|
USS Columbia
USS ''Columbia'' may refer to: * , a ''Java''-class frigate under construction, was burned in 1814 to prevent her capture by the British * was a 50-gun sailing frigate launched in 1836 and in occasional service until 1861, when she was burned to avoid capture by the Confederates * was a captured Confederate screw steamer that ran aground in 1863 * was an ironclad, also captured from the Confederates in 1865 and in use until June of that year. * , later CA-16, was a protected cruiser in service from 1894 to 1921. At the end of its career it was renamed USS ''Old Columbia''. * was originally the ''Great Northern'', a troop transport, renamed in 1921 and used until 1922 * was a light cruiser launched 17 December 1941 and active throughout the rest of World War II * USS ''Columbia'' (AOT-182), a transport oiler, was returned to her owner on 1 May 1984 * is a commissioned in 1995 and currently in active service See also * , future lead ship of the s, originally named ''Columb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
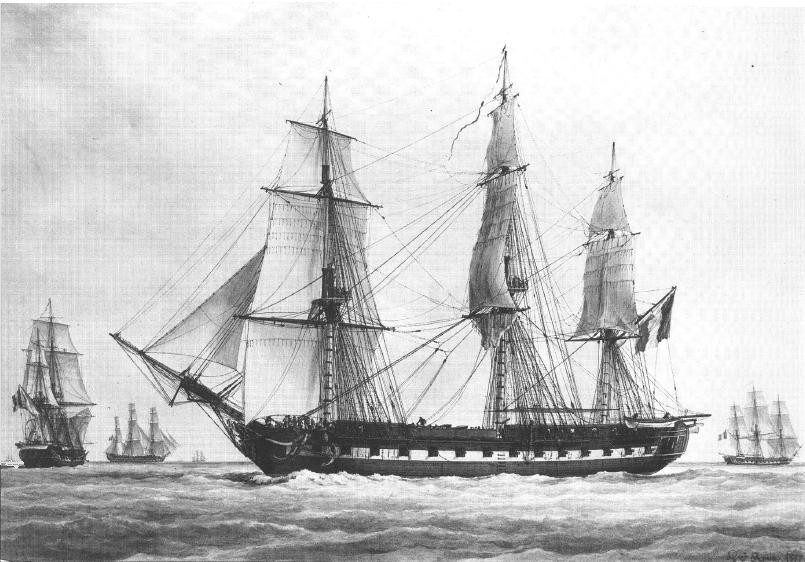
Java-class Frigate (1813)
The ''Java'' or ''Guerriere-''class frigate was a series of heavy sailing frigates built for the United States Navy during the War of 1812. Designed to shore up the fledgling Navy, the ships had a miserable service life. Of the six initially planned, only three were laid down, and only two entered service. The two ships of the class had a limited role within the Navy, stemming from poor craftsmenship and wood quality due to their war-time construction. Design and development Under the Jefferson Administration in the early 1800s, the US Navy was invisoned as a militia-based force that operated small, ad-hoc gunboats. Congress opposed expanding the Navy, which left the nation unable to defend itself at sea. It reversed course following the outbreak of the War of 1812, and ordered 6 frigates in 1813, which made them the first purpose-built vessels for the Navy since 1800. The new frigates were greatly modeled after the earlier original six frigates, with characteristics similar t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironclad
An ironclad was a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by iron armour, steel or iron armor constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary device, incendiary shell (projectile), shells. The first ironclad battleship, , was launched by the French Navy in November 1859, narrowly preempting the British Royal Navy. However, Britain built the first completely iron-hulled warships. Ironclads were first used in warfare in 1862 during the American Civil War, when they operated against wooden ships, and against each other at the Battle of Hampton Roads in Virginia. Their performance demonstrated that the ironclad had replaced the unarmored ship of the line as the most powerful warship afloat. City-class ironclad, Ironclad gunboats became very successful in the American Civil War. Ironclads were designed for several uses, including as high-seas battleships, long-range cruisers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of cruiser of the late 19th century, took their name from the armored deck, which protected vital machine-spaces from fragments released by explosive shells. Protected cruisers notably lacked a belt of armour along the sides, in contrast to armored cruisers which carried both deck and belt armour. Outside of a handful of very large designs in the major navies (which preceded the revival of armored cruisers), the majority of protected cruisers were of 'second-' or 'third-class' types, lighter in displacement and mounting fewer and/or lighter guns than armored cruisers. By the early 20th-century, with the advent of increasingly lighter yet stronger armour, even smaller vessels could afford some level of both belt and deck armour. In the place of protected cruisers, these new ' light armored cruisers' would evolve into light cruisers and heavy cruisers, the former especially taking on many of the roles originally envisioned for protected cruisers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
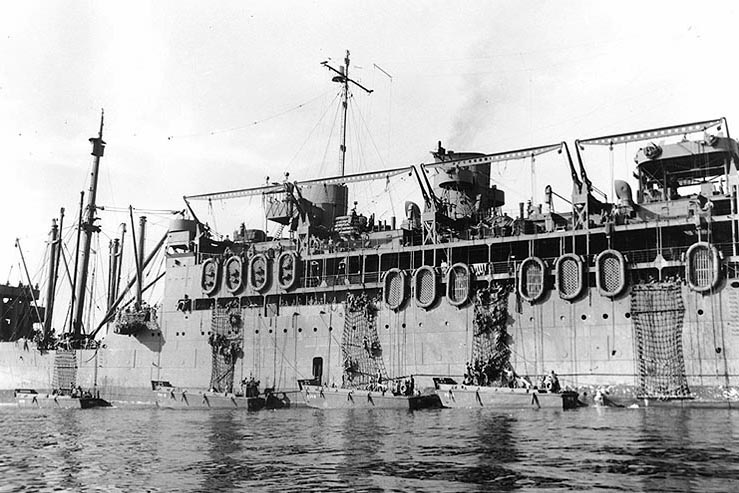
Troopship
A troopship (also troop ship or troop transport or trooper) is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable to land troops directly on shore, typically loading and unloading at a seaport or onto smaller vessels, either Ship's tender, tenders or barges. Attack transports, a variant of ocean-going troopship adapted to transporting invasion forces ashore, carry their own fleet of landing craft. Landing ships beach themselves and bring their troops directly ashore. History Ships to transport troops were used in antiquity. Ancient Rome used the navis lusoria, a small vessel powered by rowers and sail, to move soldiers on the Rhine and Danube. The modern troopship has as long a history as passenger ships do, as most maritime nations enlisted their support in military operations (either by leasing the vessels or by impressing them into service) when their normal naval forces were deemed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
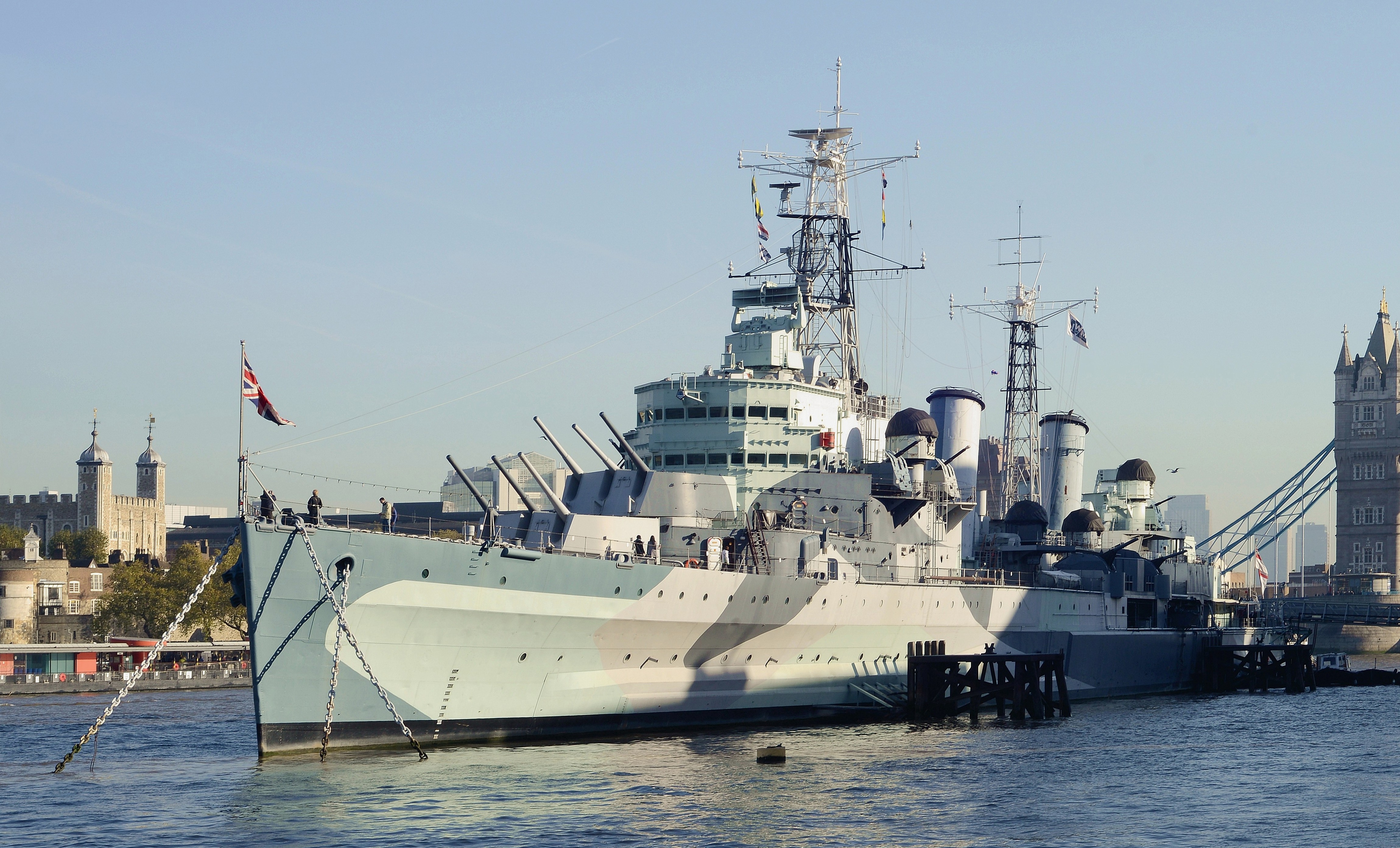
Light Cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to this smaller cruisers had been of the protected cruiser model, possessing armored decks only. While lighter and smaller than other contemporary ships they were still true cruisers, retaining the extended radius of action and self-sufficiency to act independently around the world. Cruisers mounting larger guns and heavier armor relative to most light cruisers would come to be known as heavy cruisers, though the designation of 'light' versus 'heavy' cruisers would vary somewhat between navies. Through their history light cruisers served in a variety of roles, primarily on long-range detached patrol work, covering other military operations or global shipping lanes, as scouts and fleet support vessels for battle fleets, as destroyer command ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of United States Navy Oilers
The following is a list of United States Navy oilers (Hull classification symbol, hull designations AO, AOE, AOL, AOR and AOT). It does not include gasoline tankers (AOG) or submarine oilers (AOSS). Oilers are considered to be auxiliary ship, auxiliaries by the US Navy, and this article's lists are thus a subset of this type of ship. All other auxiliaries can be found at List of auxiliaries of the United States Navy, including the List of auxiliaries of the United States Navy#Gasoline Tankers (AOG, T-AOG), gasoline tankers. Tankers commissioned into the Navy for bulk storage at mobile bases by Service Squadrons during World War II were not classed as auxiliaries but as List of unclassified miscellaneous vessels of the United States Navy, unclassified miscellaneous vessels (IX). Ship status is indicated as either currently active [A] (including ready reserve), inactive [I], or precommissioning [P]. Ships in the inactive category include only ships in the inactive reserve, ships w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ships Named SS Columbia
SS ''Columbia'' may refer to: * , a paddle steamer built by Robert Steele & Company and eventually wrecked * , an iron steamship built by Archibald Denny, Dumbarton * , a passenger/cargo vessel built by Alexander Stephen & Sons, Glasgow * , the first vessel to have electricity * SS ''Columbia'' (1889), a German Hamburg America Line passenger ship purchased by Spain for use in the Spanish–American War as the auxiliary cruiser , then returned to commercial service and later purchased by Russia for use in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905 as the auxiliary cruiser ''Terek'' * , a steam trawler built by Mackie & Thomson Govan * , a British mail ship sold to France and sunk in World War I * , a Canadian screw-driven tugboat * , an American excursion steamship * , a Scottish passenger/cargo vessel originally named HMS ''Columbella'' and subsequently named ''Moreas'', scrapped in Venice 1929 * , a passenger/cargo vessel built by New York Shipbuilding, Camden, NJ as ''Dorothy Alexa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia Rediviva
''Columbia Rediviva'' (commonly known as ''Columbia'') was a privately owned American ship under the command, first, of John Kendrick, and later Captain Robert Gray, best known for being the first American vessel to circumnavigate the globe, and her expedition to the Pacific Northwest for the maritime fur trade. "Rediviva" (''Latin'' "revived") was added to her name upon a rebuilding in 1787. Since ''Columbia'' was privately owned, she did not carry the prefix designation " USS". History Early authorities claim the ship was built in 1773 by James Briggs at Hobart's Landing on North River, in Norwell, Massachusetts and named ''Columbia''. Later historians say she was built in Plymouth, Massachusetts in 1787. In 1790 she became the first American ship to circumnavigate the globe. During the first part of this voyage, she was accompanied by '' Lady Washington'', named for Martha Washington, which served as tender for ''Columbia''. In 1792, Captain Gray entered the Columbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 11
Apollo 11 was a spaceflight conducted from July 16 to 24, 1969, by the United States and launched by NASA. It marked the first time that humans Moon landing, landed on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and Lunar Module pilot Buzz Aldrin landed the Lunar Module Eagle, Lunar Module ''Eagle'' on July 20, 1969, at 20:17 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC, and Armstrong became the first person to step onto the Moon's surface six hours and 39 minutes later, on July 21 at 02:56 UTC. Aldrin joined him 19 minutes later, and they spent about two and a quarter hours together exploring the site they had named Tranquility Base upon landing. Armstrong and Aldrin collected of lunar material to bring back to Earth as pilot Michael Collins (astronaut), Michael Collins flew the Command Module Columbia, Command Module ''Columbia'' in lunar orbit, and were on the Moon's surface for 21 hours, 36 minutes, before lifting off to rejoin ''Columbia''. Apollo 11 was launched by a Saturn V rocket from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
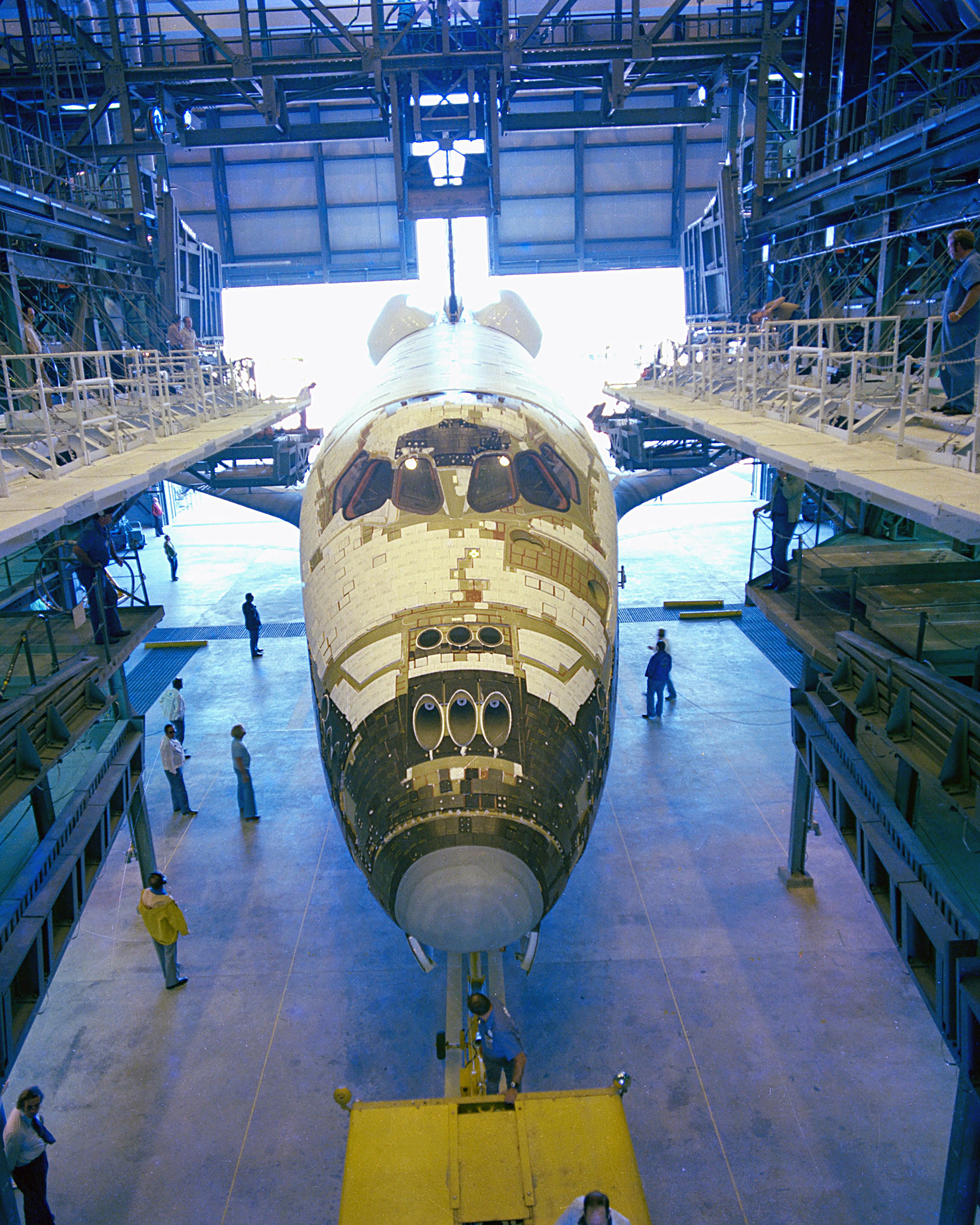
Space Shuttle Columbia
Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' (OV-102) was a Space Shuttle orbiter manufactured by Rockwell International and operated by NASA. Named after the Columbia Rediviva, first American ship to circumnavigate the globe, and the Columbia (personification), female personification of the United States, ''Columbia'' was the first of five Space Shuttle orbiters to fly in space, debuting the Space Shuttle, Space Shuttle launch vehicle on STS-1, its maiden flight on April 12, 1981 and becoming the first spacecraft to be re-used after its first flight when it launched on STS-2 on November 12, 1981. As only the second full-scale orbiter to be manufactured after the Approach and Landing Tests, Approach and Landing Test vehicle ''Space Shuttle Enterprise, Enterprise'', ''Columbia'' retained unique external and internal features compared to later orbiters, such as test instrumentation and distinctive black Chine (aeronautics), chines. In addition to a heavier aft fuselage and the retention of an inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |