|
USS Eldridge (DE-173)
USS ''Eldridge'' (DE-173), a , was a ship of the United States Navy named for Lieutenant Commander John Eldridge Jr., who led an operation for the invasion of the Solomon Islands. Namesake Eldridge was born in Buckingham County, Virginia, on 10 October 1903 and graduated from the United States Naval Academy in 1927. After flight training at Pensacola, Florida, he served at various stations on aviation duty. From 11 September 1941, he was Commander, Scouting Squadron 71, attached to ''Wasp'' (CV-7). Lieutenant Commander Eldridge was killed in action in the Solomon Islands on 2 November 1942. For his extraordinary heroism in leading the air attack on Japanese positions in the initial invasion of the Solomons on 7 August and 8 August 1942, he was posthumously awarded the Navy Cross. Construction ''Eldridge'' was laid down 22 February 1943, by the Federal Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company in Newark, New Jersey. ''Eldridge'' was launched on 25 July 1943, sponsored by Lieutenant Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Shipbuilding And Drydock Company
The Federal Shipbuilding and Drydock Company was a United States shipyard, active from 1917 to 1948. It was founded during World War I to build ships for the United States Shipping Board. During World War II, it built ships as part of the U.S. Government's Emergency Shipbuilding program. Operated by a subsidiary of the U.S. Steel, United States Steel Corporation, the shipyard was located at Kearny Point where the mouth of the Hackensack River meets Newark Bay in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The shipyard site is now part of River Terminal, a massive distribution facility that is partially a Foreign trade zones of the United States, foreign trade zone. Federal built numerous destroyers, destroyer escorts and a handful of light cruisers as well as merchant ships during and between the wars. Around 570 vessels were contracted for construction by Federal SB&DD Company with about 100 not delivered fully completed due to the end of the World War II. Federal also had a yard at Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-submarine Mortar
Anti-submarine mortars are artillery pieces deployed on ships for the purpose of sinking submarines by a direct hit with a small explosive charge. They are often larger versions of the mortar used by infantry and fire a projectile in relatively the same manner. They were created during World War II as a development of the depth charge and work on the same principle. Beginnings Anti-submarine warfare did not become an issue of great concern until World War I, when Germany used submarines in an attempt to strangle British shipping in the Atlantic Ocean and elsewhere. The earliest way to counter a submarine was in the form of depth charges, which were large canisters filled with explosives, rolled off the back of a ship and detonated by a hydrostatic fuse. Depth charges served well throughout World War I but were not without flaws. A ship had to pass directly over a submarine to score an effective hit, because of this depth charges were dropped in lines instead of more effective clu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean Sea e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Commissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before she is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and electronic systems, galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify any deficiencies needing corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Naming And Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Shipbuilding And Dry Dock Company
The Federal Shipbuilding and Drydock Company was a United States shipyard, active from 1917 to 1948. It was founded during World War I to build ships for the United States Shipping Board. During World War II, it built ships as part of the U.S. Government's Emergency Shipbuilding program. Operated by a subsidiary of the United States Steel Corporation, the shipyard was located at Kearny Point where the mouth of the Hackensack River meets Newark Bay in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The shipyard site is now part of River Terminal, a massive distribution facility that is partially a foreign trade zone. Federal built numerous destroyers, destroyer escorts and a handful of light cruisers as well as merchant ships during and between the wars. Around 570 vessels were contracted for construction by Federal SB&DD Company with about 100 not delivered fully completed due to the end of the World War II. Federal also had a yard at Port Newark during World War II that built destroyers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navy Cross
The Navy Cross is the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps' second-highest military decoration awarded for sailors and marines who distinguish themselves for extraordinary heroism in combat with an armed enemy force. The medal is equivalent to the Army's Distinguished Service Cross, the Air Force and Space Force's Air Force Cross, and the Coast Guard Cross. The Navy Cross is bestowed by the Secretary of the Navy and may also be awarded to members of the other armed services, and to foreign military personnel while serving with the U.S. naval services. The Navy Cross was established by Act of Congress ( Public Law 65-253) and approved on February 4, 1919. History The Navy Cross was instituted in part due to the entrance of the United States into World War I. Many European nations had the custom of decorating heroes from other nations, but the Medal of Honor was the sole U.S. award for valor at the time. The Army instituted the Distinguished Service Cross and Distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Wasp (CV-7)
USS ''Wasp'' (CV-7) was a United States Navy aircraft carrier commissioned in 1940 and lost in action in 1942. She was the eighth ship named , and the sole ship of a class built to use up the remaining tonnage allowed to the U.S. for aircraft carriers under the treaties of the time. As a reduced-size version of the hull, ''Wasp'' was more vulnerable than other United States aircraft carriers available at the opening of hostilities. ''Wasp'' was initially employed in the Atlantic campaign, where Axis naval forces were perceived as less capable of inflicting decisive damage. After supporting the occupation of Iceland in 1941, ''Wasp'' joined the British Home Fleet in April 1942 and twice ferried British fighter aircraft to Malta. ''Wasp'' was then transferred to the Pacific in June 1942 to replace losses at the battles of Coral Sea and Midway. After supporting the invasion of Guadalcanal, ''Wasp'' was hit by three torpedoes from Japanese submarine on 15 September 1942. The res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
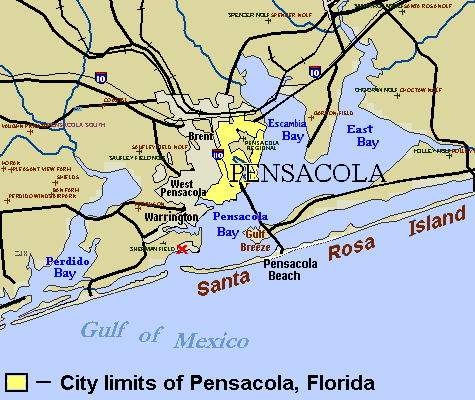
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal city of the Pensacola Metropolitan Area, which had an estimated 502,629 residents . Pensacola is the site of the first Spanish settlement within the borders of the continental United States in 1559, predating the establishment of St. Augustine by 6 years, although the settlement was abandoned due to a hurricane and not re-established until 1698. Pensacola is a seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located southwest of Pensacola near Warrington; it is the base of the Blue Angels flight demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The main campus of the University of West F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (US Naval Academy, USNA, or Navy) is a federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy is the second oldest of the five U.S. service academies and it educates midshipmen for service in the officer corps of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. The campus is located on the former grounds of Fort Severn at the confluence of the Severn River and Chesapeake Bay in Anne Arundel County, east of Washington, D.C., and southeast of Baltimore. The entire campus, known colloquially as the Yard, is a National Historic Landmark and home to many historic sites, buildings, and monuments. It replaced Philadelphia Naval Asylum, in Philadelphia, that had served as the first United States Naval Academy from 1838 to 1845, when the Naval Academy formed in Annapolis. Candidates for admission generally must apply directly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buckingham County, Virginia
Buckingham County is a rural United States county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia, and containing the geographic center of the state. Buckingham County is part of the Piedmont region of Virginia, and the county seat is Buckingham. Buckingham County was created in 1761 from the southeastern portion of Albemarle County and was predominantly farmland. The county was probably named in honor of the Duke of Buckingham, though the precise origin is uncertain. Several changes were made to the borders, until the existing boundaries were established in 1860. As of the 2020 census, the county population was 16,824. Buckingham is part of the Charlottesville Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Buckingham County, lying south of the James River and in the Piedmont at the geographic center of the state, was established on May 1, 1761 from the southeastern portion of Albemarle County. The origin of the county name probably comes from the Duke of Buckingham (Buckinghamshire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville (currently a part of Papua New Guinea), but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands. The islands have been settled since at least some time between 30,000 and 28,800 BCE, with later waves of migrants, notably the Lapita people, mixing and producing the modern indigenous Solomon Islanders population. In 1568, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña was the first European to visit them. Though not named by Mendaña, it is believed that the islands were called ''"the Solomons"'' by those who later receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1945.jpg)


_underway_2009.jpg)

_deck_edge_elevator_with_SB2U_1940.jpg)