|
Tyseley TMD
Tyseley TMD is a railway traction maintenance depot situated in Tyseley, Birmingham, England. Origins To counter the critic of the Great Western Railway (GWR) actually standing for ''"The Great Way Round"'', the GWR started a series of straightening projects between London Paddington and its two major hubs of Taunton and Birmingham. It hence sponsored the Birmingham and North Warwickshire Railway to create a more direct route between south Birmingham and Stratford-upon-Avon, which would bypass the existing route via Lapworth, effectively creating the last mainline railway built in the United Kingdom. The line also provided a new service to Henley-in-Arden, rendering redundant the original GWR branch from Rowington Junction to Henley, which consequently closed to passengers in 1915. History GWR: TYS/174 The North Warwickshire Line came into operation from 1908, and the GWR immediately adopted it and ran all services. However, its major depot in the area was at Wolverhampton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyseley Locomotive Works
Tyseley Locomotive Works, formerly the Birmingham Railway Museum, is the engineering arm of steam railtour promoter Vintage Trains based in Birmingham, England. It occupies part of the former Great Western Railway's Tyseley depot, built in 1908 to accommodate expanding operations in the West Midlands, particularly the opening of the North Warwickshire Line as a new main line from Birmingham to Bristol. As well as supporting the trust's operating wing Vintage Trains, it is home to an extensive collection of steam engines, from small industrial builds to Great Western Railway 'Castles' and 'Halls', and large ex-mainline diesel engines. Background Following the purchase of GWR Castle Class No.7029 ''Clun Castle'' in January 1966 by Patrick Whitehouse, the locomotive needed a base close to its central West Midlands supporters' base. Whitehouse found space available at Tyseley, on the site of the former GWR depot, and formed 7029 Clun Castle Ltd to own both the locomotive and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Stage
A coaling tower, coal stage, coaling plant or coaling station is a facility used to load coal as fuel into railway steam locomotives. Coaling towers were often sited at motive power depots or locomotive maintenance shops. In the early years of railways, coal was shovelled by hand into locomotive tenders, the first attempt in Britain to replace manual labour by gravity in the refuelling process being found at Shildon, County Durham, where coal drops were built by the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1847. In time, railway companies constructed more elaborate coaling towers, made from wood, steel, or reinforced concrete (ferroconcrete). In almost all cases coaling stations used a gravity fed method, with one or more large storage bunkers for the coal elevated on columns above the railway tracks, from which the coal could be released to slide down a chute into the waiting locomotive's coal storage area. The method of lifting the bulk coal into the storage bin varied. The coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
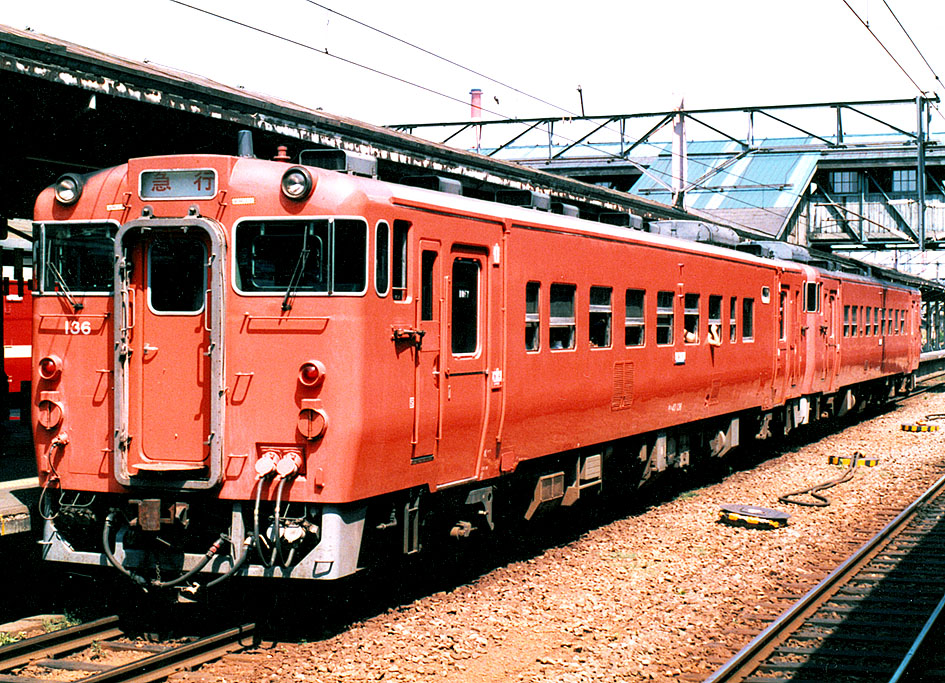
Diesel Multiple Unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are also generally classed as DMUs. Diesel-powered units may be further classified by their transmission type: diesel–mechanical DMMU, diesel–hydraulic DHMU, or diesel–electric DEMU. Design The diesel engine may be located above the frame in an engine bay or under the floor. Driving controls can be at both ends, on one end, or in a separate car. Types by transmission DMUs are usually classified by the method of transmitting motive power to their wheels. Diesel–mechanical In a diesel–mechanical multiple unit (DMMU), the rotating energy of the engine is transmitted via a gearbox and driveshaft directly to the wheels of the train, like a car. The transmissions can be shifted manually by the driver, as in the great majority of first-gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BR Standard Classes
The BR Standard steam locomotives were an effort to standardize locomotives from the motley collection of older pre-grouping locos. Construction started in 1951. Due to the controversial British Railways' modernisation plan of 1955, where steam traction was abandoned in favour of diesel and electric traction, many of the locomotives' working lives were very short: between 7 and 17 years. Many have been preserved, mainly due to their having been sent to Barry Scrapyard. ex-WD Austerity engines The first BR standards were the BR ex-WD Austerity 2-8-0 and BR ex-WD Austerity 2-10-0s. They were given the numbers 90000-732 and 90750-774. They were assigned the boiler types BR10 and BR11, and both had the tender type BR5. Background Robert Riddles put his case for continuing to build steam locomotives in his presidential address to the Institution of Locomotive Engineers in November 1950. He compared capital costs to show that steam was cheaper than the alternatives, though he d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest transport organisation, the company was also the largest commercial enterpri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Country
The West Country (occasionally Westcountry) is a loosely defined area of South West England, usually taken to include all, some, or parts of the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, Bristol, and, less commonly, Wiltshire, Gloucestershire and Herefordshire. "Which counties make up the West Country?", ''YouGov.co.uk'', 23 October 2019 Retrieved 22 June 2021 The West Country has a distinctive regional English dialect and accent, and is also home to the . Extent ...
|
South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards to include Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire. In the western extent, from Swansea westwards, local people would probably recognise that they lived in both south Wales and west Wales. The Brecon Beacons National Park covers about a third of south Wales, containing Pen y Fan, the highest British mountain south of Cadair Idris in Snowdonia. A point of some discussion is whether the first element of the name should be capitalised: 'south Wales' or 'South Wales'. As the name is a geographical expression rather than a specific area with well-defined borders, style guides such as those of the BBC and ''The Guardian'' use the form 'south Wales'. In a more authoritative style guide, the Welsh Government, in their international gateway website, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Temple Meads Railway Station
Bristol Temple Meads is the oldest and largest railway station in Bristol, England. It is located away from London Paddington. It is an important transport hub for public transport in the city; there are bus services to many parts of the city and surrounding districts, with a ferry to the city centre. Bristol's other major station, Bristol Parkway, is a more recent station on the northern outskirts of the conurbation. Temple Meads was opened on 31 August 1840, as the western terminus of the Great Western Railway. The railway, including Temple Meads, was the first to be designed by the British engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel. Soon, the station was also used by the Bristol and Exeter Railway, the Bristol and Gloucester Railway, the Bristol Harbour Railway and the Bristol and South Wales Union Railway. To accommodate the increasing number of trains, the station was expanded in the 1870s by Francis Fox and again between 1930 and 1935 by Percy Emerson Culverhouse. Brunel's termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
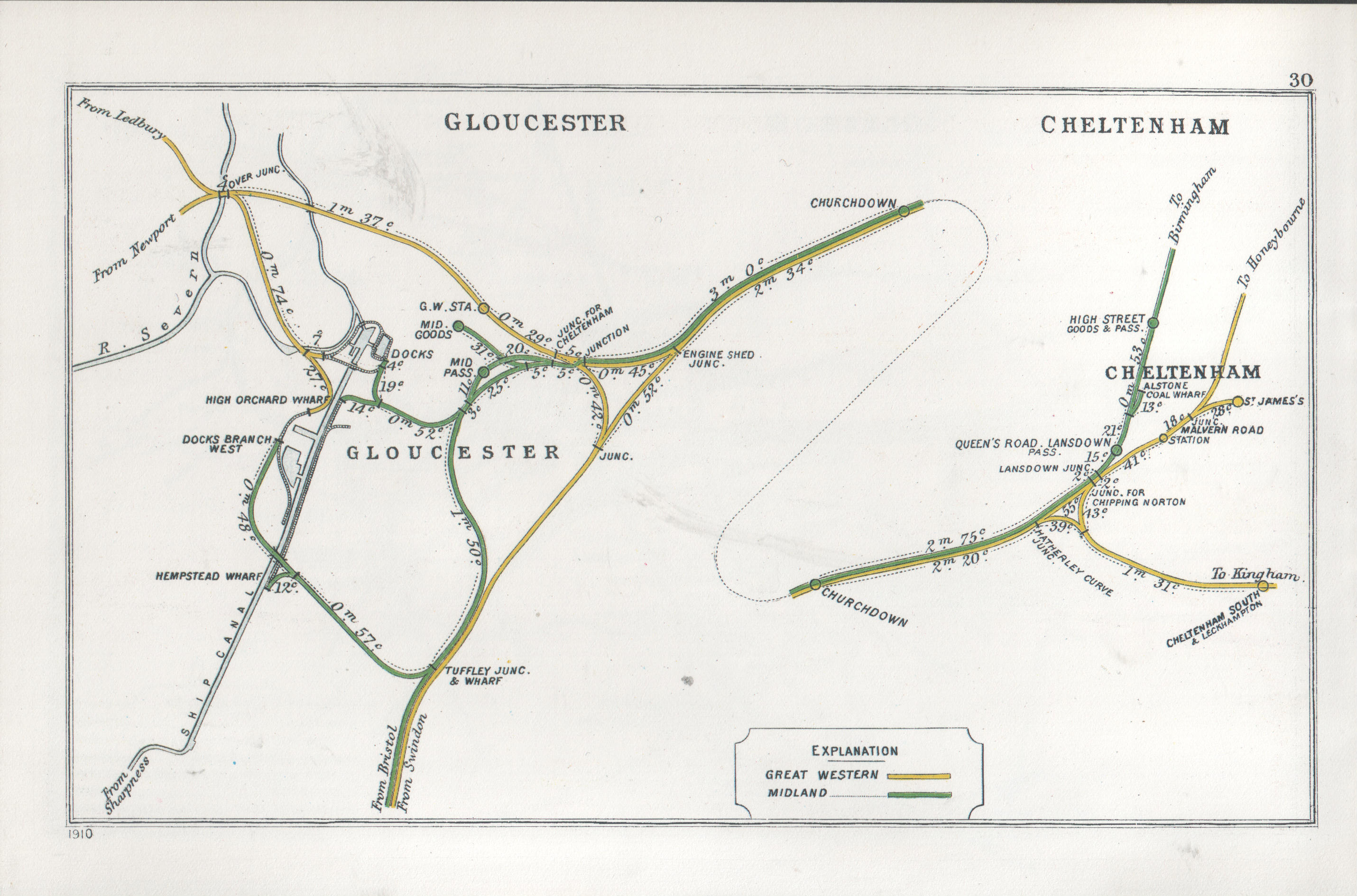
Gloucester Railway Station
Gloucester railway station (formerly known as Gloucester Central station) is a railway station serving the city of Gloucester in England. The station was originally built as the terminus of the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway in 1840, but the arrival of the (broad gauge) Bristol and Gloucester Railway and Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway in 1844, and then conversion to a through station for the South Wales Railway in 1851 resulted in a very complex layout. Subsequent closures and rationalization have left Gloucester with a station that is located off the main Bristol-Birmingham line, meaning Great Western Railway services must reverse, while CrossCountry and Transport for Wales services continue to Newport. History The railway development at Gloucester was very complex involving four different railway companies and five distinct railway stations. The first company to open was the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway, which was a standard gauge line opening 4 Novembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheltenham Spa Railway Station
Cheltenham Spa railway station is a railway station serving Cheltenham in Gloucestershire, England. Situated on the Bristol-Birmingham main line, it is managed by Great Western Railway (despite most services being operated by CrossCountry, which does not manage any stations) and is about one mile from the town centre. The official name of the town is simply ''Cheltenham'', but, when the station was renamed in 1925, the London, Midland and Scottish Railway chose to add ''Spa'' to the station name. The station is a key regional interchange and is the fifth busiest rail station in South West England. History The first railway to Cheltenham was the broad-gauge Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway (C&GWUR), authorised by Act of Parliament in 1836, and opened between Cheltenham and Gloucester in 1840. In the same year, the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway (B&GR) opened its line between Cheltenham and Bromsgrove, whence trains ran on mixed-gauge tracks to Gloucester. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearley Railway Station
Bearley railway station serves the village of Bearley in South Warwickshire, England. It is on the Leamington–Stratford line. Today it is an unstaffed rural halt, managed by West Midlands Railway. Bearley was once a junction station (a branch line to Alcester met the Stratford-upon-Avon to Hatton line here). The station dates from 1860, when it opened as part of the Stratford on Avon Railway's Hatton to Stratford branch line - the Alcester branch was added in 1876, but this closed in 1951. Originally a single track station, the line was doubled in 1939 and a second platform built; it reverted to its current status in 1969 when the line was reduced to single track once more. Facilities Bearley station is unstaffed. Tickets must be purchased from the senior conductor or train manager on the train. There is a small parking area available by the station entrance. Parking is free for rail users. Step free access is available between the entrance and the platform. Servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)