|
Tyumen City Duma
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura River. Fueled by the Russian oil and gas industry, Tyumen has experienced rapid population growth in recent years, rising to a population of 847,488 at the 2021 Census. Tyumen is among the largest cities of the Ural region and the Ural Federal District. Tyumen is often regarded as the first Siberian city, from the western direction. Tyumen was the first Russian settlement in Siberia. Founded in 1586 to support Russia's eastward expansion, the city has remained one of the most important industrial and economic centers east of the Ural Mountains. Located at the junction of several important trade routes and with easy access to navigable waterways, Tyumen rapidly developed from a small military settlement to a large commercial and industrial city. The central part of Old Tyumen retains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyumen Oblast
Tyumen Oblast (russian: Тюме́нская о́бласть, ''Tyumenskaya oblast'') is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Western Siberia region of Siberia, and is administratively part of the Urals Federal District. The oblast has administrative jurisdiction over two autonomous okrugs: Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. Tyumen Oblast including its autonomous okrugs is the third-largest federal subject by area, and has a population of 3,395,755 ( 2010). (The rank is given without the autonomous okrugs' populations; the population and percentages are given for the territory of the oblast with the autonomous okrugs) Tyumen is the largest city and capital of Tyumen Oblast, and the first Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains. Tyumen Oblast is the largest producer of oil and natural gas in the country, and has experienced an oil boom since the early 2000s. The rapid growth of the fuel industry has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudie, A. S., 2004, ''Encyclopedia of Geomorphology'', vol. 1. Routledge, New York. The soils usually consist of clays, silts, sands, and gravels deposited during floods. Because the regular flooding of floodplains can deposit nutrients and water, floodplains frequently have high soil fertility; some important agricultural regions, such as the Mississippi river basin and the Nile, rely heavily on the flood plains. Agricultural regions as well as urban areas have developed near or on floodplains to take advantage of the rich soil and fresh water. However, the risk of flooding has led to increasing efforts to control flooding. Formation Most floodplains are formed by deposition on the inside of river meanders and by overbank flow. Whereve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
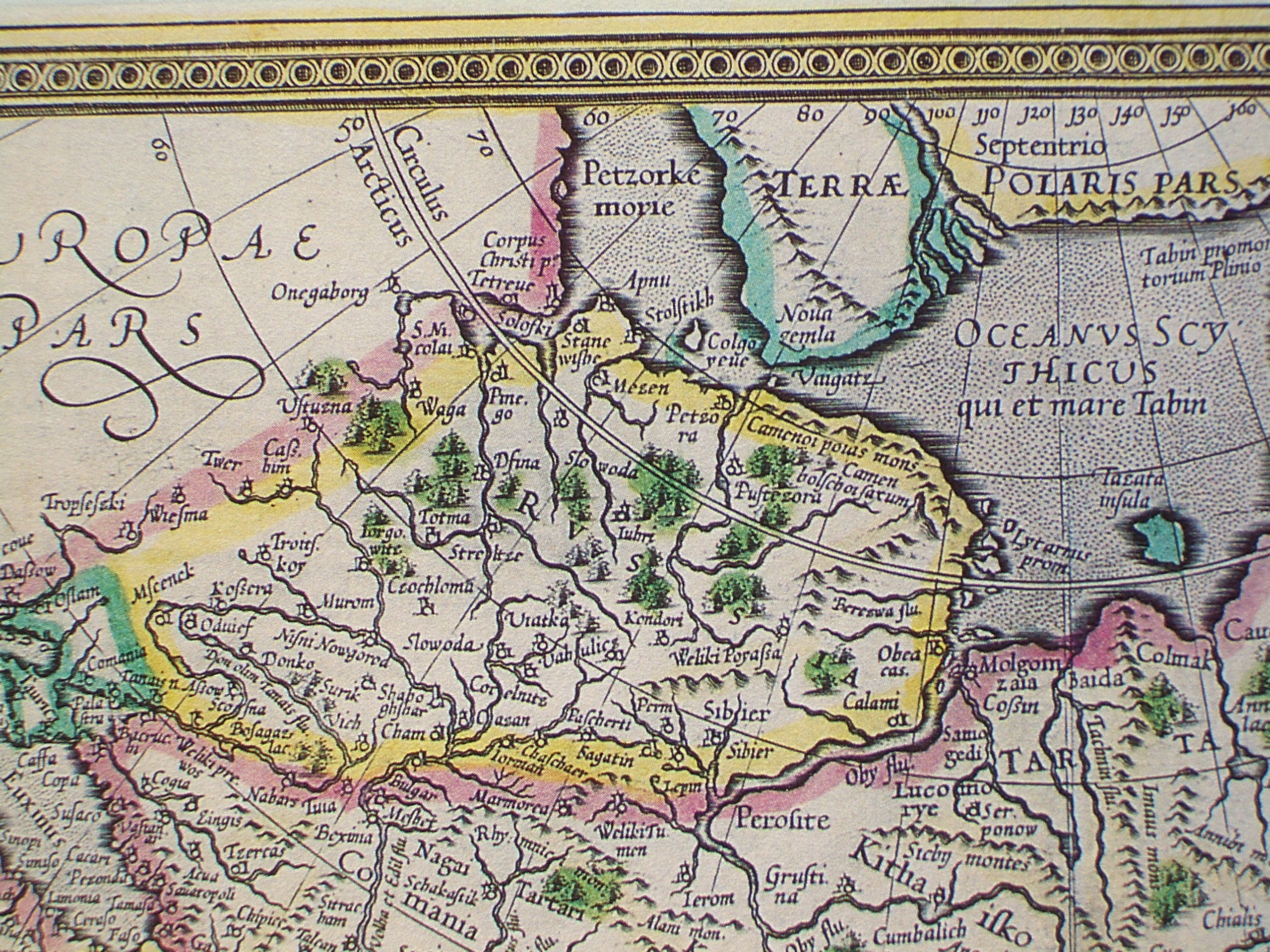
Chimgi-Tura
Chimgi-Tura or Chingi-Tura (russian: Чинги́-Тура́, Siberian Tatar: Цимке-тора) was a medieval city of the Siberian Tatars in 12th-16th centuries located in Western Siberia. It was a capital of the Khanate of Sibir until the early 16th century, when its ruler Khan Muhammad decided not to remain at Chimgi-Tura, and chose a new capital named Qashliq located on the Irtysh. After the Cossack ataman Yermak from Muscovy conquered the Siberian Khanate in the 1580s, the city of Chimgi-Tura was abandoned or burned. In 1586 the Russian fort Tyumen Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura River. Fueled by the Russian oil and gas indu ... was built nearby. Modern Tyumen, one of the centres of the Russian oil industry, covers the site where Chimgi-Tura used to stand. References Geography of Tyumen Oblast Defun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qashliq
Qashliq, Isker or Sibir (Siberian Tatar language: ''Qaşlıq'' or ''Iskär'') was a medieval (14th–16th century) Siberian Tatar fortress, in the 16th century the capital of the Khanate of Sibir, located on the right bank of the Irtysh River at its confluence with the ''Sibirka'' rivulet, some 17 km from the modern city of Tobolsk. The fortress is first mentioned in Russian sources of the 14th century. The period of the most development was in the first half of the 16th century. In 1582 the troops of Cossack ataman Yermak seized and ruined Qashliq. The ruined city was retaken by the Siberian Tatars in 1584 only to be lost forever in 1586. The nearby city of Tobolsk was founded in 1587. Sources differ on the exact location of the fortress. Most give the distance upriver from Tobolsk as 17 or 18 km, or versts, or ten to eleven miles, but others give 23 km. Sources of the early 19th century claim that the ruins of the fortress could still be made out with difficulty.e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsardom Of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I in 1721. From 1551 to 1700, Russia grew by 35,000 km2 per year. The period includes the upheavals of the transition from the Rurik to the Romanov dynasties, wars with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Sweden and the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian conquest of Siberia, to the reign of Peter the Great, who took power in 1689 and transformed the Tsardom into the Russian Empire. During the Great Northern War, he implemented substantial reforms and proclaimed the Russian Empire after victory over Sweden in 1721. Name While the oldest endonyms of the Grand Duchy of Moscow used in its documents were "Rus'" () and the "Russian land" (), a new form of its name, ''Rusia'' or ''Russia'', appeared and became common in the 15th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia Khanate
The Khanate of Sibir (also Khanate of Turan, sty, Себер ханлыгы) was a Tatar Khanate located in southwestern Siberia with a Turco-Mongol ruling class. Throughout its history, members of the Shaybanid and Taibugid dynasties often contested the rulership over the Khanate between each other; both of these competing tribes were direct patrilineal descendants of Genghis Khan through his eldest son Jochi and Jochi's fifth son Shayban (Shiban) (died 1266). The area of the Khanate had once formed an integral part of the Mongol Empire, and later came under the control of the White Horde and the Golden Horde of 1242–1502. The Khanate of Sibir had an ethnically diverse population of Turkic Siberian Tatars, Bashkirs, and speakers of various Uralic languages – including the Khanty, Mansi, and Selkup. The Sibir Khanate was the northernmost Muslim state in recorded history. Its defeat by Yermak Timofeyevich in 1582 marked the beginning of the Russian conquest of Siberia. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yermak Timofeyevich
Yermak Timofeyevich ( rus, Ерма́к Тимофе́евич, p=jɪˈrmak tʲɪmɐˈfʲejɪvʲɪtɕ; born between 1532 and 1542 – August 5 or 6, 1585) was a Cossack ataman and is today a hero in Russian folklore and myths. During the reign of Tsar Ivan the Terrible, Yermak started the Russian conquest of Siberia. Russians' fur-trade interests fueled their desire to expand east into Siberia. The Tatar Khanate of Kazan was established by Ulugh Muhammad as the best entryway into Siberia. In 1552, Ivan the Terrible's modernized army toppled the khanate.Lincoln, p. 30 After the takeover of Kazan, the tsar looked to the powerful and affluent Stroganov merchant family to spearhead the eastward expansion. In the late 1570s, the Stroganovs recruited Cossack fighters to invade Asia on behalf of the tsar.Lincoln, p. 40 These Cossacks elected Yermak as the leader of their armed forces, and in 1582 Yermak set out with an army of 840 to attack the Khanate of Sibir.Lincoln, p. 41 On O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataman
Ataman (variants: ''otaman'', ''wataman'', ''vataman''; Russian: атаман, uk, отаман) was a title of Cossack and haidamak leaders of various kinds. In the Russian Empire, the term was the official title of the supreme military commanders of the Cossack armies. The Ukrainian version of the same word is ''hetman''. ''Otaman'' in Ukrainian Cossack forces was a position of a lower rank. Etymology The etymologies of the words ''ataman'' and ''hetman'' are disputed. There may be several independent Germanic and Turkic origins for seemingly cognate forms of the words, all referring to the same concept. The ''hetman'' form cognates with German ''Hauptmann'' ('captain', literally 'head-man') by the way of Czech or Polish, like several other titles. The Russian term ''ataman'' is probably connected to Old East Slavic ''vatamanŭ,'' and cognates with Turkic ''odoman'' (Ottoman Turks). The term ''ataman'' may had also a lingual interaction with Polish ''hetman'' and German ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or , sk, kozáci , uk, козаки́ are a predominantly East Slavic Orthodox Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Ukraine and southern Russia. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic-speaking Orthodox Christians. The Cossacks were particularly noted for holding democratic traditions. The rulers of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |