|
USS Bache (DD-470)
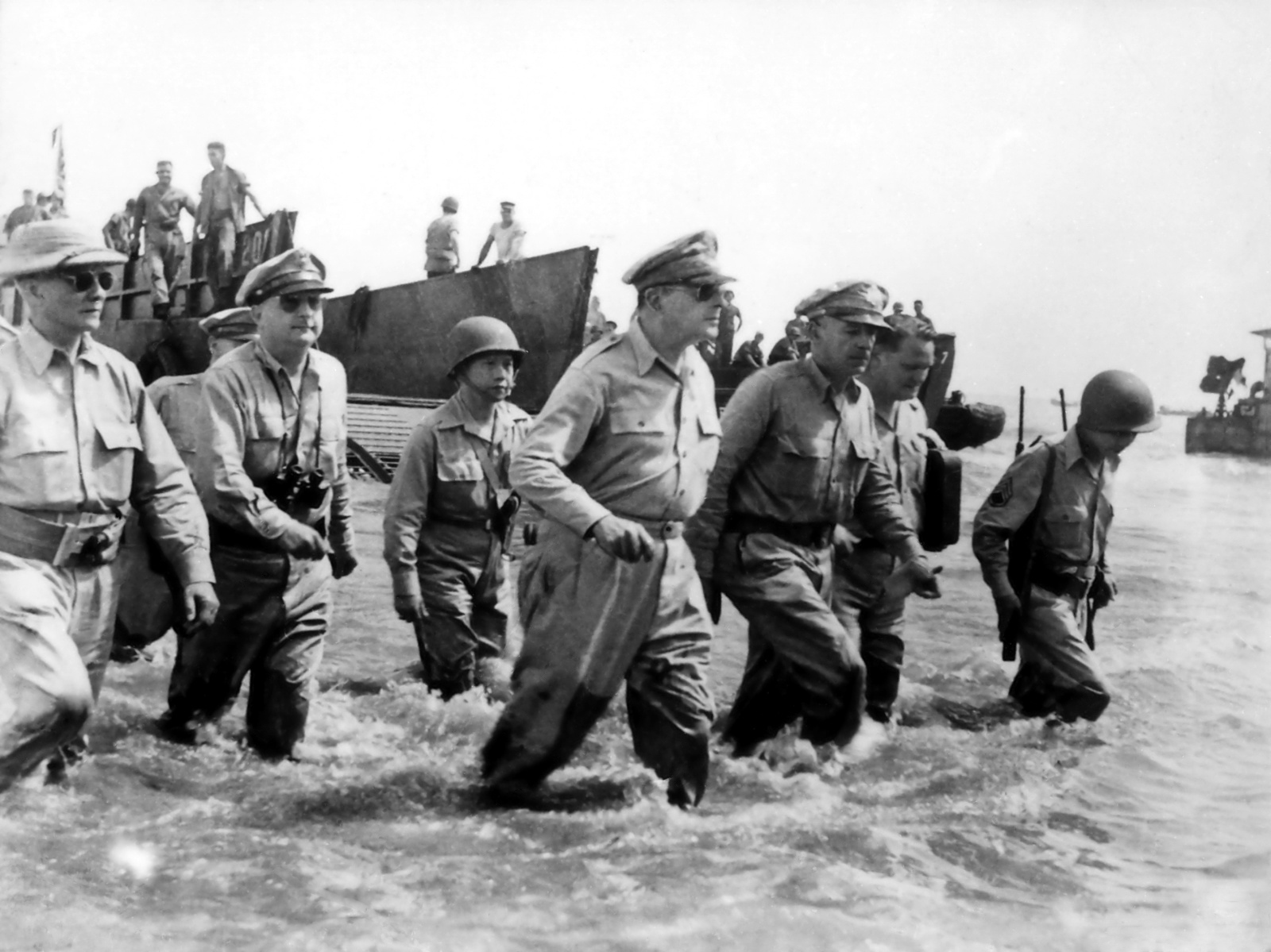
USS ''Bache'' (DD/DDE-470), a , was the second ship of the United States Navy of that name. The destroyer was named for Commander George M. Bache. ''Bache'' was launched on 7 July 1942 by Bethlehem Steel Co. at Staten Island, New York and sponsored by Miss Louise Bache, daughter of Commander Bache. The destroyer was commissioned on 14 November 1942. Service history Reporting to the Atlantic Fleet, she acted as escort to a westbound convoy to Halifax, Nova Scotia, and then returned to New York for her post-shakedown overhaul. On 6 February 1943, she left Norfolk as escort for . The vessels arrived at Pearl Harbor on 4 March 1943. On 10 May, after a training period, ''Bache'' departed for the Aleutian Islands. She served in the Aleutian area until December 1943, taking part in the bombardment of Kiska. After a brief overhaul at Pearl Harbor she joined the 7th Fleet 23 December 1943. Until 29 October 1944, ''Bache'' operated with the 7th Fleet taking part in the bombardm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George M
''George M!'' is a Broadway musical based on the life of George M. Cohan, the biggest Broadway star of his day who was known as "The Man Who Owned Broadway." The book for the musical was written by Michael Stewart, John Pascal, and Francine Pascal. Music and lyrics were by George M. Cohan himself, with revisions for the musical by Cohan's daughter, Mary Cohan. The story covers the period from the late 1880s until 1937 and focuses on Cohan's life and show business career from his early days in vaudeville with his parents and sister to his later success as a Broadway singer, dancer, composer, lyricist, theatre director and producer. The show includes such Cohan hit songs as "Give My Regards To Broadway", "You're a Grand Old Flag", and "Yankee Doodle Dandy." Productions The musical opened on Broadway at the Palace Theatre on April 10, 1968 and closed on April 26, 1969 after 433 performances and 8 previews. The show was produced by David Black and directed and choreographed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eniwetok
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; mh, Ānewetak, , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ja, ブラウン環礁) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with its 664 people (as of 2011) forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. With a land area total less than , it is no higher than and surrounds a deep central lagoon, in circumference. It is the second-westernmost atoll of the Ralik Chain and is west from Bikini Atoll. It was held by the Japanese from 1914 until its capture by the United States in February 1944, during World War II, then became Naval Base Eniwetok. Nuclear testing by the US totaling the equivalent of over 30 megatons of TNT took place during the Cold War; in 1977–1980, a concrete dome (the Runit Dome) was built on Runit Island to deposit radioactive soil and debris. The Runit Dome is deteriorating and could be breached by a typhoon, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Fifth Fleet
The Fifth Fleet is a numbered fleet of the United States Navy. It has been responsible for naval forces in the Persian Gulf, Red Sea, Arabian Sea, and parts of the Indian Ocean since 1995 after a 48-year hiatus. It shares a commander and headquarters with U.S. Naval Forces Central Command (''NAVCENT'') in Bahrain. Fifth Fleet/NAVCENT is a component command of, and reports to, U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM). Established in 1944, the Fifth Fleet conducted extensive operations against Japanese forces in the Central Pacific during World War II. World War II ended in 1945, and the Fifth Fleet was deactivated in 1947. It remained inactive until 1995, when it was reactivated and assumed its current responsibilities. World War II The Fifth Fleet was initially established during World War II on 26 April 1944 from the Central Pacific Force under the command of Admiral Raymond Spruance. Central Pacific Force was itself part of Pacific Ocean Areas. The ships of the Fifth Fleet also form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Surigao Strait
The Battle of Leyte Gulf ( fil, Labanan sa golpo ng Leyte, lit=Battle of Leyte gulf; ) was the largest naval battle of World War II and by some criteria the largest naval battle in history, with over 200,000 naval personnel involved. It was fought in waters near the Philippine islands of Leyte, Samar, and Luzon from 23 to 26 October 1944 between combined American and Australian forces and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), as part of the invasion of Leyte, which aimed to isolate Japan from the countries that it had occupied in Southeast Asia, a vital source of industrial and oil supplies. By the time of the battle, Japan had fewer capital ships (aircraft carriers and battleships) left than the Allied forces had total aircraft carriers in the Pacific, which underscored the disparity in force strength at that point in the war. Regardless, the IJN mobilized nearly all of its remaining major naval vessels in an attempt to defeat the Allied invasion, but it was repulsed by the US Navy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Islands
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no), * bik, Republika kan Filipinas * ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas * cbk, República de Filipinas * hil, Republika sang Filipinas * ibg, Republika nat Filipinas * ilo, Republika ti Filipinas * ivv, Republika nu Filipinas * pam, Republika ning Filipinas * krj, Republika kang Pilipinas * mdh, Republika nu Pilipinas * mrw, Republika a Pilipinas * pag, Republika na Filipinas * xsb, Republika nin Pilipinas * sgd, Republika nan Pilipinas * tgl, Republika ng Pilipinas * tsg, Republika sin Pilipinas * war, Republika han Pilipinas * yka, Republika si Pilipinas In the recognized optional languages of the Philippines: * es, República de las Filipinas * ar, جمهورية الفلبين, Jumhūriyyat al-Filibbīn is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is situated in the western Pacific Ocean and consists of around 7,641 islands t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyte Island
Leyte ( ) is an island in the Visayas group of islands in the Philippines. It is eighth-largest and sixth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 2,626,970 as of 2020 census. Since the accessibility of land has been depleted, Leyte has provided countless number of migrants to Mindanao. Most inhabitants are farmers. Fishing is a supplementary activity. Rice and corn (maize) are the main food crops; cash crops include coconuts, abaca, tobacco, bananas, and sugarcane. There are some manganese deposits, and sandstone and limestone are quarried in the northwest. Politically, the island is divided into two provinces: (Northern) Leyte and Southern Leyte. Territorially, Southern Leyte includes the island of Panaon to its south. To the north of Leyte is the island province of Biliran, a former sub-province of Leyte. The major cities of Leyte are Tacloban, on the eastern shore at the northwest corner of Leyte Gulf, and Ormoc, on the west coast. Leyte to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea). It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian l ...: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua (province), Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua (province), West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
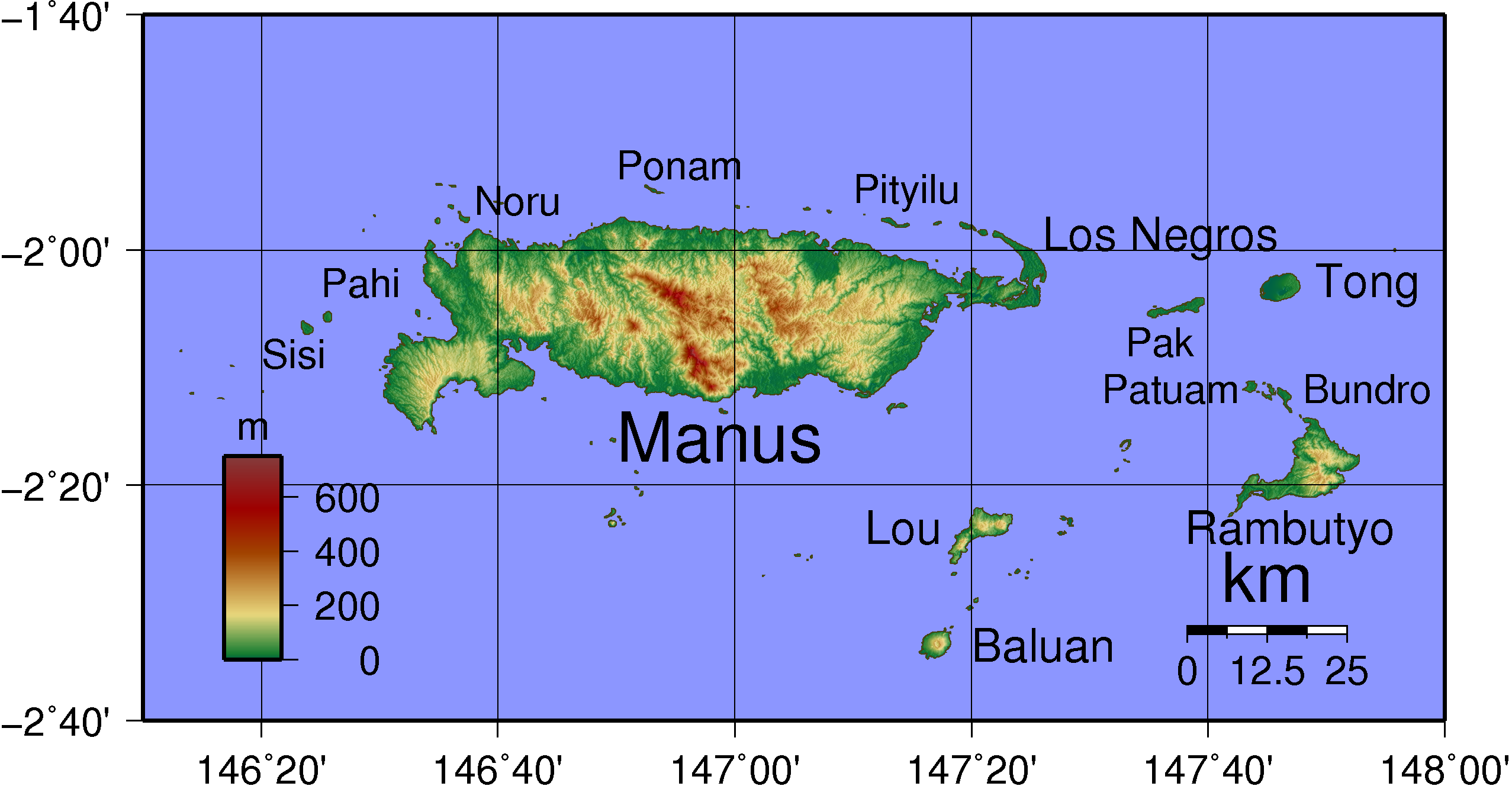
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and least-populous province of Papua New Guinea, in its Islands Region. The total area is . Many of the Admiralty Islands are atolls and uninhabited. Islands The larger islands in the center of the group are Manus Island and Los Negros Island. The other larger islands are Tong Island, Pak Island, Rambutyo Island, Lou Island, and Baluan Island to the east, Mbuke Island to the south and Bipi Island to the west of Manus Island. Other islands that have been noted as significant places in the history of Manus include Ndrova Island, Pitylu Island and Ponam Island. Geography The temperature of the Admiralty Islands varies little throughout the year, reaching daily highs of and at night. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Negros Island
Los Negros Island is the third largest of the Admiralty Islands. It is significant because it contains the main airport of Manus Province on its eastern coastline, at Momote. It is connected to Lorengau, the capital of the province, on Manus Island via a highway and bridge across the Lonui Passage, which separates Los Negros from the larger Manus Island. One of Australia's regional centres for asylum seekers caught in Australian waters, the Manus Island Regional Processing Centre, was situated on the island until it closed in November 2017. Remaining asylum seekers were housed in accommodation in Lorengau. History Los Negros was formerly a Japanese base during World War II, and was heavily assaulted on February 29, 1944 by Allied forces, during the Battle of Los Negros which was the spearhead for the Admiralty Islands campaign. After its capture by allied forces, Los Negros was developed over the spring and summer of 1944 into an important air and sea base that was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits) and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neupommern ("New Pomerania"). In common with most of the Bismarcks it was largely formed by volcanic processes, and has active volcanoes including Ulawun (highest volcano nationally), Langila, the Garbuna Group, the Sulu Range, and the volcanoes Tavurvur and Vulcan of the Rabaul caldera. A major eruption of Tavurvur in 1994 destroyed the East New Britain provincial capital of Rabaul. Most of the town still lies under metres of ash, and the capital has been moved to nearby Kokopo. Geography New Britain e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |