|
UW Solution
Viaspan was the trademark under which the University of Wisconsin cold storage solution (also known as University of Wisconsin solution or UW solution) was sold. Currently, UW solution is sold under the Belzer UW trademark and others like Bel-Gen or StoreProtect. UW solution was the first solution designed for use in organ transplantation, and became the first intracellular-like preservation medium. Developed in the late 1980s by Folkert Belzer and James Southard for pancreas preservation, the solution soon displaced EuroCollins solution as the preferred medium for cold storage of livers and kidneys, as well as pancreas. The solution has also been used for hearts and other organ (anatomy), organs. University of Wisconsin cold storage solution remains what is often called the ''Gold standard (other), gold standard'' for organ preservation, despite the development of other solutions that are in some respects superior. Development The guiding principles for the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
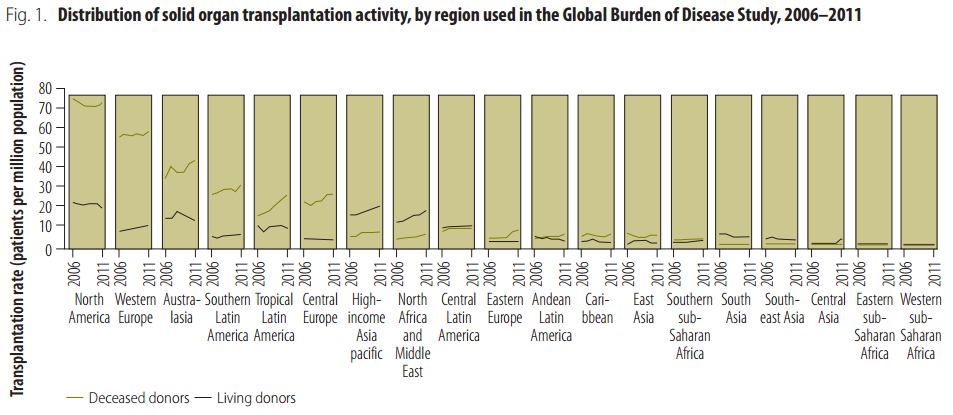
Organ Transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source. Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the heart, kidneys, Liver transplantation, liver, Lung transplantation, lungs, Pancreas transplantation, pancreas, Intestinal transplant, intestine, Thymus transplantation, thymus and uterus transplantation, uterus. Tissues include Bone grafting, bones, tendons (both referred to as musculoskeletal grafts), corneal transplantation, corneae, skin grafting, skin, Artificial heart valve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source. Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the heart, kidneys, Liver transplantation, liver, Lung transplantation, lungs, Pancreas transplantation, pancreas, Intestinal transplant, intestine, Thymus transplantation, thymus and uterus transplantation, uterus. Tissues include Bone grafting, bones, tendons (both referred to as musculoskeletal grafts), corneal transplantation, corneae, skin grafting, skin, Artificial heart valve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biostasis
Biostasis or Cryptobiosis is the ability of an organism to tolerate environmental changes without having to actively adapt to them. Biostasis is found in organisms that live in habitats that likely encounter unfavorable living conditions, such as drought, freezing temperatures, change in pH levels, pressure, or temperature. Insects undergo a type of dormancy to survive these conditions, called diapause. Diapause may be obligatory for these insects to survive. The insect may also be able to undergo change prior to the arrival of the initiating event. Microorganisms Biostasis in this context is also synonymous for viable but nonculturable state. In the past when bacteria were no longer growing on culture media it was assumed that they were dead. Now we can understand that there are many instances where bacteria cells may go into biostasis or suspended animation, fail to grow on media, and on resuscitation are again culturable. VBNC state differs from 'starvation survival state' (wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate
Histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate, or Custodiol HTK solution, is a high-flow, low-potassium preservation solution used for organ transplantation. The solution was initially developed by Hans-Jürgen Bretschneider. HTK solution is intended for perfusion and flushing of donor liver, kidney, heart, lung and pancreas prior to removal from the donor and for preserving these organs during hypothermic storage and transport to the recipient. HTK solution is based on the principle of inactivating organ function by withdrawal of extracellular sodium and calcium, together with intensive buffering of the extracellular space by means of histidine/histidine hydrochloride, so as to prolong the period during which the organs will tolerate interruption of oxygenated blood. The composition of HTK is similar to that of extracellular fluid. All of the components of HTK occur naturally in the body. The osmolarity of HTK is 310 mOsm/L. Composition * Sodium: 15 mmol/L * Potassium: 9 mmol/L * Magnesium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allopurinol
Allopurinol is a medication used to decrease high blood uric acid levels. It is specifically used to prevent gout, prevent specific types of kidney stones and for the high uric acid levels that can occur with chemotherapy. It is taken by mouth or injected into a vein. Common side effects when used by mouth include itchiness and rash. Common side effects when used by injection include vomiting and kidney problems. While not recommended historically, starting allopurinol during an attack of gout appears to be safe. In those already on the medication, it should be continued even during an acute gout attack. While use during pregnancy does not appear to result in harm, this use has not been well studied. Allopurinol is in the xanthine oxidase inhibitor family of medications. Allopurinol was approved for medical use in the United States in 1966. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Allopurinol is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine. Biosynthesis and occurrence Glutathione biosynthesis involves two adenosine triphosphate-dependent steps: *First, γ-glutamylcysteine is synthesized from L- glutamate and cysteine. This conversion requires the enzyme glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL, glutamate cysteine synthase). This reaction is the rate-limiting step in glutathione synthesis. *Second, glycine is added to the C-terminal of γ-glutamylcysteine. This condensation is catalyzed by glutathione synthetase. While all animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine
Adenosine ( symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building blocks of RNA (and its derivative deoxyadenosine is a building block of DNA), which are essential for all life. Its derivatives include the energy carriers adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphate, also known as AMP/ADP/ATP. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is pervasive in signal transduction. Adenosine is used as an intravenous medication for some cardiac arrhythmias. Adenosyl (abbreviated Ado or 5'-dAdo) is the chemical group formed by removal of the 5′-hydroxy (OH) group. It is found in adenosylcobalamin (an active form of vitamin B12) and as a radical in radical SAM enzymes. Medical uses Supraventricular tachycardia In individuals with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify and convert the rhyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raffinose
Raffinose is a trisaccharide composed of galactose, glucose, and fructose. It can be found in beans, cabbage, brussels sprouts, broccoli, asparagus, other vegetables, and whole grains. Raffinose can be hydrolyzed to D-galactose and sucrose by the enzyme α-galactosidase (α-GAL), an enzyme which in the lumen of the human digestive tract is only produced by bacteria in the large intestine. α-GAL also hydrolyzes other α-galactosides such as stachyose, verbascose, and galactinol, if present. The enzyme does not cleave β-linked galactose, as in lactose. Chemical properties The raffinose family of oligosaccharides (RFOs) are alpha-galactosyl derivatives of sucrose, and the most common are the trisaccharide raffinose, the tetrasaccharide stachyose, and the pentasaccharide verbascose. RFOs are almost ubiquitous in the plant kingdom, being found in a large variety of seeds from many different families, and they rank second only to sucrose in abundance as soluble carbohydrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate (in English-speaking countries other than the US) is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula , consisting of magnesium cations (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions . It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water but not in ethanol. Magnesium sulfate is usually encountered in the form of a hydrate , for various values of ''n'' between 1 and 11. The most common is the heptahydrate , known as Epsom salt, which is a household chemical with many traditional uses, including bath salts. The main use of magnesium sulfate is in agriculture, to correct soils deficient in magnesium (an essential plant nutrient because of the role of magnesium in chlorophyll and photosynthesis). The monohydrate is favored for this use; by the mid 1970s, its production was 2.3 million tons per year. The anhydrous form and several hydrates occur in nature as minerals, and the salt is a significant component of the water from some springs. Hydrates Magnesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Phosphate
Potassium phosphate is a generic term for the salt (chemistry), salts of potassium and phosphate ions including: * Monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4) (Molar mass approx: 136 g/mol) * Dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4) (Molar mass approx: 174 g/mol) * Tripotassium phosphate (K3PO4) (Molar mass approx: 212.27 g/mol) As food additives, potassium phosphates have the E number E340. References E-number additives Potassium compounds Phosphates {{Inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Lactobionate
Lactobionic acid (4-''O''-β-galactopyranosyl-D-gluconic acid) is a sugar acid. It is a disaccharide formed from gluconic acid and galactose. It can be formed by oxidation of lactose. The carboxylate anion of lactobionic acid is known as lactobionate. As an acid, lactobionic acid can form salts with mineral cations such as calcium, potassium, sodium and zinc. Calcium lactobionate is a food additive used as a stabilizer. Potassium lactobionate is added to organ preservation solutions such as Viaspan or CoStorSol to provide osmotic support and prevent cell swelling. Mineral salts of lactobionic acid are also used for mineral supplementation. Lactobionic acid is also used in the cosmetics industry as an antioxidant{{Cite journal , last1=Tasic-Kostov , first1=M. , last2=Pavlovic , first2=D. , last3=Lukic , first3=M. , last4=Jaksic , first4=I. , last5=Arsic , first5=I. , last6=Savic , first6=S. , date=2012-10-12 , title=Lactobionic acid as antioxidant and moisturizing active in alk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |