|
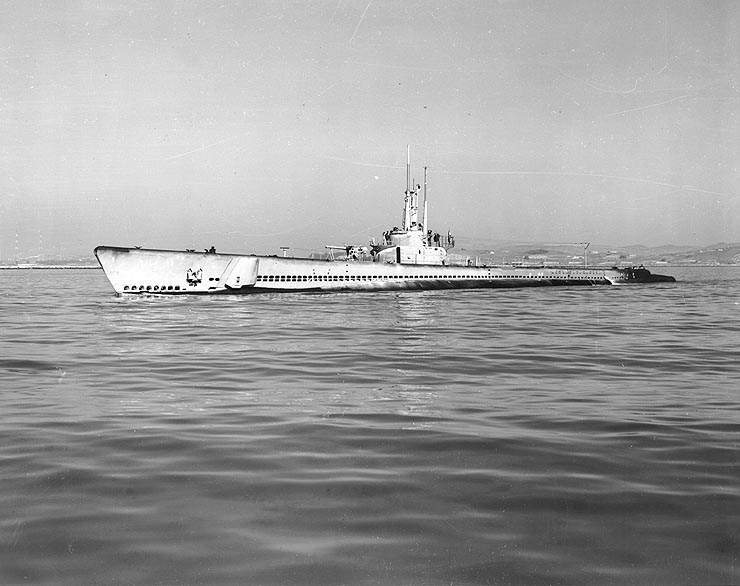
USS Goldring (SS-360)
The ''Balao'' class was a successful design of United States Navy submarine used during World War II, and with 120 boats completed, the largest class of submarines in the United States Navy. An improvement on the earlier , the boats had slight internal differences. The most significant improvement was the use of thicker, higher yield strength steel in the pressure hull skins and frames, which increased their test depth to . ''Tang'' actually achieved a depth of during a test dive, and exceeded that test depth when taking on water in the forward torpedo room while evading a destroyer. Design The ''Balao''s were similar to the ''Gato''s, except they were modified to increase test depth from to . In late 1941, two of the Navy's leading submarine designers, Captain Andrew McKee and Commander Armand Morgan, met to explore increasing diving depth in a redesigned ''Gato''. A switch to a new High-Tensile Steel (HTS) alloy, combined with an increase in hull thickness from to , wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery (electricity)
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded, as the electrode materials are irreversibly changed during discharge; a common example is the alkaline battery used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairwater (submarine)
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water (mostly though not necessarily on the sea). Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin ''nauticus'', from Greek ''nautikos'', from ''nautēs'': "sailor", from ''naus'': "ship". Further information on nautical terminology may also be found at Nautical metaphors in English, and additional military terms are listed in the Multiservice tactical brevity code article. Terms used in other fields associated with bodies of water can be found at Glossary of fishery terms, Glossary of underwater diving terminology, Glossary of rowing terms, and Glossary of meteorology. This glossary is split into two articles: * terms starting with the letters A to L are at Glossary of nautical terms (A-L) * terms starting with the letters M to Z are at Glossary of nautical terms (M-Z). __NO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Ships
The United States Navy's Bureau of Ships (BuShips) was established by Congress on 20 June 1940, by a law which consolidated the functions of the Bureau of Construction and Repair (BuC&R) and the Bureau of Engineering (BuEng). The new bureau was to be headed by a chief and deputy-chief, one selected from the Engineering Corps (Marine Engineer) and the other from the Construction Corps (Naval Architect). The chief of the former Bureau of Engineering, Rear Admiral Samuel M. "Mike" Robinson, was named BuShips' first chief, while the former chief of the Bureau of Construction & Repair, Rear Admiral Alexander H. Van Keuren, was named as BuShips' first Deputy-Chief. The bureau's responsibilities included supervising the design, construction, conversion, procurement, maintenance, and repair of ships and other craft for the Navy; managing shipyards, repair facilities, laboratories, and shore stations; developing specifications for fuels and lubricants; and conducting salvage operations. Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew McKee
Rear Admiral Andrew I. McKee (February 17, 1896 – January 24, 1976) was a pioneer in modern submarine design and development. The destroyer was named for his maternal great-grandfather, Admiral James F. Schenck. McKee graduated from the United States Naval Academy at the top of his class in navigation and was commissioned an Ensign in March 1917.Alden, John D., CDR USN "Andrew Irwin McKee, Naval Constructor" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' June 1979 p.50 He served with USS ''Huntington'' until he severely injured both legs in a fall from the mast in August 1917. He was declared unfit for sea duty, and assigned first to the Naval Academy as a navigation and physics instructor, and then as the supervisory naval constructor at Bethlehem Steel Corporation Fore River Shipyard in Quincy, Massachusetts, pending admission to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). In 1921 he received a master's degree in naval architecture from MIT, and was assigned to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The National Interest
''The National Interest'' (''TNI'') is an American bimonthly international relations magazine edited by American journalist Jacob Heilbrunn and published by the Center for the National Interest, a public policy think tank based in Washington, D.C., that was established by former U.S. President Richard Nixon in 1994 as the Nixon Center for Peace and Freedom. The magazine is associated with the realist school of international studies. History Founded in 1985 by American columnist and neoconservatism advocate Irving Kristol, the magazine was until 2001 edited by Australian academic Owen Harries. In 2001, The National Interest was acquired by The Center for the National Interest, a public policy think tank based in Washington, D.C., that was established by former U.S. President Richard Nixon on January 20, 1994, as the Nixon Center for Peace and Freedom. In 2005, ten editors of ''The National Interest'' resigned due to different viewpoints regarding the magazine's acquisition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Tang (SS-306)
USS ''Tang'' (SS-306) was a ''Balao''-class submarine of World War II, the first ship of the United States Navy to bear the name Tang. She was built and launched in 1943, serving until being sunk by her own torpedo off China in the Taiwan Strait on 24 October 1944. In her short career in the Pacific War, ''Tang'' sank 33 ships totalling 116,454 tons. Commander Richard O'Kane received the Medal of Honor for her last two engagements (23 and 24 October 1944). ''Tang'' was sunk during the last engagement by a circular run of her final torpedo, going down in of water. 78 men were lost, and the five survivors were picked up by a Japanese frigate and taken prisoner of war. This was the only time that a Momsen lung was used to escape a sunken submarine. Construction The contract to build USS ''Tang'' was awarded to Mare Island Naval Shipyard on 15 December 1941, and her keel was laid down on 15 January 1943. She was launched on 17 August sponsored by Mrs. Alix M. Pitre, wife of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Depth
Depth ratings are primary design parameters and measures of a submarine's ability to operate underwater. The depths to which submarines can dive are limited by the strengths of their hulls. Ratings The hull of a submarine must be able to withstand the forces created by the outside water pressure being greater than the inside air pressure. The outside water pressure increases with depth and so the stresses on the hull also increase with depth. Each 10 metres (33 feet) of depth puts another atmosphere (1 bar, 14.7 psi, 101 kPa) of pressure on the hull, so at 300 metres (1,000 feet), the hull is withstanding thirty atmospheres (30 bar, 441 psi, 3,000 kPa) of water pressure. Test depth The maximum depth at which a submarine is permitted to operate under normal peacetime circumstances, and is tested during sea trials. The test depth is set at two-thirds (0.66) of the design depth for United States Navy submarines, while the Royal Navy sets test depth at 4/7 (0.57) the design depth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Hull
A submarine hull has two major components, the ''light hull'' and the ''pressure hull''. The light hull (''casing'' in British usage) of a submarine is the outer non-watertight hull which provides a hydrodynamically efficient shape. The pressure hull is the inner hull of a submarine that maintains structural integrity with the difference between outside and inside pressure at depth. Shapes Modern submarines are usually cigar-shaped. This design, already visible on very early submarines, is called a "teardrop hull". It is structurally efficient for withstanding external pressure, and significantly reduces the hydrodynamic drag on the sub when submerged, but decreases the sea-keeping capabilities and increases drag while surfaced. History The concept of an outer hydrodynamically streamlined light hull separated from the inner pressure hull was first introduced in the early pioneering submarine Ictineo I designed by the Spanish inventor Narcís Monturiol in 1859. However, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield (engineering)
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible and is known as plastic deformation. The yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically. The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producing permanent deformation. In some materials, such as aluminium, there is a gradual onset of non-linear behavior, making the precise yield point difficult to determine. In such a case, the offset yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)


