|
USS Halford (DD-480)
USS ''Halford'' (DD-480), a , was a ship of the United States Navy named for Lieutenant William Halford (1841–1919), a recipient of the Medal of Honor. ''Halford'' was laid down on 3 June 1941 at the Puget Sound Navy Yard, Bremerton, Washington; launched on 29 October 1942, sponsored by Miss Eunice Halford, daughter of Lieutenant Halford; and commissioned on 10 April 1943. ''Halford'' was one of the three ''Fletcher''-class destroyers to be completed (out of six planned) with a catapult for a float plane, the others being and . The catapult and an aircraft crane were located just aft of the number 2 smokestack, in place of the after torpedo tube mount, 5 inch mount number 3, and the 2nd deck of the after deck house which normally carried a twin 40 mm anti-aircraft gun on most ships of the class. (The twin 40 mm mount was moved to the fantail, just forward of the depth charge racks, where most ships of the class carried 20 mm mounts.) It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Halford (DD-480) Off Mare Island 1943
USS ''Halford'' (DD-480), a , was a ship of the United States Navy named for Lieutenant William Halford (1841–1919), a recipient of the Medal of Honor. ''Halford'' was laid down on 3 June 1941 at the Puget Sound Navy Yard, Bremerton, Washington; launched on 29 October 1942, sponsored by Miss Eunice Halford, daughter of Lieutenant Halford; and commissioned on 10 April 1943. ''Halford'' was one of the three ''Fletcher''-class destroyers to be completed (out of six planned) with a catapult for a float plane, the others being and . The catapult and an aircraft crane were located just aft of the number 2 smokestack, in place of the after torpedo tube mount, 5 inch mount number 3, and the 2nd deck of the after deck house which normally carried a twin 40 mm anti-aircraft gun on most ships of the class. (The twin 40 mm mount was moved to the fantail, just forward of the depth charge racks, where most ships of the class carried 20 mm mounts.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
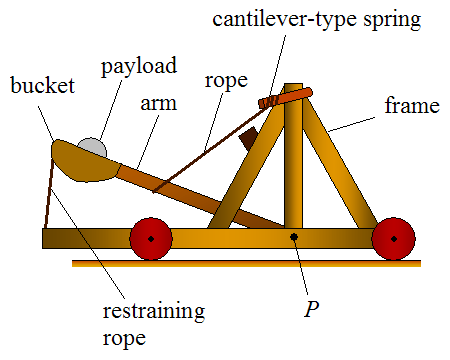
Catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert tension or torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms. In use since ancient times, the catapult has proven to be one of the most persistently effective mechanisms in warfare. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with King Uzziah, of Judah, recorded as equipping the walls of Jerusalem with machines that shot "great stones". Catapults are mentioned in Yajurveda un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
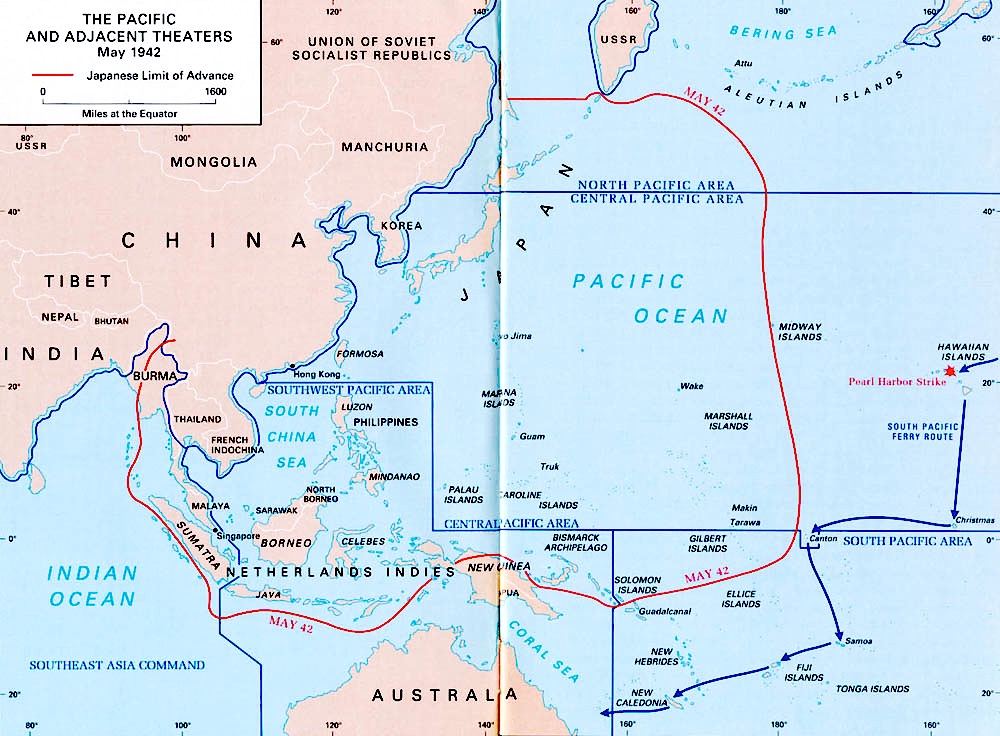
South Pacific Area
The South Pacific Area (SOPAC) was a multinational U.S.-led military command active during World War II. It was a part of the U.S. Pacific Ocean Areas under Admiral Chester Nimitz. The delineation and establishment of the Pacific Ocean Areas was negotiated by the Allied governments of the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in March–April 1942 in response to the Japanese attacks in Southeast Asia and the Pacific. The South Pacific Area was bounded on the west by the Southwest Pacific Area, on the north by the Central Pacific Area, and on the east by the Southeast Pacific Area. It originally encompassed the Ellice, Phoenix, Marquesas, Tuamotu, Samoa, Fiji, and New Hebrides island groups plus New Caledonia and New Zealand. Its western boundary was shifted to just west of Guadalcanal on 1 August 1942 to facilitate operations against that island. Background The assignment orders for Major General Millard Harmon as the Comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mare Island Naval Shipyard
The Mare Island Naval Shipyard (MINSY) was the first United States Navy base established on the Pacific Ocean. It is located northeast of San Francisco in Vallejo, California. The Napa River goes through the Mare Island Strait and separates the peninsula shipyard (Mare Island, California) from the main portion of the city of Vallejo. MINSY made a name for itself as the premier U.S. West Coast submarine port as well as serving as the controlling force in San Francisco Bay Area shipbuilding efforts during World War II. The base closed in 1996 and has gone through several redevelopment phases. It was registered as a California Historical Landmark in 1960, and parts of it were declared a National Historic Landmark District in 1975. Beginnings In September 1849, Lieutenant Commander William Pope McArthur was placed in command of the US survey schooner ''Ewing'', which had been brought around Cape Horn to the West Coast by Lieutenant Washington Allon Bartlett. Upon reaching San Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a naval force to project air power worldwide without depending on local bases for staging aircraft operations. Carriers have evolved since their inception in the early twentieth century from wooden vessels used to deploy balloons to nuclear-powered warships that carry numerous fighters, strike aircraft, helicopters, and other types of aircraft. While heavier aircraft such as fixed-wing gunships and bombers have been launched from aircraft carriers, these aircraft have not successfully landed on a carrier. By its diplomatic and tactical power, its mobility, its autonomy and the variety of its means, the aircraft carrier is often the centerpiece of modern combat fleets. Tactically or even strategically, it replaced the battleship in the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands are now a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet. The U.S. government first obtained exclusive use of the inlet and the right to maintain a repair and coaling station for ships here in 1887. The surprise attack by the Imperial Japanese Navy on December 7, 1941, led the United States to declare war on the Empire of Japan, making the attack on Pearl Harbor the immediate cause of the United States' entry into World War II. History Pearl Harbor was originally an extensive shallow embayment called ''Wai Momi'' (meaning, “Waters of Pearl”) or ''Puuloa'' (meaning, “long hill”) by the Hawaiians. Puuloa was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
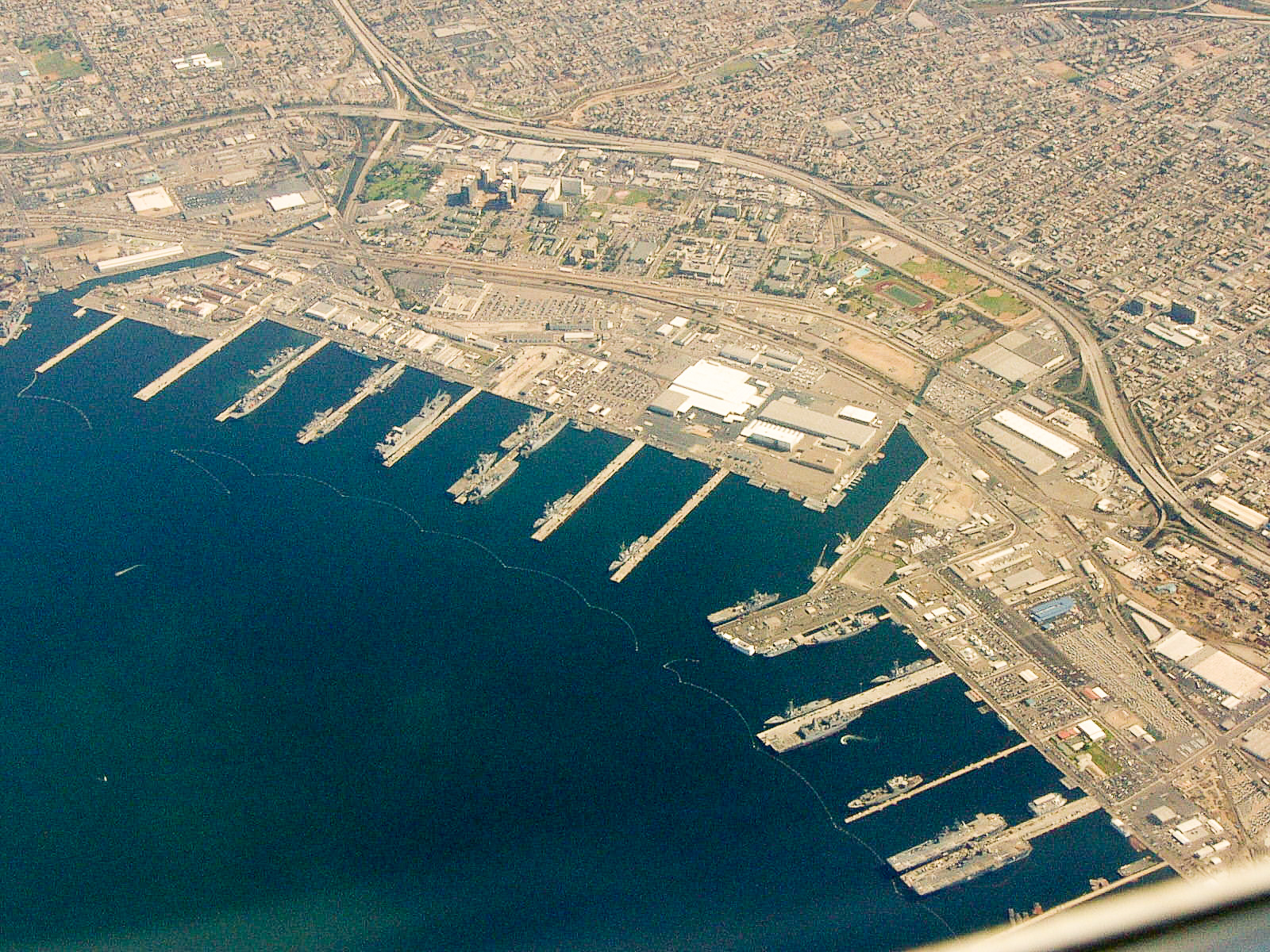
Naval Station San Diego
Naval Base San Diego, also known as 32nd Street Naval Station, is the second largest surface ship base of the United States Navy and is located in San Diego, California. Naval Base San Diego is the principal homeport of the Pacific Fleet, consisting of over 50 ships and over 150 tenant commands. The base is composed of 13 piers stretched over of land and of water. The total on base population is over 24,000 military personnel and over 10,000 civilians. History The of land on which the Naval Base sits today was occupied in 1918 by a coalition of concrete ship building firms known as the Emergency Fleet Corporation, under the single company name Pacific Marine Construction. But Pacific Marine began to lose profits with the conclusion of World War I, and negotiated a return of the land back to the City of San Diego. Meanwhile, the Navy was exploring the small tract of land to establish a west coast ship repair facility and moved on the opportunity to acquire the land. By 1920, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples. The region has a tropical marine climate and is part of the Oceanian realm. It includes four main archipelagos—the Caroline Islands, the Gilbert Islands, the Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands—as well as numerous islands that are not part of any archipelago. Political control of areas within Micronesia varies depending on the island, and is distributed among six sovereign nations. Some of the Caroline Islands are part of the Republic of Palau and some are part of the Federated States of Micronesia (often shortened to "FSM" or "Micronesia"—not to be confused with the identical name for the overall region). The Gilbert Islands (along with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Halford (DD-480), July 1943
USS ''Halford'' (DD-480), a , was a ship of the United States Navy named for Lieutenant William Halford (1841–1919), a recipient of the Medal of Honor. ''Halford'' was laid down on 3 June 1941 at the Puget Sound Navy Yard, Bremerton, Washington; launched on 29 October 1942, sponsored by Miss Eunice Halford, daughter of Lieutenant Halford; and commissioned on 10 April 1943. ''Halford'' was one of the three ''Fletcher''-class destroyers to be completed (out of six planned) with a catapult for a float plane, the others being and . The catapult and an aircraft crane were located just aft of the number 2 smokestack, in place of the after torpedo tube mount, 5 inch mount number 3, and the 2nd deck of the after deck house which normally carried a twin 40 mm anti-aircraft gun on most ships of the class. (The twin 40 mm mount was moved to the fantail, just forward of the depth charge racks, where most ships of the class carried 20 mm mounts.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
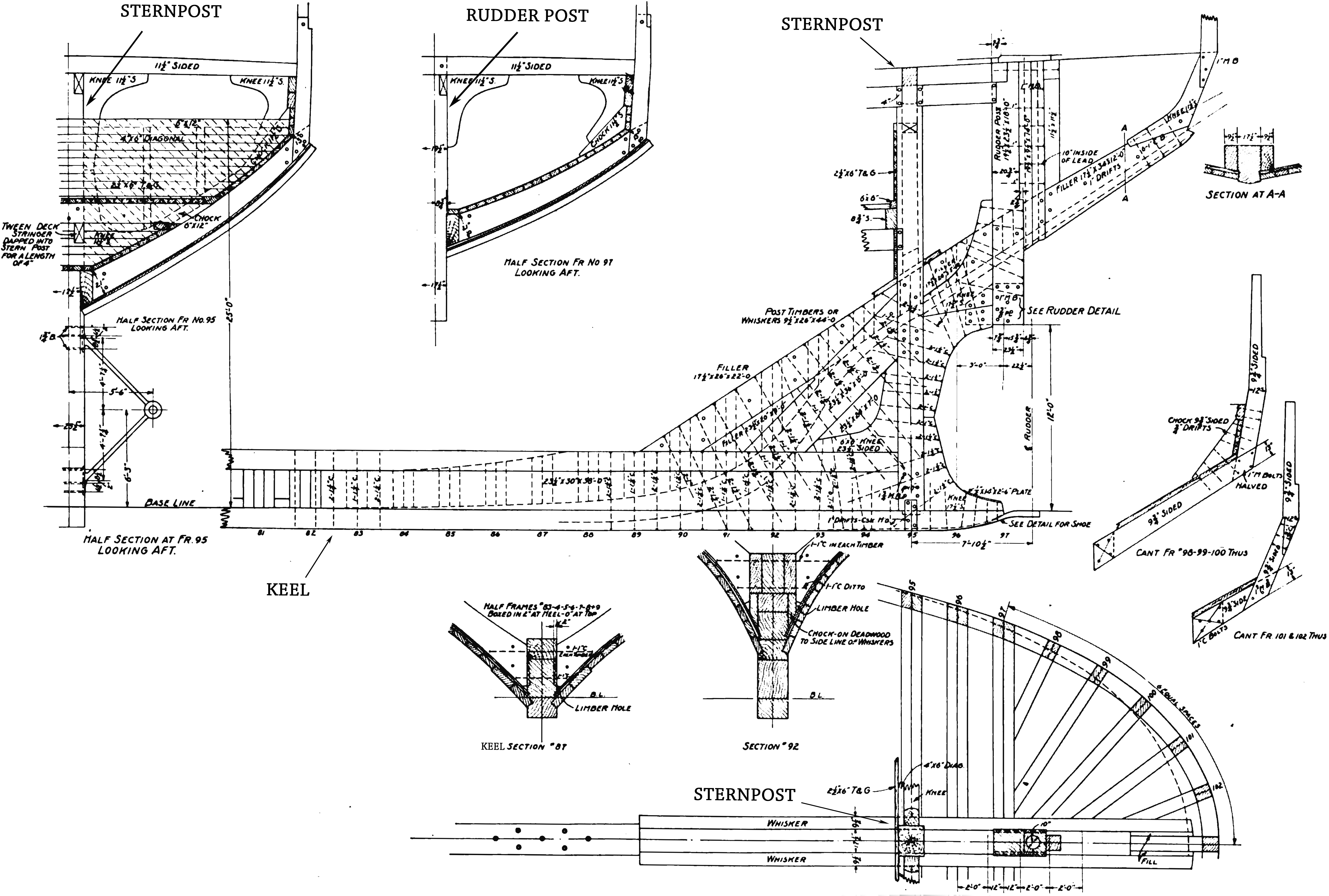
Fantail (ship)
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, subsurface ( submarine launched), and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures (e.g. barrage balloons). It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries, the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight. In some countries, such as Britain and Germany during the Second World War, the Soviet Union, and modern NATO and the United States, ground-based air defence and air defence aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes. There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboard surface vessels. Deck-mounted torpedo launchers are usually designed for a specific type of torpedo, while submarine torpedo tubes are general-purpose launchers, and are often also capable of deploying naval mine, mines and cruise missiles. Most modern launchers are standardized on a diameter for light torpedoes (deck mounted aboard ship) or a diameter for heavy torpedoes (underwater tubes), although other sizes of torpedo tube have been used: see Torpedo#Classes and diameters, Torpedo classes and diameters. Submarine torpedo tube A submarine torpedo tube is a more complex mechanism than a torpedo tube on a surface ship, because the tube has to accomplish the function of moving the torpedo from the normal atmospheric pressure within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |