|
USS Cape Esperance (CVE-88)
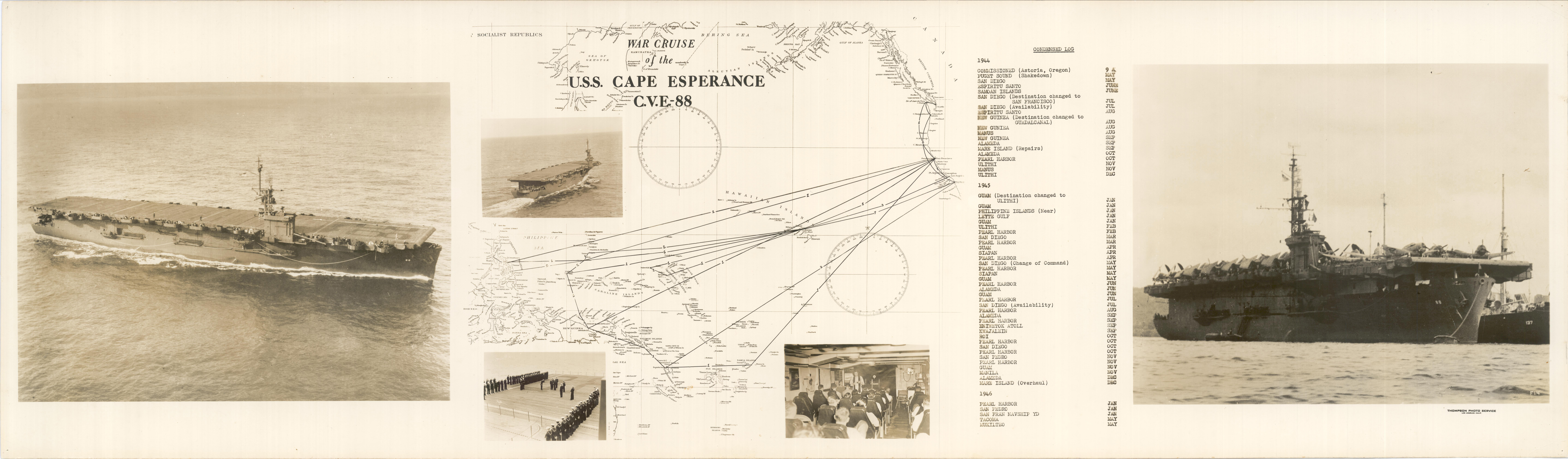
USS ''Cape Esperance'' (CVE-88) was a of the United States Navy. She was named after the Battle of Cape Esperance, an inconclusive naval engagement in support of the Guadalcanal campaign. Built for service during World War II, the ship was launched in March 1944, and commissioned in April, and served as a replenishment carrier. Postwar, she participated in Operation Magic Carpet. She was decommissioned in August 1946, when she was mothballed in the Pacific Reserve Fleet. However, she was recommissioned in August 1950, and assigned to become an auxiliary vessel as a part of Military Sealift Command. She was decommissioned again in January 1959, and ultimately, she was sold for scrapping in May 1959. Design and description ''Cape Esperance'' was a ''Casablanca''-class escort carrier, the most numerous type of aircraft carriers ever built, and designed specifically to be mass-produced using prefabricated sections, in order to replace heavy war losses sustained in the early enga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Wales Island (Alaska)
Prince of Wales Island (Tlingit: ''Taan'') is one of the islands of the Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle. It is the fourth-largest island in the United States (after Hawaii, Kodiak Island, and Puerto Rico) and the 97th-largest island in the world. Geography and ecology The island is long, wide and has an area of , about one-tenth the size of Ireland and slightly larger than the state of Delaware. Approximately 6,000 people live on the island. Craig is the largest community; founded as a saltery in the early 20th century, it has a population of 1,500. Some 900 people live in Klawock, a long-established village that grew with the fishing industry. Hollis was a boom and bust mining town from 1900 to about 1915. Abandoned, it was re-established as a logging camp in the 1950s. It now has a population of 100 and is the location of the ferry terminal. Mountain peaks, all but the tallest of which were buried by Pleistocene glaciation, reach over . Fjords, steep-si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inboard And Outboard Profiles Of A Casablanca-class Escort Carrier, 1946
An inboard motor is a marine propulsion system for boats. As opposed to an outboard motor where an engine is mounted outside the hull of the craft, an ''inboard motor'' is an engine enclosed within the hull of the boat, usually connected to a propulsion screw by a driveshaft. In international shipping the marine diesel engines are the largest most powerful engines ever produced. History The first marine craft to utilize inboard motors were steam engines going back to 1805 and the ''Clermont'' and the '' Charlotte Dundas''. Harbour tugs, and small steam launches had inboard steam engines. In the 1880s the naphtha engine made its appearance and a few boat engines appeared. Such engines had low power and high fuel consumption. The gasoline (petrol) engine pioneer Gottlieb Daimler and Maybach built a four-cycle boat engine and tested it in 1887 on the Neckar River. Sintz in America built several commercially available engines from 1893. Sizes Inboard motors may be of seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaft (mechanical Engineering)
A shaft is a rotating machine element, usually circular in cross section, which is used to transmit power from one part to another, or from a machine which produces power to a machine which absorbs power. Types They are mainly classified into two types. * Transmission shafts are used to transmit power between the source and the machine absorbing power; e.g. counter shafts and line shafts. * Machine shafts are the integral part of the machine itself; e.g. crankshaft. *Axle shaft. *Spindle shaft. Materials The material used for ordinary shafts is mild steel. When high strength is required, an alloy steel such as nickel, nickel-chromium or chromium-vanadium steel is used. Shafts are generally formed by hot rolling and finished to size by cold drawing or turning and grinding. Standard sizes Source:Mahadevan K and Reddy K.Balaveera, (2015), 'Design data hand book', CBS publishers and Distributors (P) ltd., New-Delhi, Machine shafts * Up to 25 mm steps of 0.5 mm Transmission sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skinner Unaflow
The uniflow type of steam engine uses steam that flows in one direction only in each half of the cylinder. Thermal efficiency is increased by having a temperature gradient along the cylinder. Steam always enters at the hot ends of the cylinder and exhausts through ports at the cooler centre. By this means, the relative heating and cooling of the cylinder walls is reduced. Design details Steam entry is usually controlled by poppet valves (which act similarly to those used in internal combustion engines) that are operated by a camshaft. The inlet valves open to admit steam when minimum expansion volume has been reached at the start of the stroke. For a period of the crank cycle, steam is admitted, and the poppet inlet is then closed, allowing continued expansion of the steam during the stroke, driving the piston. Near the end of the stroke, the piston will uncover a ring of exhaust ports mounted radially around the centre of the cylinder. These ports are connected by a manifold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Deck
The flight deck of an aircraft carrier is the surface from which its aircraft take off and land, essentially a miniature airfield at sea. On smaller naval ships which do not have aviation as a primary mission, the landing area for helicopters and other VTOL aircraft is also referred to as the flight deck. The official U.S. Navy term for these vessels is "air-capable ships". Flight decks have been in use upon ships since 1910, the American pilot Eugene Ely being the first individual to take off from a warship. Initially consisting of wooden ramps built over the forecastle of capital ships, a number of battlecruisers, including the British and , the American and , and the Japanese Akagi and battleship Kaga, were converted to aircraft carriers during the interwar period. The first aircraft carrier to feature a full-length flight deck, akin to the configuration of the modern vessels, was the converted liner . The armoured flight deck was another innovation pioneered by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangar
A hangar is a building or structure designed to hold aircraft or spacecraft. Hangars are built of metal, wood, or concrete. The word ''hangar'' comes from Middle French ''hanghart'' ("enclosure near a house"), of Germanic origin, from Frankish *''haimgard'' ("home-enclosure", "fence around a group of houses"), from *''haim'' ("home, village, hamlet") and ''gard'' ("yard"). The term, ''gard'', comes from the Old Norse ''garðr'' ("enclosure, garden"). Hangars are used for protection from the weather, direct sunlight and for maintenance, repair, manufacture, assembly and storage of aircraft. History The Wright brothers stored and repaired their aircraft in a wooden hangar constructed in 1902 at Kill Devil Hills in North Carolina for their glider. After completing design and construction of the ''Wright Flyer'' in Ohio, the brothers returned to Kill Devil Hills only to find their hangar damaged. They repaired the structure and constructed a new workshop while they waited for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-load Displacement
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p.5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks" (or "load lines"). A merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Displacement
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p.5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks" (or "load lines"). A merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p.5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks" (or "load lines"). A mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (nautical)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Overall
__NOTOC__ Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth (for example, £2.50 per metre LOA). LOA is usually measured on the hull alone. For sailing ships, this may ''exclude'' the bowsprit and other fittings added to the hull. This is how some racing boats and tall ships use the term LOA. However, other sources may include bowsprits in LOA. Confusingly, LOA has different meanings. "Sparred length", "Total length including bowsprit", "Mooring length" and "LOA including bowsprit" are other expressions that might indicate the full length of a sailing ship. LOD Often used to distinguish between the length of a vessel including projections (e.g. bow sprits, etc.) from the length of the hull itself, the Length on Deck or LOD is often repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)
