|
U.S. Bureau Of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms And Explosives
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (BATFE), commonly referred to as the ATF, is a domestic law enforcement agency within the United States Department of Justice. Its responsibilities include the investigation and prevention of federal offenses involving the unlawful use, manufacture, and possession of firearms and explosives; acts of arson and bombings; and illegal trafficking and tax evasion of alcohol and tobacco products. The ATF also regulates via licensing the sale, possession, and transportation of firearms, ammunition, and explosives in interstate commerce. Many of the ATF's activities are carried out in conjunction with task forces made up of state and local law enforcement officers, such as Project Safe Neighborhoods. The ATF operates a unique fire research laboratory in Beltsville, Maryland, where full-scale mock-ups of criminal arson can be reconstructed. The ATF had 5,285 employees and an annual budget of almost $1.5 billion in 2021. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Dollar
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100 cents, and authorized the minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of Federal Reserve Notes, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color. The monetary policy of the United States is conducted by the Federal Reserve System, which acts as the nation's central bank. The U.S. dollar was originally defined under a bimetallic standard of (0.7735 troy ounces) fine silver or, from 1837, fine gold, or $20.67 per troy ounce. The Gold Standard Act of 1900 linked the dollar solely to gold. From 1934, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATF Fire Research Laboratory
The Fire Research Laboratory (FRL) is part of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), an investigative agency within the United States Department of Justice.{{Cite web, url=https://www.atf.gov/arson/atf-fire-research-laboratory, title=ATF Fire Research Laboratory {{! Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, website=www.atf.gov, language=en, access-date=2018-04-18 Located in Beltsville, Maryland, the FRL is a partnership among law enforcement, fire services, public safety agencies, academia and the private sector that uses the most advanced scientific, technical, educational, and training methods in fire investigation science to serve and protect the public. Functionality The Fire Research Laboratory does the following: * Conducts scientific research that validates fire scene indicators and improves fire scene reconstruction and fire evidence analysis; * Supports fire and arson investigations and the resolution of fire related crimes; * Develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Control Act Of 1968
The Gun Control Act of 1968 (GCA or GCA68) is a U.S. federal law that regulates the firearms industry and firearms ownership. Due to constitutional limitations, the Act is primarily based on regulating interstate commerce in firearms by generally prohibiting interstate firearms transfers except by manufacturers, dealers and importers licensed under a scheme set up under the Act. The GCA was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson on October 22, 1968, and is Title I of the U.S. federal firearms laws. The National Firearms Act of 1934 (NFA) is Title II. Both GCA and NFA are enforced by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF). GCA repealed the Federal Firearms Act of 1938, though many of its provisions were reenacted as part of the GCA, which revised the FFA and its predecessor, the National Firearms Act of 1934 (NFA). History The bill was initially prompted by the assassination of U.S. President John F. Kennedy in 1963. The President was shot and ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Untouchables (law Enforcement)
The Untouchables were special agents of the U.S. Bureau of Prohibition led by Eliot Ness, who, from 1930 to 1932, worked to end Al Capone's illegal activities by aggressively enforcing Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition laws against his organization. Legendary for being fearless and incorruptible, they earned the nickname "The Untouchables" after several agents refused large bribes from members of the Chicago Outfit. Due to its significant success and enduring legacy, the unit has subsequently had a lasting impact on the techniques and methods of modern organized crime law enforcement units. Mission Shortly after taking office in 1929, Herbert Hoover, the 31st President of the United States, gave United States Secretary of the Treasury, Secretary of the Treasury Andrew Mellon and United States Attorney General, Attorney General William D. Mitchell a plan for attacking large bootlegging gangs with small teams of Prohibition agents working under special United States Atto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
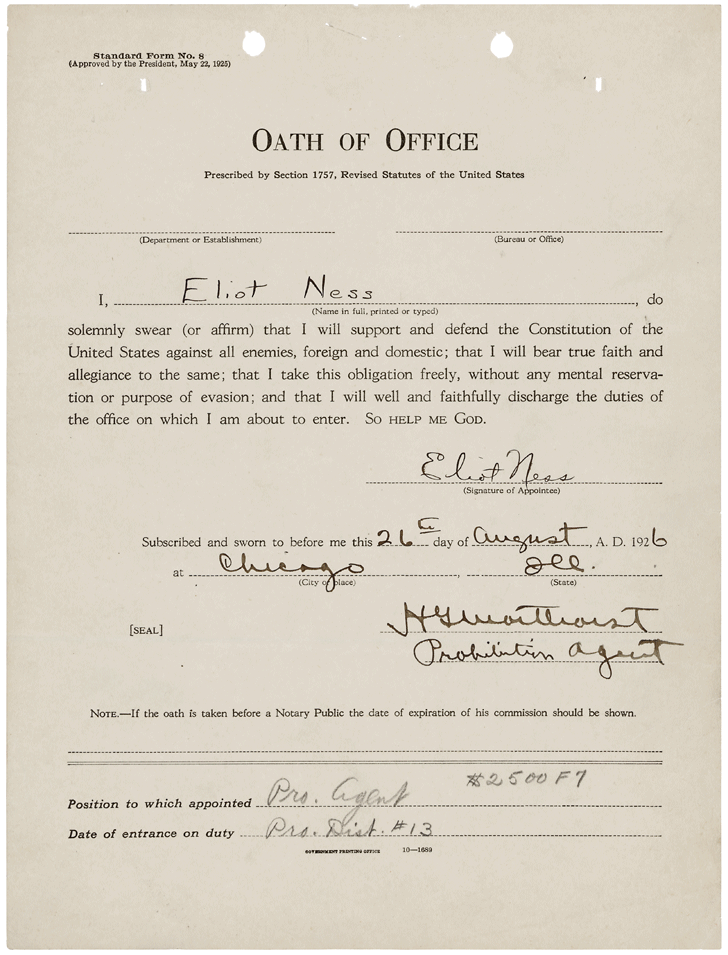
Eliot Ness
Eliot Ness (April 19, 1903 – May 16, 1957) was an American Prohibition agent known for his efforts to bring down Al Capone and enforce Prohibition in Chicago. He was the leader of a team of law enforcement agents, nicknamed The Untouchables. His co-authorship of an autobiography, ''The Untouchables'', which was released shortly after his death, launched several television and motion picture portrayals establishing Ness's posthumous fame as an incorruptible crime fighter. Early life Eliot Ness was born on April 19, 1903, in the Kensington neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. He was the youngest of five children born to Peter Ness (1850–1931) and Emma King (1863–1937). His parents, both Norwegian immigrants, operated a bakery. Ness attended Christian Fenger High School in Chicago. He was educated at the University of Chicago, graduating in 1925 with a degree in political science and business administration, and was a member of Sigma Alpha Epsilon. He began his career as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeal
A repeal (O.F. ''rapel'', modern ''rappel'', from ''rapeler'', ''rappeler'', revoke, ''re'' and ''appeler'', appeal) is the removal or reversal of a law. There are two basic types of repeal; a repeal with a re-enactment is used to replace the law with an updated, amended, or otherwise related law, or a repeal without replacement so as to abolish its provisions altogether. Removal of secondary legislation is normally referred to as revocation rather than repeal in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Under the common law of England and Wales, the effect of repealing a statute was "to obliterate it completely from the records of Parliament as though it had never been passed." This, however, is now subject to savings provisions within the Interpretation Act 1978. In parliamentary procedure, the motion to rescind, repeal, or annul is used to cancel or countermand an action or order previously adopted by the assembly. Partial or full repeals A partial repeal occurs when a specified part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prohibition In The United States
In the United States from 1920 to 1933, a Constitution of the United States, nationwide constitutional law prohibition, prohibited the production, importation, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages. The alcohol industry was curtailed by a succession of state legislatures, and finally ended nationwide under the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified on January 16, 1919. Prohibition ended with the ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment to the United States Constitution, Twenty-first Amendment, which repealed the Eighteenth Amendment on December 5, 1933. Led by Pietism, pietistic Protestantism in the United States, Protestants, prohibitionists first attempted to end the trade in alcoholic drinks during the 19th century. They aimed to heal what they saw as an ill society beset by alcohol-related problems such as alcoholism, Domestic violence, family violence, and Saloon bar, saloon-based political corruption. Many communities introduced al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volstead Act
The National Prohibition Act, known informally as the Volstead Act, was an act of the 66th United States Congress, designed to carry out the intent of the 18th Amendment (ratified January 1919), which established the prohibition of alcoholic drinks. The Anti-Saloon League's Wayne Wheeler conceived and drafted the bill, which was named after Andrew Volstead, Chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, who managed the legislation. Procedure The Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibited the production, sale, and transport of "intoxicating liquors," but it did not define "intoxicating liquors" or provide penalties. It granted both the federal government and the states the power to enforce the ban by "appropriate legislation." A bill to do so was introduced in the United States Congress in 1919. The act was voided by the ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment in 1933. The bill was vetoed by President Woodrow Wilson on October 27, 1919, largely on tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Bureau Of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, the FBI is also a member of the U.S. Intelligence Community and reports to both the Attorney General and the Director of National Intelligence. A leading U.S. counterterrorism, counterintelligence, and criminal investigative organization, the FBI has jurisdiction over violations of more than 200 categories of federal crimes. Although many of the FBI's functions are unique, its activities in support of national security are comparable to those of the British MI5 and NCA; the New Zealand GCSB and the Russian FSB. Unlike the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), which has no law enforcement authority and is focused on intelligence collection abroad, the FBI is primarily a domestic agency, maintaining 56 field offices in major cities throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Prohibition
The Bureau of Prohibition (or Prohibition Unit) was the United States federal law enforcement agency formed to enforce the National Prohibition Act of 1919, commonly known as the Volstead Act, which enforced the 18th Amendment to the United States Constitution regarding the prohibition of the manufacture, sale, and transportation of alcoholic beverages. When it was first established in 1920, it was a unit of the Bureau of Internal Revenue. On April 1, 1927, it became an independent entity within the Department of the Treasury, changing its name from the Prohibition Unit to the Bureau of Prohibition. In 1930, it became part of the Department of Justice. By 1933, with the repeal of Prohibition imminent, it was briefly absorbed into the FBI, or "Bureau of Investigation" as it was then called, and became the Bureau's "Alcohol Beverage Unit," though, for practical purposes it continued to operate as a separate agency. Very shortly after that, once repeal became a reality, and the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Revenue Service
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the revenue service for the United States federal government, which is responsible for collecting U.S. federal taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of the federal statutory tax law. It is an agency of the Department of the Treasury and led by the Commissioner of Internal Revenue, who is appointed to a five-year term by the President of the United States. The duties of the IRS include providing tax assistance to taxpayers; pursuing and resolving instances of erroneous or fraudulent tax filings; and overseeing various benefits programs, including the Affordable Care Act. The IRS originates from the Commissioner of Internal Revenue, a federal office created in 1862 to assess the nation's first income tax to fund the American Civil War. The temporary measure provided over a fifth of the Union's war expenses before being allowed to expire a decade later. In 1913, the Sixteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |