|
USS Iwo Jima (LHD-7)
USS ''Iwo Jima'' (LHD-7) is a of the United States Navy. The ship was named for the Battle of Iwo Jima of World War II. The ship was commissioned in 2001 and is in service. Construction and career Fabrication work for ''Iwo Jima'' began at Ingalls shipyard on 3 September 1996, and the ship's keel was laid on 12 December 1997. At the keel laying ceremony, United States Army Captain Jacklyn H. Lucas, who was awarded the Medal of Honor for his actions during while serving as a Marine at the Battle of Iwo Jima, placed his Medal of Honor citation in the hull of the ship, where it remains today. She was launched on 4 February 2000. USS ''Iwo Jima'' was christened by her sponsor, Mrs. Zandra Krulak, wife of General Charles C. Krulak, the former Commandant of the Marine Corps, in Pascagoula, Mississippi on 25 March 2000. The commissioning crew moved aboard in April 2001, and made the ship's maiden voyage on 23 June 2001, accompanied by more than 2,000 World War II veterans – many o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the north and Saudi Arabia to the south. Kuwait also shares maritime borders with Iran. Kuwait has a coastal length of approximately . Most of the country's population reside in the urban agglomeration of the capital city Kuwait City. , Kuwait has a population of 4.45 million people of which 1.45 million are Kuwaiti citizens while the remaining 3.00 million are foreign nationals from over 100 countries. Historically, most of present-day Kuwait was part of ancient Mesopotamia. Pre-oil Kuwait was a strategic trade port between Mesopotamia, Persia and India. Oil reserves were discovered in commercial quantities in 1938. In 1946, crude oil was exported for the first time. From 1946 to 1982, the country underwent large-scale modernization, largely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AV-8B Harrier II
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) AV-8B Harrier II is a single-engine ground-attack aircraft that constitutes the second generation of the Harrier family, capable of vertical or short takeoff and landing (V/STOL). The aircraft is primarily employed on light attack or multi-role missions, ranging from close air support of ground troops to armed reconnaissance. The AV-8B is used by the United States Marine Corps (USMC), the Spanish Navy, and the Italian Navy. A variant of the AV-8B, the British Aerospace Harrier II, was developed for the British military, while another, the TAV-8B, is a dedicated two-seat trainer. The project that eventually led to the AV-8B's creation started in the early 1970s as a cooperative effort between the United States and United Kingdom, aimed at addressing the operational inadequacies of the first-generation Hawker Siddeley Harrier. Early efforts centered on a larger, more powerful Pegasus engine to dramatically improve the capabilities of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M2 Browning Machine Gun
The M2 machine gun or Browning .50 caliber machine gun (informally, "Ma Deuce") is a heavy machine gun that was designed towards the end of World War I by John Browning. Its design is similar to Browning's earlier M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge. The M2 uses Browning's larger and more powerful .50 BMG (12.7 mm) cartridge. The design has had many designations; the official U.S. military designation for the current infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It is effective against infantry, unarmored or lightly armored vehicles and boats, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft. The gun has been used extensively as a vehicle weapon and for aircraft armament by the United States since the 1930s. It was heavily used during World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Falklands War, the Soviet–Afghan War, the Gulf War, the Iraq War, and the War in Afghanistan. It is the primary heavy machine gun of NATO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
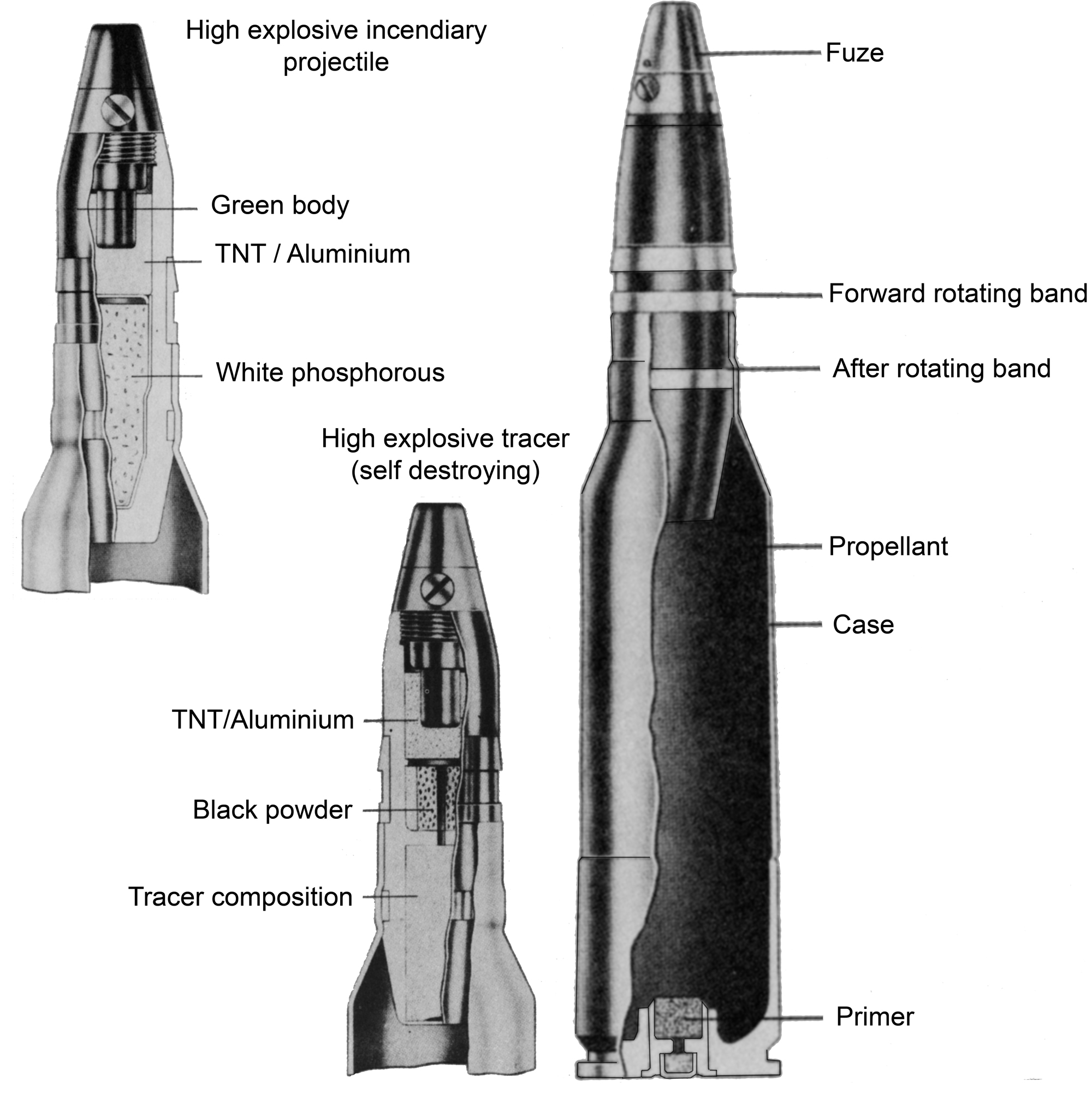
50 BMG
The .50 Browning Machine Gun (.50 BMG, 12.7×99mm NATO and designated as the 50 Browning by the C.I.P.) is a caliber cartridge developed for the M2 Browning heavy machine gun in the late 1910s, entering official service in 1921. Under STANAG 4383, it is a standard service cartridge for NATO forces as well as many non-NATO countries. The cartridge itself has been made in many variants: multiple generations of regular ball, tracer, armor-piercing (AP), incendiary, and saboted sub-caliber rounds. The rounds intended for machine guns are made into a continuous belt using metallic links. The .50 BMG cartridge is also used in anti-materiel rifles. A wide variety of ammunition is available, and the availability of match grade ammunition has increased the usefulness of .50 caliber rifles by allowing more accurate fire than lower quality rounds. History In response to the need for new anti-aircraft weaponry during World War I, John Browning developed the .50 BMG. He wanted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Gun
A chain gun is a type of autocannon or machine gun that uses an external source of power to cycle the weapon's action, rather than diverting excess energy from the cartridges' propellant as in a typical automatic firearm, and does so via a continuous loop of chain drive similar to that used on a motorcycle or bicycle. History In 1972, Hughes Helicopters began a company-funded research effort to design a single machine gun to fire the U.S. Army's M50 round. By April 1973, the program had fired test rounds in more powerful WECOM linked ammunition, from a prototype (A model). In January 1975 a model "C" was added, a linkless version for the proposed Advanced Attack Helicopter YAH-64; the helicopter was later adopted as the Hughes Model 77/AH-64A Apache, with the model C (receiving the designation M230 chain gun) as standard armament. In 1976, Hughes Helicopters successfully patented the chain gun, and it has since been further developed into several other system of different c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
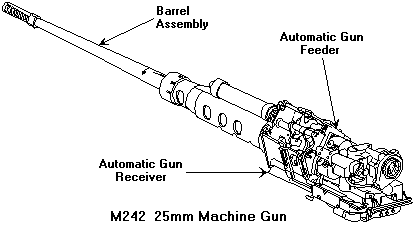
M242 Bushmaster
The M242 Bushmaster chain gun is a 25 mm (25×137mm) single-barrel chain-driven autocannon. It is used extensively by the U.S. military, such as in the Bradley fighting vehicle, as well as by other NATO members and some other nations in ground combat vehicles and various watercraft. Hughes Helicopters in Culver City, California was the original designer and manufacturer. McDonnell Douglas Helicopters acquired Hughes Helicopters in 1985, and merged into Boeing Corporation in 1997. In 2002, it was sold again to Alliant Techsystems, which merged with Orbital Sciences Corporation in 2015 to form Orbital Science ATK and was, in turn, bought out by Northrop Grumman in 2018. , Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems produces the gun. It is an externally powered, chain-driven, single-barrel weapon, that may be fired in semi-automatic, burst, or automatic modes. It is fed by a metallic link belt and has dual-feed capability. The term "chain gun" derives from the use of a roller chain tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
25 Mm Caliber
25 mm caliber is a specific size of popular autocannon ammunition. It has also been recently used for the Barrett XM109 anti-materiel rifle. Such ammunition includes the NATO-standard 25×137mm and 25×184mm, the Soviet 25x218mmSR, and the Chinese 25×183mmB. Usage The 25 mm round can be used in both an anti-materiel and anti-personnel fashion. When operating in the anti-personnel role, a 25 mm weapon armed with HE rounds can effectively kill large numbers of opposing troops either in the open or in light fortifications. When operating in the anti-materiel role, a 25 mm weapon armed with armor-piercing rounds can disable many aircraft and vehicles, including some main battle tanks. The US military uses 25 mm weapons in their AV-8B Harrier, AC-130 gunship, M2 Bradley, LAV-25, F-35 Lightning II and as a standard ship-based munition in the Mk 38 autocannon. Types of 25 mm ammunition Several sub-types of the NATO 25 mm ammunition are available—the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx CIWS
The Phalanx CIWS (often spoken as "sea-wiz") is a gun-based close-in weapon system to defend military watercraft automatically against incoming threats such as aircraft, missiles, and small boats. It was designed and manufactured by the General Dynamics Corporation, Pomona Division,Thomas, Vincent C. ''The Almanac of Seapower 1987'' Navy League of the United States (1987) p.191 later a part of Raytheon. Consisting of a radar-guided Vulcan cannon mounted on a swiveling base, the Phalanx has been used by the United States Navy and the naval forces of 15 other countries. The US Navy deploys it on every class of surface combat ship, except the and . Other users include the British Royal Navy, the Royal Australian Navy, the Royal New Zealand Navy, the Royal Canadian Navy and the US Coast Guard (aboard its - and s). A land variant, the LPWS (Land Phalanx Weapon System), part of the C-RAM system, was developed. It was deployed to counter rocket, artillery and mortar attacks du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RIM-7 Sea Sparrow
RIM-7 Sea Sparrow is a U.S. ship-borne short-range anti-aircraft and anti-missile weapon system, primarily intended for defense against anti-ship missiles. The system was developed in the early 1960s from the AIM-7 Sparrow air-to-air missile as a lightweight "point-defense" weapon that could be retrofitted to existing ships as quickly as possible, often in place of existing gun-based anti-aircraft weapons. In this incarnation, it was a very simple system guided by a manually aimed radar illuminator. After its introduction, the system underwent significant development into an automated system similar to other US Navy missiles like the RIM-2 Terrier. Contemporary improvements being made to the Sparrow for the air-to-air role led to similar improvements in the Sea Sparrow through the 1970s and 80s. After that point the air-to-air role passed to the AIM-120 AMRAAM and the Sea Sparrow underwent a series of upgrades strictly for the naval role. It now resembles the AIM-7 only in general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RIM-116 Rolling Airframe Missile
The RIM-116 Rolling Airframe Missile (RAM) is a small, lightweight, infrared homing surface-to-air missile in use by the German, Japanese, Greek, Turkish, South Korean, Saudi Arabian, Egyptian, Mexican, UAE, and U.S. Navies. It was originally intended and used primarily as a point-defense weapon against anti-ship missiles. As its name indicates, RAM rolls as it flies. The missile must roll during flight because the RF tracking system uses a two-antenna interferometer that can measure phase interference of the electromagnetic wave in one plane only. The rolling interferometer permits the antennas to look at all planes of incoming energy. In addition, because the missile rolls, only one pair of steering canards is required. , it is the only U.S. Navy missile to operate in this manner. The Rolling Airframe Missiles, together with the Mk 49 Guided Missile Launching System (GMLS) and support equipment, make up the RAM Mk 31 Guided Missile Weapon System (GMWS). The Mk-144 Guided M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_launches_RIM-116_missile_2013.jpg)