|
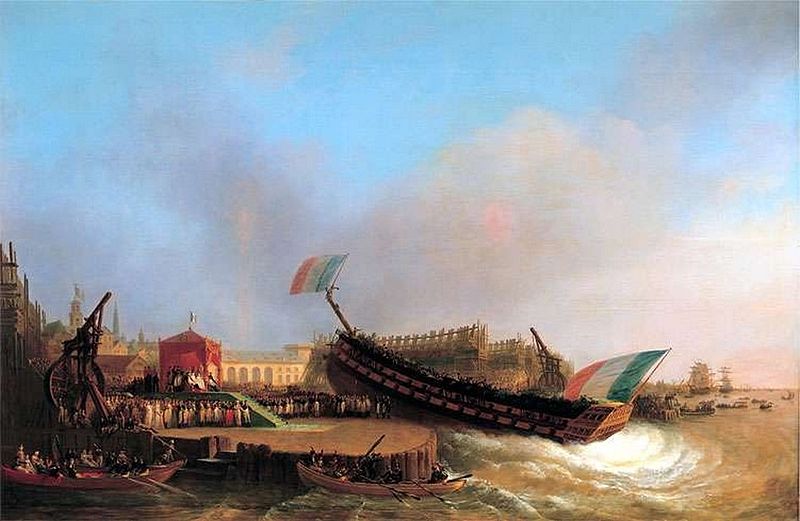
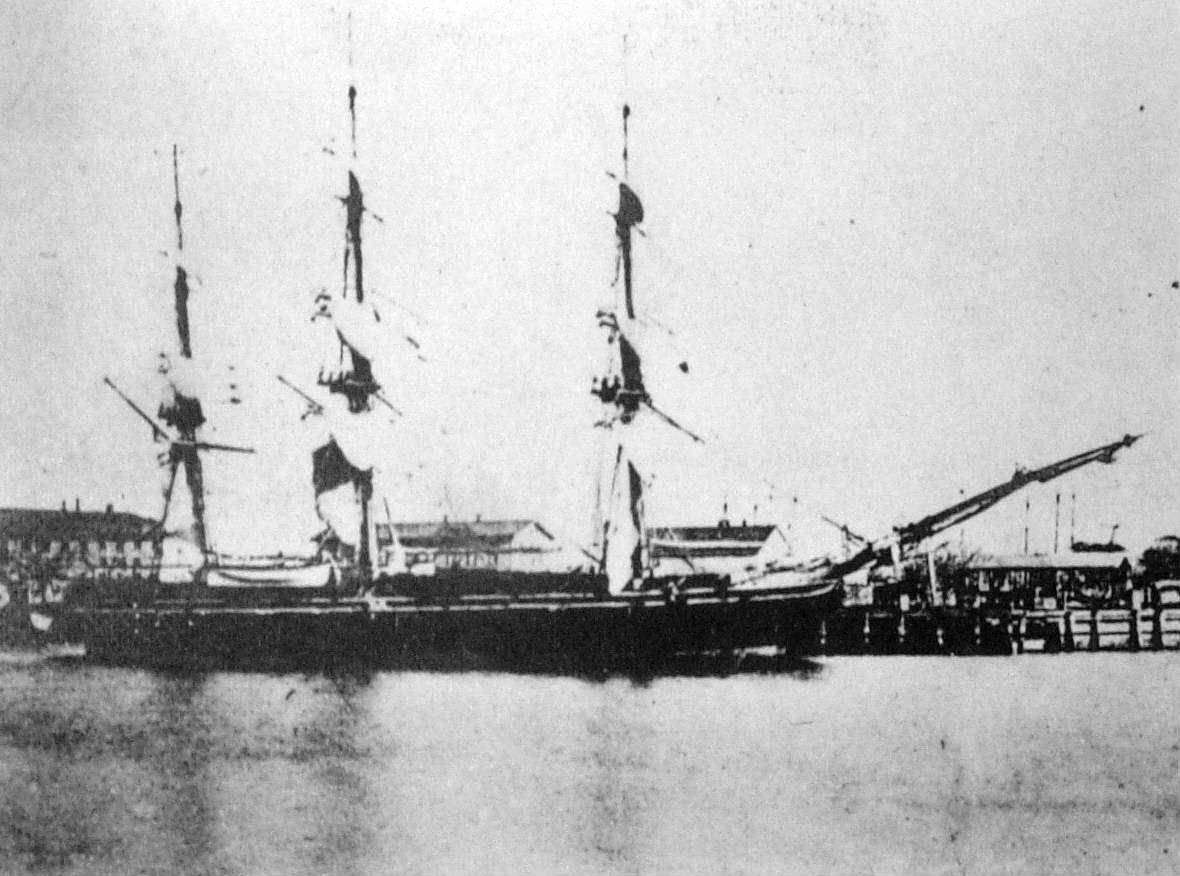
USS Saratoga (1842)
USS ''Saratoga'', a sloop-of-war, was the third ship of the United States Navy to be named for the Battle of Saratoga of the American Revolutionary War. Her keel was laid down in the summer of 1841 by the Portsmouth Navy Yard. She was launched on 26 July 1842 and commissioned on 4 January 1843 with Commander Josiah Tattnall III in command. Service history Ivory Coast Expedition The ship sailed from Portsmouth, New Hampshire, on 16 March 1843, but was dismasted in a gale the next day and forced to return to Portsmouth for repairs. She got underway again on 3 May and proceeded down the coast to New York Harbor to prepare for service in the Ivory Coast Expedition. On the morning of 5 June, she was towed to Sandy Hook, New Jersey, where, at noon, Commodore Matthew Perry came on board and broke his broad pennant as Commander of the Africa Squadron. At mid-afternoon, the ship stood out to sea, proceeded via the Canary Islands and the Cape Verde Islands and reached Monrovia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
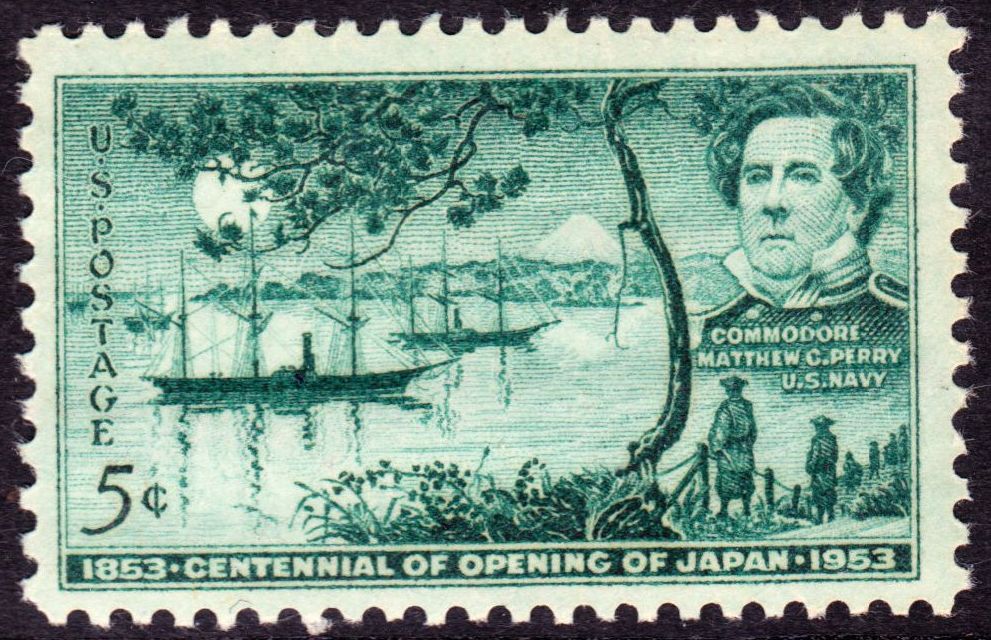
Kurofune 2
The Black Ships (in ja, 黒船, translit=kurofune, Edo period term) was the name given to Western vessels arriving in Japan in the 16th and 19th centuries. In 1543 Portuguese people, Portuguese initiated the first contacts, establishing a trade route linking Goa to Nagasaki. The large carracks engaged in this trade had the hull painted black with Pitch (resin), pitch, and the term came to represent all Western vessels. In 1639, after suppressing Shimabara Rebellion, a rebellion blamed on the influence of Christian thought, the ruling Tokugawa shogunate retreated into an isolationist policy, the Sakoku. During this "locked state", contact with Japan by Westerners was restricted to Dejima island at Nagasaki. In 1844, William II of the Netherlands urged Japan to open, but was rejected. On July 8, 1853, the U.S. Navy sent four warships into the bay at Edo and threatened to attack if Japan did not begin trade with the West. Their arrival marked the reopening of the country to pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Blockade
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading. The blockade was proclaimed by President Abraham Lincoln in April 1861, and required the monitoring of of Atlantic and Gulf coastline, including 12 major ports, notably New Orleans and Mobile. Those blockade runners fast enough to evade the Union Navy could carry only a small fraction of the supplies needed. They were operated largely by foreign citizens, making use of neutral ports such as Havana, Nassau and Bermuda. The Union commissioned around 500 ships, which destroyed or captured about 1,500 blockade runners over the course of the war. Proclamation of blockade and legal implications On April 19, 1861, President Lincoln issued a ''Proclamation of Blockade Against Southern Ports'': Whereas an insurrection against the Government of the United States has broken out in the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocco. They are the southernmost of the autonomous communities of Spain. The islands have a population of 2.2 million people and they are the most populous special territory of the European Union. The seven main islands are (from largest to smallest in area) Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, La Palma, La Gomera, and El Hierro. The archipelago includes many smaller islands and islets, including La Graciosa, Alegranza, Isla de Lobos, Montaña Clara, Roque del Oeste, and Roque del Este. It also includes a number of rocks, including those of Salmor, Fasnia, Bonanza, Garachico, and Anaga. In ancient times, the island chain was often referred to as "the Fortunate Isles". The Canary Islands are the southernmost region of Spain, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa Squadron
The Africa Squadron was a unit of the United States Navy that operated from 1819 to 1861 in the Blockade of Africa to suppress the slave trade along the coast of West Africa. However, the term was often ascribed generally to anti-slavery operations during the period leading up to the American Civil War. The squadron was an outgrowth of the 1819 treaty between the United States and the United Kingdom that was an early step in stopping the trade, and further defined by the Webster–Ashburton Treaty of 1842. Although technically coordinated with a British West Africa Squadron based in Sierra Leone, in practice the American contingent worked on its own. Matthew Perry (naval officer), Matthew Perry was the first commander of the squadron, and based himself in Portuguese Cape Verde. The squadron was generally ineffective, since the ships were too few, and since much of the trading activity had shifted to the Niger River delta area (present-day Nigeria), which was not being cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Perry (naval Officer)
Matthew Calbraith Perry (April 10, 1794 – March 4, 1858) was a commodore of the United States Navy who commanded ships in several wars, including the War of 1812 and the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). He played a leading role in the opening of Japan to the West with the Convention of Kanagawa in 1854. Perry was interested in the education of naval officers and assisted in the development of an apprentice system that helped establish the curriculum at the United States Naval Academy. With the advent of the steam engine, he became a leading advocate of modernizing the U.S. Navy and came to be considered "The Father of the Steam Navy" in the United States. Lineage Matthew Perry was a member of the Perry family, a son of Sarah Wallace ( née Alexander) (1768–1830) and Navy Captain Christopher Raymond Perry (1761–1818). He was born April 10, 1794, South Kingstown, Rhode Island. His siblings included Oliver Hazard Perry, Raymond Henry Jones Perry, Sarah Wallace Perry, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy Hook, New Jersey
Sandy Hook is a barrier spit in Middletown Township, Monmouth County, New Jersey, United States. The barrier spit, approximately in length and varying from wide, is located at the north end of the Jersey Shore. It encloses the southern entrance of Lower New York Bay south of New York City, protecting it from the open waters of the Atlantic Ocean to the east. The Dutch called the area "Sant Hoek", with the English "Hook" deriving from the Dutch "Hoek" (corner, angle), meaning "spit of land". For over three centuries mariners tasked with guiding ships across the Sandy Hook bar have been known as Sandy Hook pilots. Most of Sandy Hook is owned and managed by the National Park Service as the Sandy Hook Unit of Gateway National Recreation Area. Description Geologically, Sandy Hook is a large sand spit or barrier spit, the extension of a barrier peninsula along the coast of New Jersey, separated from the mainland by the estuary of the Shrewsbury River. On its western side, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in the world, and is frequently named the best natural harbor in the world. It is also known as Upper New York Bay, which is enclosed by the New York City boroughs of Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Staten Island and the Hudson County, New Jersey municipalities of Jersey City and Bayonne. The name may also refer to the entirety of New York Bay including Lower New York Bay. Although the United States Board on Geographic Names does not use the term, ''New York Harbor'' has important historical, governmental, commercial, and ecological usages. Overview The harbor is fed by the waters of the Hudson River (historically called the North River as it passes Manhattan), as well as the Gowanus Canal. It is connected to Lower New York Bay by the Narrows, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth, New Hampshire
Portsmouth is a city in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. At the 2020 census it had a population of 21,956. A historic seaport and popular summer tourist destination on the Piscataqua River bordering the state of Maine, Portsmouth was formerly the home of the Strategic Air Command's Pease Air Force Base, since converted to Portsmouth International Airport at Pease. History American Indians of the Abenaki and other Algonquian languages-speaking nations, and their predecessors, inhabited the territory of coastal New Hampshire for thousands of years before European contact. The first known European to explore and write about the area was Martin Pring in 1603. The Piscataqua River is a tidal estuary with a swift current, but forms a good natural harbor. The west bank of the harbor was settled by European colonists in 1630 and named Strawbery Banke, after the many wild strawberries growing there. The village was protected by Fort William and Mary on what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josiah Tattnall III
Commodore Josiah Tattnall (November 9, 1795 – June 14, 1871) was an officer in the United States Navy during the War of 1812, the Second Barbary War and the Mexican–American War. He later served in the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War. Schooling and War of 1812 Josiah was the son of Josiah Tattnall, who was Governor and U.S. Senator from Georgia. He was born on his father's Bonaventure Plantation, near Savannah, Georgia. After studying in England, he was appointed a midshipman on January 1, 1812, and attended the Naval academy at Washington, D.C., until 1 August when he was assigned to the frigate ''Constellation''. When his ship tried to slip out to sea, the strong British squadron operating in the Chesapeake Bay forced her to put into Norfolk, Virginia. ''Constellation'' remained bottled up in Hampton Roads for the duration of the War of 1812, but Tattnall and his comrades still managed to get into the fray. He was among the 100 or so sailors and marines a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Commissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before she is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and electronic systems, galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify any deficiencies needing corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Naming And Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_underway_2009.jpg)
