|
Typhoon Dot (1989)
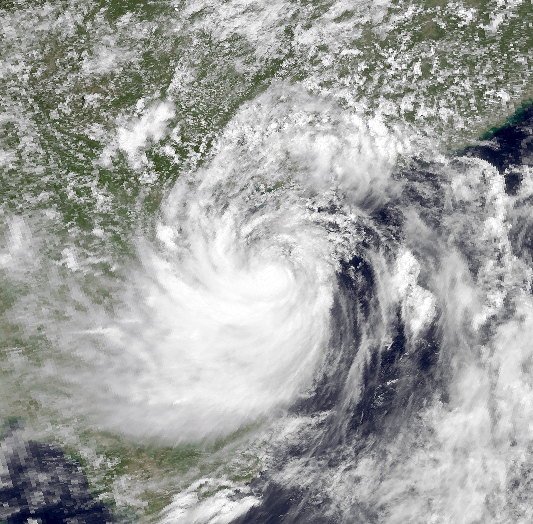
Typhoon Dot, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Kuring, was one of several tropical cyclones to impact southern China and northern Vietnam during the 1989 Pacific typhoon season. Originating from a tropical disturbance near Palau on June 4, Dot tracked west-northwestward towards the Philippines. Crossing the country on June 6, the system moved over the South China Sea and attained typhoon status. Late on June 8, Dot reached its peak intensity with winds estimated at . The system weakened slightly the next day before making landfall in Hainan Island. A weakened storm then entered the Gulf of Tonkin before striking northern Vietnam and dissipating on June 12. Throughout its course, Typhoon Dot produced heavy rains in the Philippines, China and Vietnam, resulting in significant damage and eight fatalities. The most severe impacts took place on Hainan Island where 1,400 homes were destroyed and another 60,000 were damaged. In Vietnam, Dot exacerbated flood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hainan Island
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly larger, is claimed but not controlled by the PRC. It is instead controlled by the Republic of China, a ''de facto'' separate country. makes up the vast majority (97%) of the province. The name means "south of the sea", reflecting the island's position south of the Qiongzhou Strait, which separates it from Leizhou Peninsula. The province has a land area of , of which Hainan the island is and the rest is over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos: Zhongsha, Xisha and Nansha. It was part of Guangdong from 1950–88, after which it resumed as a top-tier entity and almost immediately made the largest Special Economic Zone by Deng Xiaoping as part of the then-ongoing Chinese economic reform program. Indigenous peoples like the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samar Island
Samar ( ) is the third-largest and seventh-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 1,909,537 as of the 2020 census. It is located in the eastern Visayas, which are in the central Philippines. The island is divided into three provinces: Samar (formerly Western Samar), Northern Samar, and Eastern Samar. These three provinces, along with the provinces on the nearby islands of Leyte and Biliran, are part of the Eastern Visayas region. About a third of the island of Samar is protected as a natural park, known as the Samar Island Natural Park. On June 19, 1965, through Republic Act No. 4221, Samar was divided into three provinces: Northern Samar, (Western) Samar and Eastern Samar. The capitals of these provinces are, respectively, Catarman, Catbalogan City, and Borongan City. In commemoration of the establishment of these provinces, June 19 is celebrated as an annual holiday and many have the day off from work. Geography Samar is the third-lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanya
Sanya (; also spelled Samah) is the southernmost city on Hainan Island, and one of the four prefecture-level cities of Hainan Province in South China. According to the 2020 census, the total population of Sanya was 1,031,396 inhabitants, living in an area of . Nevertheless, its built-up (or metro) area encompassing Haitang and Jiyang Districts was home to 801,020 inhabitants as of 2020. The city is renowned for its tropical climate and has emerged as a popular tourist destination, also serving as the training site of the Chinese national beach volleyball team. Sanya is home to small concentrations of Utsul people. Sanya is also the location of Yulin Naval Base, a major military facility on the South China Sea which is home to the People's Liberation Army Navy ballistic nuclear missile fleet. History Known in ancient times as Yazhou, postal romanization: Aichow (), literally "cliff state or prefecture", Sanya's history dates to the Qin Dynasty (221–206 BCE). Due to its r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inches Of Mercury
Inch of mercury (inHg and ″Hg) is a non- SI unit of measurement for pressure. It is used for barometric pressure in weather reports, refrigeration and aviation in the United States. It is the pressure exerted by a column of mercury in height at the standard acceleration of gravity. Conversion to metric units depends on the temperature of mercury, and hence its density; typical conversion factors are: In older literature, an "inch of mercury" is based on the height of a column of mercury at .Barry N. Taylor, ''Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI),'' 1995, NIST Special Publication 811, Appendix /ref> :1 inHg60 °F = In Imperial units: 1 inHg60 °F = 0.489 771 Pounds per square inch, psi, or 2.041 771 inHg60 °F = 1 psi. Applications Aircraft and automobiles Aircraft altimeters measure the relative pressure difference between the lower ambient pressure at altitude and a calibrated reading on the ground. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (unit)
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI), and is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is defined as one newton per square metre and is equivalent to 10 barye (Ba) in the CGS system. The unit of measurement called standard atmosphere (atm) is defined as 101,325 Pa. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Canada these reports are given in kilopascal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar (unit)
The bar is a metric unit of pressure, but not part of the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as exactly equal to 100,000 Pa (100 kPa), or slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level (approximately 1.013 bar). By the barometric formula, 1 bar is roughly the atmospheric pressure on Earth at an altitude of 111 metres at 15 °C. The bar and the millibar were introduced by the Norwegian meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes, who was a founder of the modern practice of weather forecasting. The International System of Units, despite previously mentioning the bar, now omits any mention of it.. The bar has been legally recognised in countries of the European Union since 2004.British Standard BS 350:2004 ''Conversion Factors for Units''. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) deprecates its use except for "limited use in meteorology" and lists it as one of several units that "must not be introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Sustained Wind
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are determined via their sampling and averaging the sampled results over a period of time. Wind measuring has been standardized globally to reflect the winds at above the Earth's surface, and the maximum sustained wind represents the highest average wind over either a one-minute (US) or ten-minute time span (see the definition, below), anywhere within the tropical cyclone. Surface winds are highly variable due to friction between the atmosphere and the Earth's surface, as well as near hills and mountains over land. Over the ocean, satellite imagery determines the value of the maximum sustained winds within a tropical cyclone. Land, ship, aircraft reconnaissance observations, and radar imagery can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category 3 Hurricane
Category, plural categories, may refer to: Philosophy and general uses *Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally *Category of being * ''Categories'' (Aristotle) *Category (Kant) *Categories (Peirce) *Category (Vaisheshika) *Stoic categories *Category mistake Mathematics * Category (mathematics), a structure consisting of objects and arrows * Category (topology), in the context of Baire spaces * Lusternik–Schnirelmann category, sometimes called ''LS-category'' or simply ''category'' * Categorical data, in statistics Linguistics * Lexical category, a part of speech such as ''noun'', ''preposition'', etc. *Syntactic category, a similar concept which can also include phrasal categories *Grammatical category, a grammatical feature such as ''tense'', ''gender'', etc. Other * Category (chess tournament) * Objective-C categories, a computer programming concept * Pregnancy category * Prisoner security categories in the United Kingdom * W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weather and highest winds occur. The cyclone's lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye and can be as much as 15 percent lower than the pressure outside the storm. In strong tropical cyclones, the eye is characterized by light winds and clear skies, surrounded on all sides by a towering, symmetric eyewall. In weaker tropical cyclones, the eye is less well defined and can be covered by the central dense overcast, an area of high, thick clouds that show up brightly on satellite imagery. Weaker or disorganized storms may also feature an eyewall that does not completely encircle the eye or have an eye that features heavy rain. In all storms, however, the eye is the location of the storm's minimum barometric pressure—where the atmospheric pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on the control of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |