|
UFM100
Ubiquitin-fold modifier 1, also known as UFM1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''UFM1'' gene. UFM1 is a ubiquitin-like protein that is conjugated to target proteins by E1-like activating enzyme UBA5 and E2-like conjugating enzyme UFC1. This process is often referred to as UFMylation. Function UFM1 shares several common properties with ubiquitin (Ub) and the other ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs). Ufm1 has similar tertiary structure to Ub but lacks any obvious sequence similarity. It is synthesized as an inactive precursor form (pro-Ufm1) which has 2 additional amino acids beyond the conserved glycine. The mechanism of Ufm1 conjugation is similar to that of ubiquitin. Mature Ufm1 has an exposed C-terminal glycine which is essential for subsequent activation by its cognate E1 protein (Uba5). This activation step results in the formation of a high-energy thiolester bond in the presence of ATP. The Ufm1 is subsequently transferred to its cognate E2-like enzyme (Ufc1) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or, alternatively, ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UBE1DC1
Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''UBA5'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... This gene encodes a member of the E1-like activating enzyme family. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin-fold Modifier Conjugating Enzyme 1
Ubiquitin-fold modifier conjugating enzyme 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UFC1 gene. Function UFC1 is an E2-like conjugating enzyme for ubiquitin Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...-fold modifier-1 (UFM1; MIM 610553) (Komatsu et al., 2004 ubMed 15071506. upplied by OMIM, Mar 2008 References Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin-like Protein
Ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs) are a family of small proteins involved in post-translational modification of other proteins in a cell, usually with a regulatory function. The UBL protein family derives its name from the first member of the class to be discovered, ubiquitin (Ub), best known for its role in regulating protein degradation through covalent modification of other proteins. Following the discovery of ubiquitin, many additional evolutionarily related members of the group were described, involving parallel regulatory processes and similar chemistry. UBLs are involved in a widely varying array of cellular functions including autophagy, protein trafficking, inflammation and immune responses, transcription, DNA repair, RNA splicing, and cellular differentiation. Discovery Ubiquitin itself was first discovered in the 1970s and originally named "ubiquitous immunopoietic polypeptide". Subsequently, other proteins with sequence similarity to ubiquitin were occasionally reported i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure.Branden C. and Tooze J. "Introduction to Protein Structure" Garland Publishing, New York. 1990 and 1991. A number of tertiary structures may fold into a quaternary structure.Kyte, J. "Structure in Protein Chemistry." Garland Publishing, New York. 1995. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioconjugation
Bioconjugation is a chemical strategy to form a stable covalent link between two molecules, at least one of which is a biomolecule. Function Recent advances in the understanding of biomolecules enabled their application to numerous fields like medicine and materials. Synthetically modified biomolecules can have diverse functionalities, such as tracking cellular events, revealing enzyme function, determining protein biodistribution, imaging specific biomarkers, and delivering drugs to targeted cells. Bioconjugation is a crucial strategy that links these modified biomolecules with different substrates. Synthesis Synthesis of bioconjugates involves a variety of challenges, ranging from the simple and nonspecific use of a fluorescent dye marker to the complex design of antibody drug conjugates. As a result, various bioconjugation reactions – chemical reactions connecting two biomolecules together – have been developed to chemically modify proteins. Common types of bioconjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
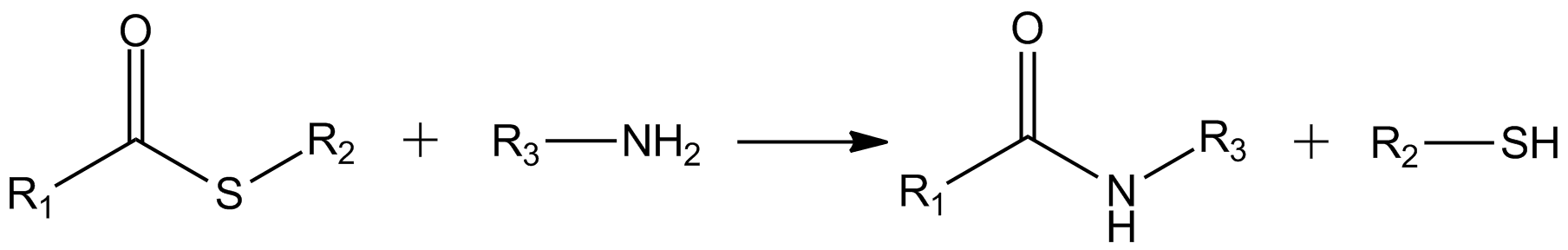
Thioester
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. They are the product of esterification between a carboxylic acid () and a thiol (). In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA.Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. Synthesis The most typical route to thioester involves the reaction of an acid chloride with an alkali metal salt of a thiol: :RSNa + R'COCl -> R'COSR + NaCl Another common route entails the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid. For example, thioacetate esters are commonly prepared by alkylation of potassium thioacetate: :CH3COSK + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |