|
US Airforce Flight Dynamics Laboratory
US Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory (or just Flight Dynamics Laboratory) is located on Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and is part of the Air Force Wright Laboratory. The Laboratory was eventually merged into the Air Force Research Laboratory in 1997. The plan for FDL's 1988 fiscal year said about the laboratory's mission: The Flight Dynamics Laboratory (FDL) is part of the Air Force Wright Aeronautical Laboratories (AFWAL), a four-laboratory organization which is part of the Aeronautical System Division located at Wright-Patterson AFB OH. The FDL is responsible for planning, formulating, and executing the USAF technology programs for aerospace vehicles in the technical domains of structures and dynamics, vehicle equipment/subsystems, flight control, and aeromechanics. The FDL maintains a superior technical base by exploring promising approaches in science and technology which will provide options in the development of Air Force systems and prevent technological surprise. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene County, Ohio, Greene and Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patterson Fields, which were originally Wilbur Wright Field and Fairfield Aviation General Supply Depot. Patterson Field is approximately northeast of Dayton, Ohio, Dayton; Wright Field is approximately northeast of Dayton. The host unit at Wright-Patterson AFB is the 88th Air Base Wing (88 ABW), assigned to the Air Force Life Cycle Management Center and Air Force Materiel Command. The 88 ABW operates the airfield, maintains all infrastructure and provides security, communications, medical, legal, personnel, contracting, finance, transportation, air traffic control, weather forecasting, public affairs, recreation and chaplain services for more than 60 associate units. The base's origins begin with the establishment of Wilbur Wright Field on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Laboratory
Wright Laboratory was a research and development organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command on Wright-Patterson AFB starting in 1990. The Laboratory was eventually merged into the Air Force Research Laboratory The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of aerospace warfighting technologies, pl ... in 1997. The Laboratory was named after the Wright brothers, American pioneers of aviation and the namesake of Wright-Patterson AFB. References Research installations of the United States Air Force {{USAF-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force Research Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of aerospace warfighting technologies, planning and executing the Air Force science and technology program, and providing warfighting capabilities to United States air, space, and cyberspace forces. It controls the entire Air Force science and technology research budget which was $2.4 billion in 2006. The Laboratory was formed at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base near Dayton, Ohio, on 31 October 1997 as a consolidation of four Air Force laboratory facilities (Wright, Phillips, Rome, and Armstrong) and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under a unified command. The Laboratory is composed of eight technical directorates, one wing, and the Office of Scientific Research. Each technical directorate emphasizes a particular area of research within the AFRL mission which it s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
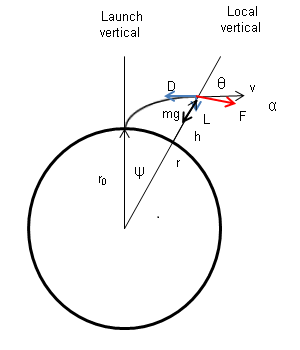
Flight Dynamics
Flight dynamics in aviation and spacecraft, is the study of the performance, stability, and control of vehicles flying through the air or in outer space. It is concerned with how forces acting on the vehicle determine its velocity and attitude with respect to time. For a fixed-wing aircraft, its changing orientation with respect to the local air flow is represented by two critical angles, the angle of attack of the wing ("alpha") and the angle of attack of the vertical tail, known as the sideslip angle ("beta"). A sideslip angle will arise if an aircraft yaws about its centre of gravity and if the aircraft sideslips bodily, i.e. the centre of gravity moves sideways.Flightwise - Volume 2 - Aircraft Stability And Control, Chris Carpenter 1997, Airlife Publishing Ltd., , p.145 These angles are important because they are the principal source of changes in the aerodynamic forces and moments applied to the aircraft. Spacecraft flight dynamics involve three main forces: propulsive (ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryan Model 147G
The Ryan Model 147 Lightning Bug is a jet-powered drone, or unmanned aerial vehicle, produced and developed by Ryan Aeronautical from the earlier Ryan Firebee target drone series. Beginning in 1962, the Model 147 was introduced as a reconnaissance RPV (Remotely Piloted Vehicle, nomenclature of that era) for a United States Air Force project named Fire Fly. Over the next decade — assisted with secret funding from the recently formed National Reconnaissance Office along with support of the Strategic Air Command and Ryan Aeronautical's own resources — the basic Model 147 design would be developed into a diverse series of variants configured for a wide array of mission-specific roles, with multiple new systems, sensors and payloads used, modified and improved upon during the operational deployment of these drones in Southeast Asia. Missions performed by the Model 147 series RPVs included high- and low-altitude photographic and electronic aerial reconnaissance, surveillance, dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wingbox
The wingbox of a fixed-wing aircraft refers to the primary load-carrying structure of the wing, which forms the structural centre of the wings and also the attachment point for other wing components such as leading edge flaps, trailing edge flaps and wing-tip devices. The wingbox continues beyond the visible wing roots and interfaces with the fuselage in the ''centre wingbox,'' which forms the structural core of an aircraft. The wingbox is so called since, on many designs, the combination of the forward and rear wing spars and the upper and lower wing skins together form a natural "box" shape running through the wing. While internal wing structure commonly provides much of the strength via a combination of spars, ribs and stringers, the external skin also typically carries a proportion of the loads too. On many aircraft, the inner volume of the wingbox has also be used to store fuel, which is commonly referred to as being a wet wing design. In recent years, there has been an inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of an aircraft, marine craft or spacecraft without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator's control of the vehicle, allowing the operator to focus on broader aspects of operations (for example, monitoring the trajectory, weather and on-board systems). When present, an autopilot is often used in conjunction with an autothrottle, a system for controlling the power delivered by the engines. An autopilot system is sometimes colloquially referred to as ''"George"'' (e.g. ''"we'll let George fly for a while"''). The etymology of the nickname is unclear: some claim it is a reference to inventor George De Beeson, who patented an autopilot in the 1930s, while others claim that Royal Air Force pilots coined the term during World War II to symbolize that their aircraft technically belonged to King George VI. First autopilots In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |