District (russian: Ми́рнинский район; sah, Мирнэй улууһа, ''Mirney uluuha'') is an administrativeConstitution of the Sakha Republic, Article 45 and municipalLaw #172-Z #351-III district (raion, or ''ulus''), one of the thirty-four in the Sakha Republic, Russia. It is located in the west of the republic and borders Olenyoksky District in the north and northeast, Nyurbinsky and Suntarsky Districts in the east, Lensky District in the south, and Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai in the west. The area of the district is .Registry of the Administrative-Territorial Divisions of the Sakha Republic Its administrative center is the town of Mirny. As of the 2010 Census, the total population of the district (excluding its administrative center) was 38,802. Geography The Vilyuy and its tributary Ulakhan-Botuobuya are the main rivers in the district.Google Earth Climate Average January temperature ranges from in the south to in the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuquicamata
Chuquicamata ( ; referred to as Chuqui for short) is the largest open pit copper mine in terms of excavated volume in the world. It is located in the north of Chile, just outside Calama, at above sea level. It is northeast of Antofagasta and north of the capital, Santiago. Flotation and smelting facilities were installed in 1952, and expansion of the refining facilities in 1968 made 500,000 tons annual copper production possible in the late 1970s. Previously part of Anaconda Copper, the mine is now owned and operated by Codelco, a Chilean state enterprise, since the Chilean nationalization of copper in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Its depth of makes it the second deepest open-pit mine in the world, after Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah, United States. Etymology There are several versions of the meaning of ''Chuquicamata''.''Cierre Cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-pit Mines
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow. This form of mining differs from extractive methods that require tunnelling into the earth, such as long wall mining. Open-pit mines are used when deposits of commercially useful ore or rocks are found near the surface. It is applied to ore or rocks found at the surface because the overburden is relatively thin or the material of interest is structurally unsuitable for tunnelling (as would be the case for cinder, sand, and gravel). In contrast, minerals that have been found underground but are difficult to retrieve due to hard rock, can be reached using a form of underground mining. To create an open-pit mine, the miners must determine the information of the ore that is underground. This is done through drilling of probe holes in the ground, then plotting eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatremes Of Russia
A diatreme, sometimes known as a maar-diatreme volcano, is a volcanic pipe formed by a gaseous explosion. When magma rises up through a crack in Earth's crust and makes contact with a shallow body of groundwater, rapid expansion of heated water vapor and volcanic gases can cause a series of explosions. A relatively shallow crater (known as a ''maar'') is left, and a rock-filled fracture (the actual diatreme) in the crust. Diatremes breach the surface and produce a steep, inverted cone shape. The term ''diatreme'' has been applied more generally to any concave body of broken rock formed by explosive or hydrostatic forces, whether or not it is related to volcanism. The word comes . Global distribution Maar-diatreme volcanoes are not uncommon, reported as the second most common type of volcano on continents and islands. Igneous intrusions cause the formation of a diatreme only in the specific setting where groundwater exists; thus most igneous intrusions do not produce diatreme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Mines In The Soviet Union
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Mines In Russia
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
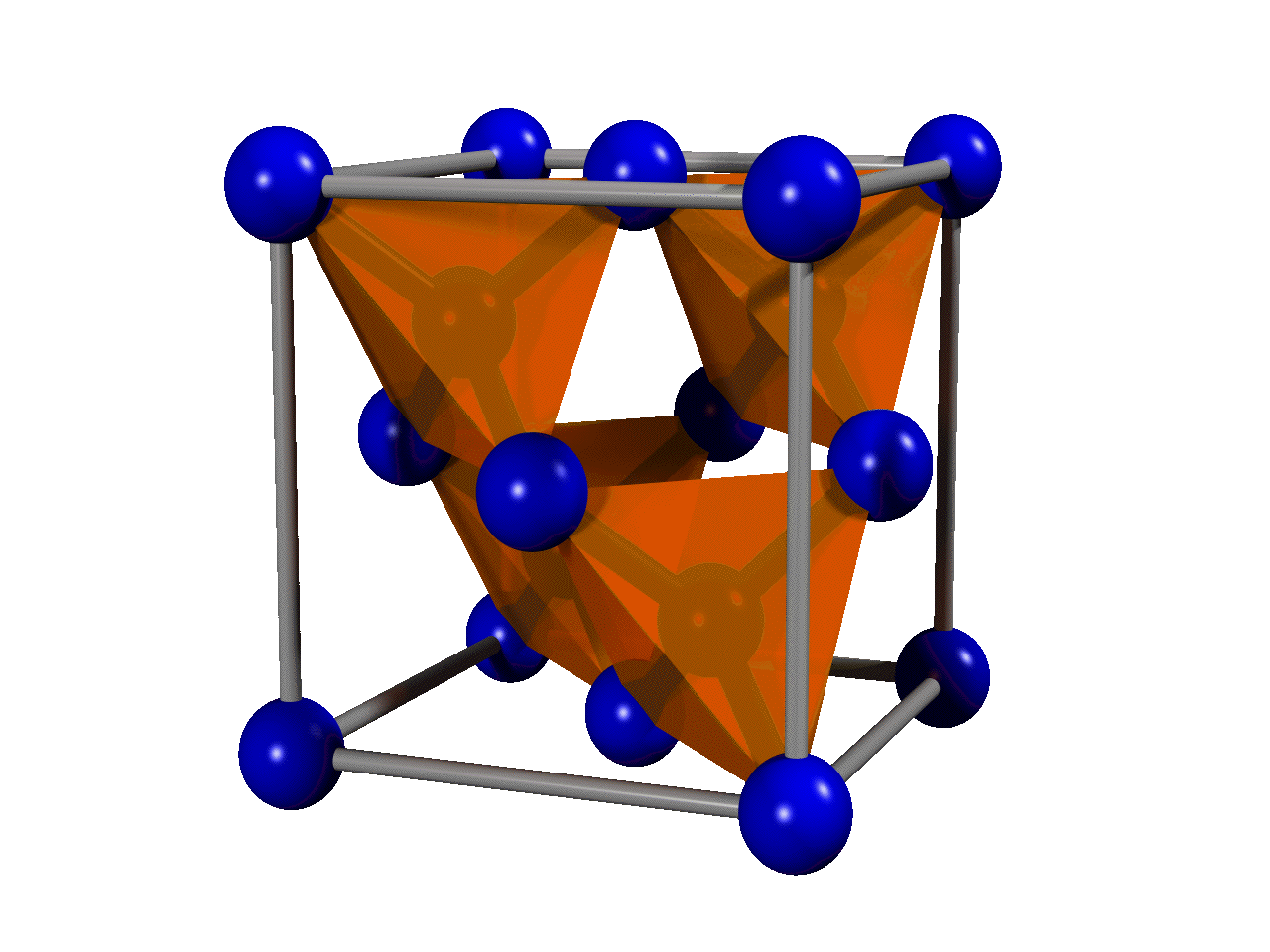
Volcanic Pipe
Volcanic pipes or volcanic conduits are subterranean geological structures formed by the violent, supersonic eruption of deep-origin volcanoes. They are considered to be a type of ''diatreme''. Volcanic pipes are composed of a deep, narrow cone of solidified magma (described as "carrot-shaped"), and are usually largely composed of one of two characteristic rock types — kimberlite or lamproite. These rocks reflect the composition of the volcanoes' deep magma sources, where the Earth is rich in magnesium. Volcanic pipes are relatively rare. They are well known as the primary source of diamonds, and are mined for this purpose. Formation Volcanic pipes form as the result of violent eruptions of deep-origin volcanoes. These volcanoes originate at least three times as deep as most other volcanoes, and the resulting magma that is pushed toward the surface is high in magnesium and volatile compounds such as water and carbon dioxide. As the body of magma rises toward the surface, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Mine
The Mir mine (russian: кимберлитовая алмазная трубка «Мир» ''kimberlitovaya almaznaya trubka "Mir"''; English: kimberlite diamond pipe "Peace"), also called the Mirny mine, is an open pit diamond mine located in Mirny, Sakha Republic, in the Siberian region of eastern Russia. The mine is more than 525 meters (1,722 ft) deep (4th in the world), has a diameter of 1,200 m (3,900 ft), and is one of the largest excavated holes in the world. Open-pit mining began in 1957 and was discontinued in 2001. Since 2009, it has been active as an underground diamond mine. Discovery The diamond-bearing deposits were discovered on June 13, 1955, by Soviet geologists Yuri Khabardin, Ekaterina Elagina and Viktor Avdeenko during the large Amakinsky Expedition in Yakut ASSR. They found traces of the volcanic rock kimberlite, which is usually associated with diamonds. This finding was the second success in the search for kimberlite in Russia, after numerous failed expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamonds
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udachny
Udachny ( rus, Удачный, p=ʊˈdatɕnɨj, lit. ''successful'' or ''lucky''; sah, Удачнай, ''Udaçnay'') is a town in Mirninsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located on the Markha River, from Mirny, the administrative center of the district. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 12,613. History The Udachnaya pipe diamond deposit was discovered in 1955. Due to its isolated location, it was not exploited until the 1960s. In conjunction with the beginnings of diamond production, the urban-type settlement of Udachny was founded in 1968; town status was granted to it in 1987.''Registry of the Administrative-Territorial Divisions of the Sakha Republic'' As part of a plan to create the basin for a tailings dam for the nearby diamond mine, a 1.7 kiloton atomic bomb was detonated underground near Udachny on October 2, 1974. Original plans had called for eight similar explosions to be conducted; however, due to radioactive fallout being far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bingham Canyon Mine
The Bingham Canyon Mine, more commonly known as Kennecott Copper Mine among locals, is an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City, Utah, in the Oquirrh Mountains. The mine is the largest man-made excavation, and deepest open-pit mine in the world, which is considered to have produced more copper than any other mine in history – more than . The mine is owned by Rio Tinto Group, a British-Australian multinational corporation. The copper operations at Bingham Canyon Mine are managed through Kennecott Utah Copper Corporation which operates the mine, a concentrator plant, a smelter, and a refinery. The mine has been in production since 1906, and has resulted in the creation of a pit over deep, wide, and covering . It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1966 under the name Bingham Canyon Open Pit Copper Mine. The mine experienced a massive landslide in April 2013 and a smaller slide in September 2013. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakha Republic
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia),, is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far Eastern Federal District, and is the world's largest country subdivision, covering over 3,083,523 square kilometers (1,190,555 sq mi). ''Sakha'' following regular sound changes in the course of development of the Yakut language) as the Evenk and Yukaghir exonyms for the Yakuts. It is pronounced as ''Haka'' by the Dolgans, whose language is either a dialect or a close relative of the Yakut language.Victor P. Krivonogov, "The Dolgans’Ethnic Identity and Language Processes." ''Journal of Siberian Federal University'', Humanities & Social Sciences 6 (2013 6) 870–888. Geography * ''Borders'': ** ''internal'': Chukotka Autonomous Okrug (660 km)(E), Magadan Oblast (1520 km)(E/SE), Khabarovsk Krai (2130 km)(SE), Amur Oblast (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |