|
USS Alton
The first USS ''Chicago'' (later CA-14) was a protected cruiser of the United States Navy, the largest of the original three authorized by Congress for the "New Navy" and one of the U.S. Navy's first four steel ships. She was launched on 5 December 1885 by Delaware River Iron Ship Building and Engine Works of Chester, Pennsylvania, sponsored by Edith Cleborne (daughter of Navy Medical Director Cuthbert J. Cleborne) and commissioned on 17 April 1889. Design and construction ''Chicago'' was ordered as part of the "ABCD" ships, the others being the cruisers and and the dispatch vessel . These were the first steel-hulled ships of the "New Navy". All were ordered from the same shipyard, Delaware River Iron Ship Building and Engine Works of Chester, Pennsylvania. However, when Secretary of the Navy William C. Whitney initially refused to accept ''Dolphin'', claiming her design was defective, the Roach yard went bankrupt and ''Chicago''s completion was delayed about three years whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago (protected)
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = U.S. state, State , subdivision_type2 = List of counties in Illinois, Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook County, Illinois, Cook and DuPage County, Illinois, DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Municipal corporation, Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council government, Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor of Chicago, Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6"/30 Caliber Gun
The 6"/30 caliber gun Mark 1 (spoken "six-inch-thirty-caliber") were used for the primary battery of the United States Navy's dispatch vessel with the Mark 2 being used in the secondary batteries for its "New Navy" protected cruisers , , and and the Mark 3 used for the primary and secondary batteries in the succeeding early protected cruisers in addition to secondary batteries in the "Second Class Battleships" and . Design The 6-inch/30 caliber Mark 1, 2, and 3 guns were developed before the Spanish–American War and still used black powder or brown powder, in later years they were not considered strong enough to withstand the higher chamber pressures generated by the newer smokeless powder adopted around 1898 and were obsolete before the start of World War I. The Mark 1, gun No. 1, was constructed of tube, jacket, 16 hoops, an elevating band and integral trunnions with a screwed on muzzle bell. The Mark 2 also trunnioned with the Mark 2 Mod 1 only having 10 hoops, jacket, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers resembled armored cruisers, which had in addition a belt of armour along the sides. Evolution From the late 1850s, navies began to replace their fleets of wooden ships-of-the-line with armoured ironclad warships. However, the frigates and sloops which performed the missions of scouting, commerce raiding and trade protection remained unarmoured. For several decades, it proved difficult to design a ship which had a meaningful amount of protective armour but at the same time maintained the speed and range required of a "cruising warship". The first attempts to do so, armored cruisers like , proved unsatisfactory, generally lacking enough speed for their cruiser role. During the 1870s the increasing power of armour-piercing shells made armou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5"/40 Caliber Gun
The 5″/40 caliber gun (spoken "five-inch-forty-caliber") were used in the secondary batteries of the United States Navy's early battleships, armored cruisers, protected cruisers, unprotected cruisers, and auxiliary cruisers. Design The Mark 2, Nos. 3 – 70, was a 40 Caliber (artillery), caliber naval gun that fired Shell (projectile)#Separate loading cased charge, semi-fixed ammunition. The Mark 2 consisted of tube, jacket, and 2 Hoop gun, hoops, being hooped to from the muzzle. The Mod 1 had different exterior dimensions for the hoops and chase and was primarily intended to be used with the Mark 2 Mods 1 and 4 mounts. Mod 2 had a cylindrical jacket that was in diameter for to the rear of the mounting threads. It was intended for the Mark 2 Mods 1 and 4 and Mark 3 Mods 1 and 6 mounts. Mod 3 was the same as the Mod 2 but without the cylindrical section. It was designed to use the Mark 2 Mods 1, 2, 4, and 5 and the Mark 3 Mods 1, 4, 6, and 9 mounts. The Mod 4 only differed fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8"/35 Caliber Gun
The 8"/35 caliber gun Mark 3 and Mark 4 (spoken "eight-inch-thirty-five--caliber") were used for the main batteries of the United States Navy's first armored cruisers and the secondary batteries for their first battleships, the . The 8"/40 caliber gun Mark 5 initially armed the armored cruisers. Mark 3 The Mark 3 Experimental was a 30 caliber gun that used trunnions and had 11 hoops with the outer hoop starting from the breech and running out to the muzzle. The Mark 3s consisted of gun Nos. 9 – 27, 33 – 37, and 51. The production Mark 3 Mod 0 had removable trunnions, from the breech, 35 caliber gun that had 11 hoops with the outer hoop starting 4 inches from the breech and running out to from the muzzle. This gun was removed from service prior to World War I. The Mark 3 Mod 1 was constructed of tube Tube or tubes may refer to: * ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film * ''The Tube'' (TV series), a music related TV series by Channel 4 in the United Kingdom * "Tubes" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babcock & Wilcox Boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam. The heated water/steam mixture then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn off the top of the drum. In some services, the steam passes through tubes in the hot gas path, (a superheater) to become superheated. Superheated steam is defined as steam that is heated above the boiling point at a given pressure. Superheated steam is a dry gas and therefore is typically used to drive turbines, since water droplets can severely damage turbine blades. Saturated water at the bottom of the steam drum returns to the lower dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Expansion Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conning Tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and ground tackle. It is usually located as high on the ship as practical, to give the conning team good visibility of the entirety of the ship, ocean conditions, and other vessels. The naval term "conn" may derive from the Middle English ''conne'' (study, become acquainted with) or French ''conduire'' from Latin ''conducere'' (conduct). Surface ships On surface ships, the conning tower was a feature of all battleships and armored cruisers from about 1860 to the early years of World War II. Located at the front end of the superstructure, the conning tower was a heavily armored cylinder, with tiny slit windows on three sides providing a reasonable field of view. Designed to shield just enough personnel and devices for navigation during battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deck (ship)
A deck is a permanent covering over a compartment or a hull of a ship. On a boat or ship, the primary or upper deck is the horizontal structure that forms the "roof" of the hull, strengthening it and serving as the primary working surface. Vessels often have more than one level both within the hull and in the superstructure above the primary deck, similar to the floors of a multi-storey building, that are also referred to as decks, as are certain compartments and decks built over specific areas of the superstructure. Decks for some purposes have specific names. Structure The main purpose of the upper or primary deck is structural, and only secondarily to provide weather-tightness and support people and equipment. The deck serves as the lid to the complex box girder which can be identified as the hull. It resists tension, compression, and racking forces. The deck's scantling is usually the same as the topsides, or might be heavier if the deck is expected to carry heavier loads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
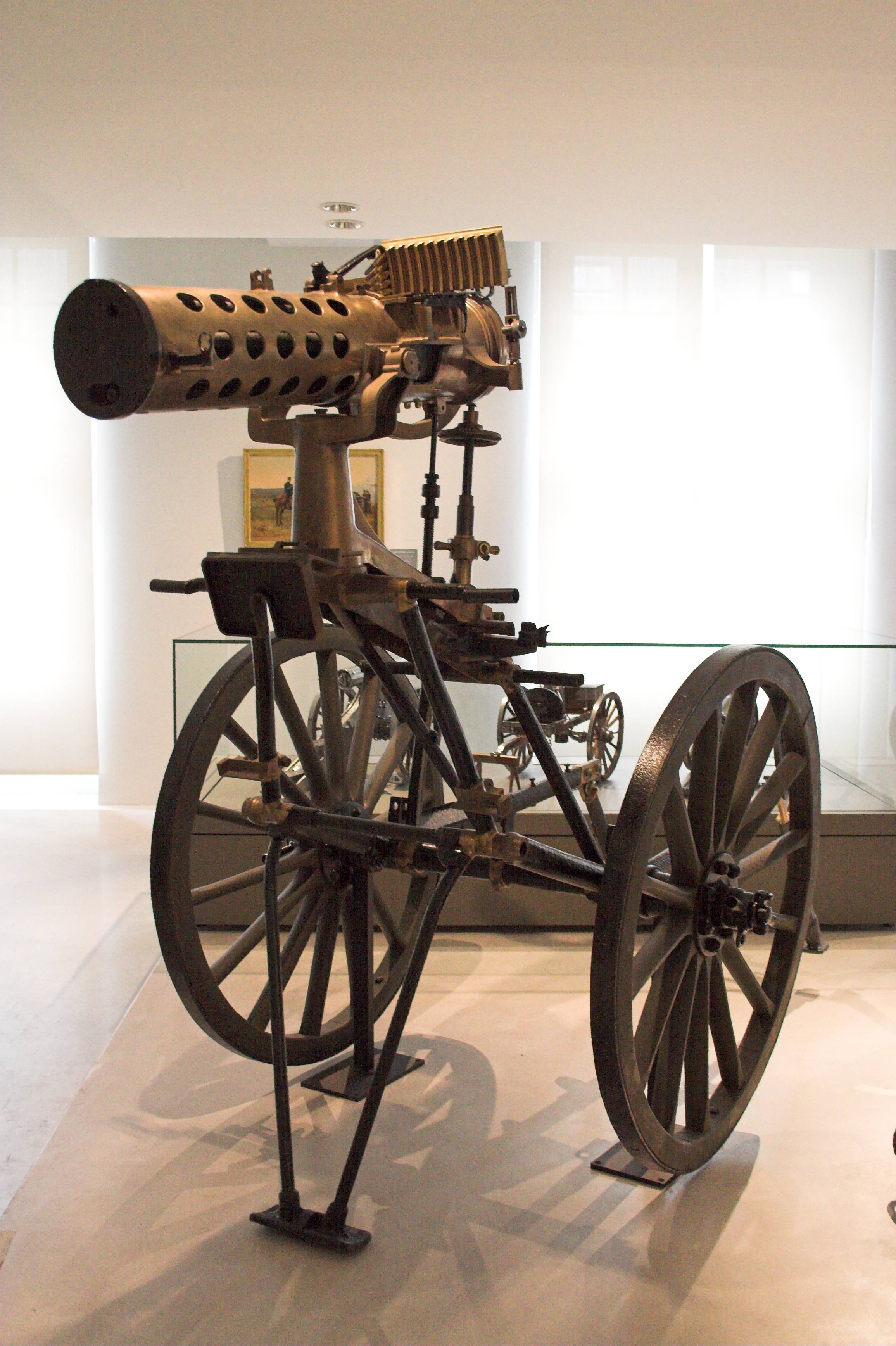
Gatling Gun
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon. The Gatling gun's operation centered on a cyclic multi-barrel design which facilitated cooling and synchronized the firing-reloading sequence. As the handwheel is cranked, the barrels rotate and each barrel sequentially loads a single cartridge from a top-mounted magazine, fires off the shot when it reaches a set position (usually at 4 o'clock), then ejects the spent casing out of the left side at the bottom, after which the barrel is empty and allowed to cool until rotated back to the top position and gravity-fed another new round. This configuration eliminated the need for a single reciprocating bolt design and allowed higher rates of fire to be achieved without the barrels overheating quickly. One of the best-known early rapid-fire firearms, the Gatling gun saw occasional use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
45-70
The .45-70 rifle cartridge, also known as the .45-70 Government, was developed at the U.S. Army's Springfield Armory for use in the Springfield Model 1873, which is known to collectors as the "Trapdoor Springfield." The new cartridge was a replacement for the stop-gap .50-70 Government cartridge, which had been adopted in 1866, one year after the end of the American Civil War. Nomenclature The new cartridge was completely identified as the ''.45-70-405'', but was also referred to as the ".45 Government" cartridge in commercial catalogs. The nomenclature of the time was based on three properties of the cartridge: * .45: nominal diameter of bullet, measured in decimal inches, i.e., 0.458 inches (11.63 mm); * 70: weight of black powder, measured in grains, i.e., 70 grains (4.56 g); * 405: weight of lead bullet, measured in grains, i.e., 405 grains (26.38 g). The minimum acceptable accuracy of the .45-70 from the 1873 Springfield was approximately at , however, the heavy, slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotchkiss Gun
The Hotchkiss gun can refer to different products of the Hotchkiss arms company starting in the late 19th century. It usually refers to the 1.65-inch (42 mm) light mountain gun; there were also a navy (47 mm) and a 3-inch (76 mm) Hotchkiss guns. The 42 mm gun was intended to be mounted on a light carriage or packed on two mules to accompany a troop of cavalry or an army travelling in rough country. Descriptions 1.65-inch gun The gun and accessories could be packed on two mules. The gun was introduced as a modern replacement for the aging twelve-pounder mountain howitzer. The first gun purchased by the U.S. military from the French arms firm of Hotchkiss was employed against the Nez Percé in 1877. Over the next twenty years the U.S. purchased 56. They were used at the Wounded Knee Massacre in 1890, and again in Cuba at the Battle of Las Guasimas, the Battle of El Caney and the attack on San Juan Hill during the Spanish–American War of 1898. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
._Port_bow%2C_1891_-_NARA_-_512893.jpg)