|
Tzanck Test
In dermatopathology, the Tzanck test, also Tzanck smear, is scraping of an ulcer base to look for Tzanck cells. It is sometimes also called the chickenpox skin test and the herpes skin test. It is a simple, low-cost, and rapid office based test. Tzanck cells (acantholytic cells) are found in: *Herpes simplex * Varicella and herpes zoster *Pemphigus vulgaris *Cytomegalovirus Arnault Tzanck did the first cytological examinations in order to diagnose skin diseases. To diagnose pemphigus, he identified acantholytic cells, and to diagnose of herpetic infections he identified multinucleated giant cells and acantholytic cells. He extended his cytologic findings to certain skin tumors as well. Even though cytological examination can provide rapid and reliable diagnosis for many skin diseases, its use is limited to a few diseases. In endemic regions, Tzanck test is used to diagnose leishmaniasis and leprosy. For other regions, Tzanck test is mainly used to diagnose pemphigus and herpeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatopathology
Dermatopathology (from Greek , ''derma'' 'skin' + , ''pathos'' 'fate, harm' + , '' -logia'' 'study of') is a joint subspecialty of dermatology and pathology or surgical pathology that focuses on the study of cutaneous diseases at a microscopic and molecular level. It also encompasses analyses of the potential causes of skin diseases at a basic level. Dermatopathologists work in close association with clinical dermatologists, with many possessing further clinical training in dermatology. Dermatologists are able to recognize most skin diseases based on their appearances, anatomic distributions, and behavior. Sometimes, however, those criteria do not allow a conclusive diagnosis to be made, and a skin biopsy is taken to be examined under the microscope or are subject to other molecular tests. That process reveals the histology of the disease and results in a specific diagnostic interpretation. In some cases, additional specialized testing needs to be performed on biopsies, including i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved. More than 20 types of ''Candida'' can cause infection with ''Candida albicans'' being the most common. Infections of the mouth are most common among children less than one month old, the elderly, and those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darier's Disease
Darier's disease (DAR) is an inherited skin disorder that presents with multiple greasy, crusting, thick brown bumps that merge into patches. It is an autosomal dominant disorder discovered by French dermatologist Ferdinand-Jean Darier. Darier's is characterized by dark crusty patches on the skin that are mildly greasy and that emit a strong odor. These patches, also known as keratotic papules, keratosis follicularis, or dyskeratosis follicularis, most often appear on the scalp, forehead, upper arms, chest, back, knees, elbows, and behind the ear. Mild forms of the disease are the most common, consisting solely of skin rashes that flare up under certain conditions such as high humidity, high stress, or tight-fitting clothes. Short stature, when combined with poorly-formed fingernails that contain vertical striations, is diagnostic even for mild forms of DAR. Symptoms will usually appear in late childhood or early adulthood between the ages of 15 to 30 years and will vary over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
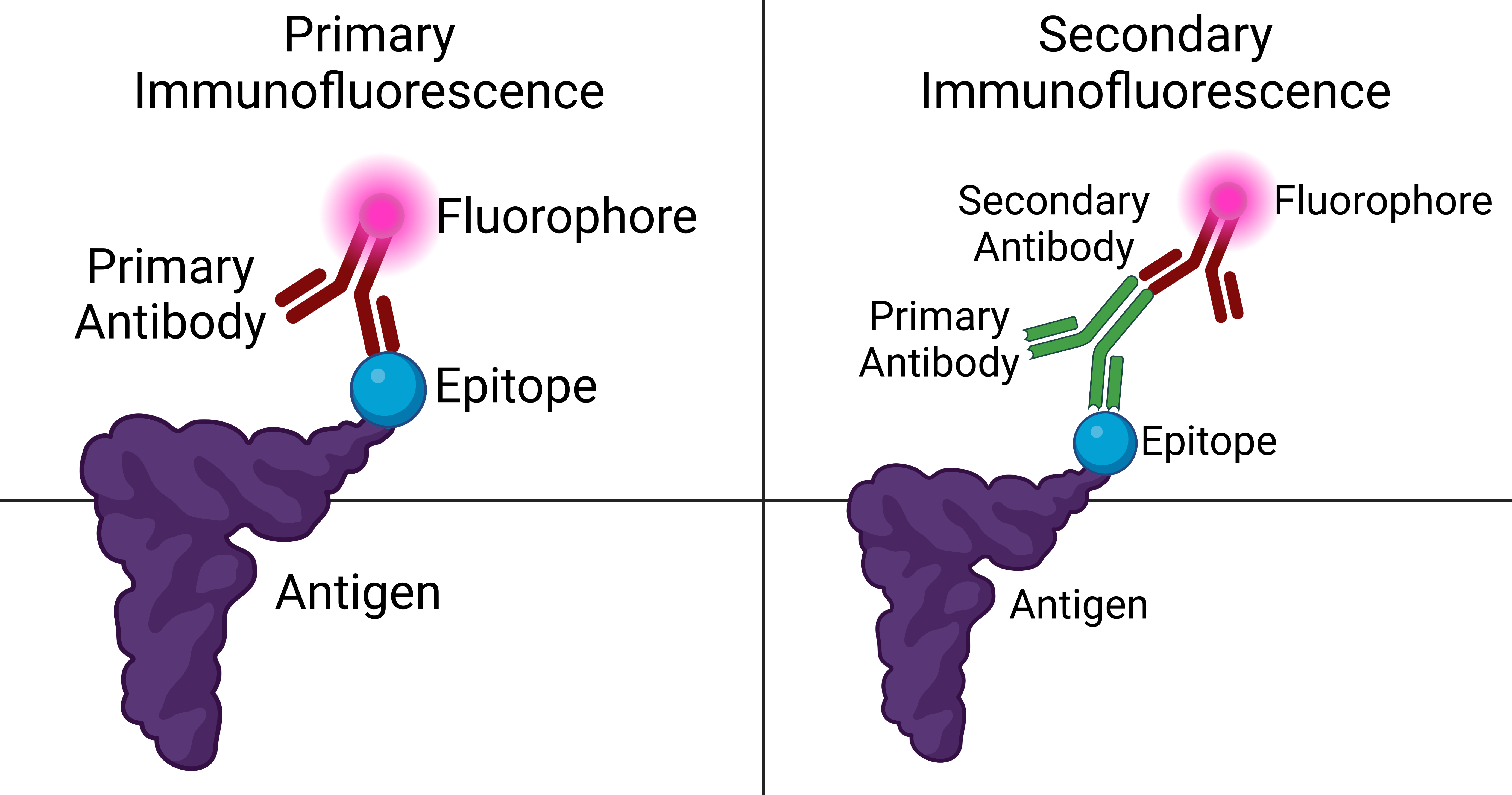
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. There have been efforts in epitope mapping since many antibodies can bind the same epitope and levels of binding between antibodies that recognize the same epitope can vary. Additionally, the binding of the fluorophore to the antibody itself cannot interfere with the immunological specificity of the antibody or the binding capacity of its antigen. Immunofluorescence is a widely used example of immunostaining (using antibodies to stain proteins) and is a specific example of immunohistochemistry (the use of the antibody-antigen rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hailey–Hailey Disease
Hailey–Hailey disease, or familial benign chronic pemphigus or familial benign pemphigus, was originally described by the Hailey brothers (Hugh Edward and William Howard) in 1939. It is a genetic disorder that causes blisters to form on the skin. Signs and symptoms HHD is characterized by outbreaks of rashes and blisters on the skin. Affected areas of skin undergo repeated blistering and inflammation, and may be painful to the touch. Areas where the skin folds, as well as the armpits, groin, neck, buttocks and under the breasts are most commonly affected. In addition to blistering, other symptoms which accompany HHD include acantholysis, erythema and hyperkeratosis. Causes The cause of the disease is a haploinsufficiency of the enzyme ATP2C1; the ATP2C1 gene is located on chromosome 3, which encodes the protein hSPCA1. A mutation on one copy of the gene causes only half of this necessary protein to be made and the cells of the skin do not adhere together properly due to malform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pemphigus
Pemphigus ( or ) is a rare group of blistering autoimmune diseases that affect the skin and mucous membranes. The name is derived from the Greek root ''pemphix'', meaning "pustule". In pemphigus, autoantibodies form against desmoglein, which forms the "glue" that attaches adjacent epidermal cells via attachment points called desmosomes. When autoantibodies attack desmogleins, the cells become separated from each other and the epidermis becomes detached, a phenomenon called acantholysis. This causes blisters that slough off and turn into sores. In some cases, these blisters can cover a large area of the skin. Originally, the cause of this disease was unknown, and "pemphigus" was used to refer to any blistering disease of the skin and mucosa. In 1964, researchers found that the blood of patients with pemphigus contained antibodies to the layers of skin that separate to form the blisters. In 1971, an article investigating the autoimmune nature of this disease was published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous Amoebiasis
__NOTOC__ Cutaneous amoebiasis, refers to a form of amoebiasis that presents primarily in the skin. It can be caused by ''Acanthamoeba'' or ''Entamoeba histolytica''. When associated with ''Acanthamoeba'', it is also known as "cutaneous acanthamoebiasis". ''Balamuthia mandrillaris'' can also cause cutaneous amoebiasis, but can prove fatal if the amoeba enters the bloodstream __TOC__ Diagnosis It is characterized by ulcers. Diagnosis of amebiasis cutis calls for high degree of clinical suspicion. This needs to be backed with demonstration of trophozoites from lesions. Unless an early diagnosis can be made such patients can develop significant morbidity. See also * Skin lesion A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this s ... References External links Cutaneous conditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demodex Folliculorum
''Demodex folliculorum'' is a microscopic mite that can only survive on the skin of humans. Most people have ''D.folliculorum'' on their skin. Usually, the mites do not cause any harm, so are considered an example of commensalism rather than parasitism. ''D.folliculorum''-caused disease, though, is known as demodicosis. Anatomy Due to being adapted to live inside hair follicles, ''D. folliculorum'' is thin and worm-like, with short legs. As an adult, ''D.folliculorum'' measures long. Adults have four pairs of legs; larvae and nymphs have only three pairs. ''D.folliculorum'' has a rudimentary gut and anus. Reproduction and life cycle The entire life cycle of ''D.folliculorum'' takes 14–16 days. Adult mites copulate at the top of the hair follicle, near the skin surface. Eggs are deposited in the sebaceous gland inside the hair follicle. The heart-shaped egg is long, and hatches into a six-legged larva. Seven days are needed for the larva to develop into a mature adult, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver. Infections in humans are caused by more than 20 species of ''Leishmania''. Risk factors include poverty, malnutrition, deforestation, and urbanization. All three types can be diagnosed by seeing the parasites under microscopy. Additionally, visceral disease can be diagnosed by blood tests. Leishmaniasis can be partl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum (MC), sometimes called water warts, is a viral infection of the skin that results in small raised pink lesions with a dimple in the center. They may become itchy or sore, and occur singularly or in groups. Any area of the skin may be affected, with abdomen, legs, arms, neck, genital area, and face being the most common. Onset of the lesions is around seven weeks after infection. They usually go away within a year without scarring. The infection is caused by a poxvirus called the '' molluscum contagiosum virus'' (MCV). The virus is spread either by direct contact, including sexual activity, or via contaminated objects such as towels. The condition can also be spread to other areas of the body by the person themselves. Risk factors include a weak immune system, atopic dermatitis, and crowded living conditions. Following one infection, it is possible to get re-infected. Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance of the lesions. Prevention includes hand w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
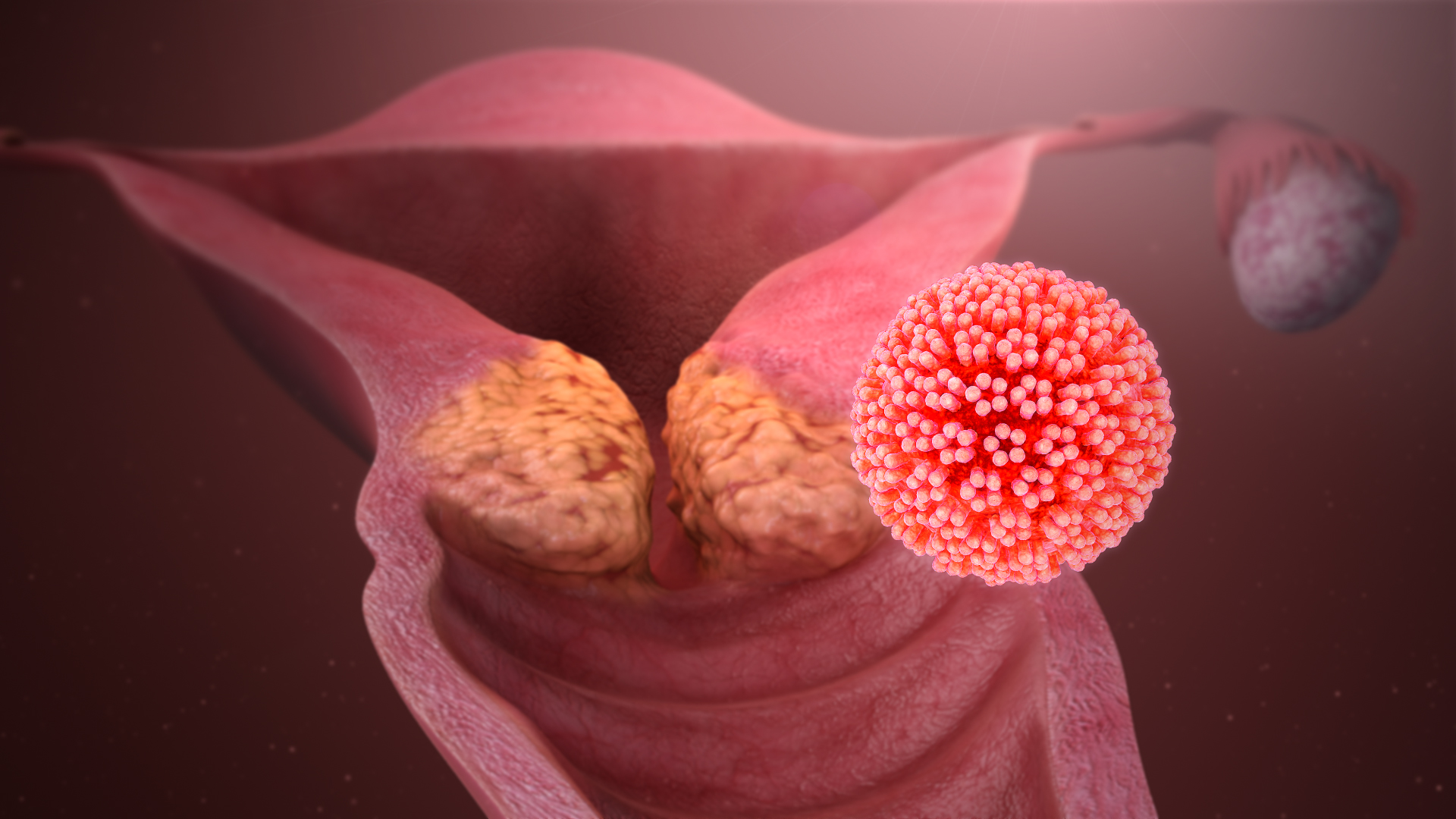
Human Papillomavirus Infection
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand, Foot, And Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infection caused by a group of enteroviruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blister, on the hands, feet and mouth and occasionally buttocks and groin. Signs and symptoms normally appear 3–6 days after exposure to the virus. The rash generally resolves on its own in about a week. Fingernail and toenail loss may occur a few weeks later, but they will regrow with time. The viruses that cause HFMD are spread through close personal contact, through the air from coughing and the feces of an infected person. Contaminated objects can also spread the disease. Coxsackievirus A16 is the most common cause, and enterovirus 71 is the second-most common cause. Other strains of coxsackievirus and enterovirus can also be responsible. Some people may carry and pass on the virus despite having no symptoms of disease. Other animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |