|
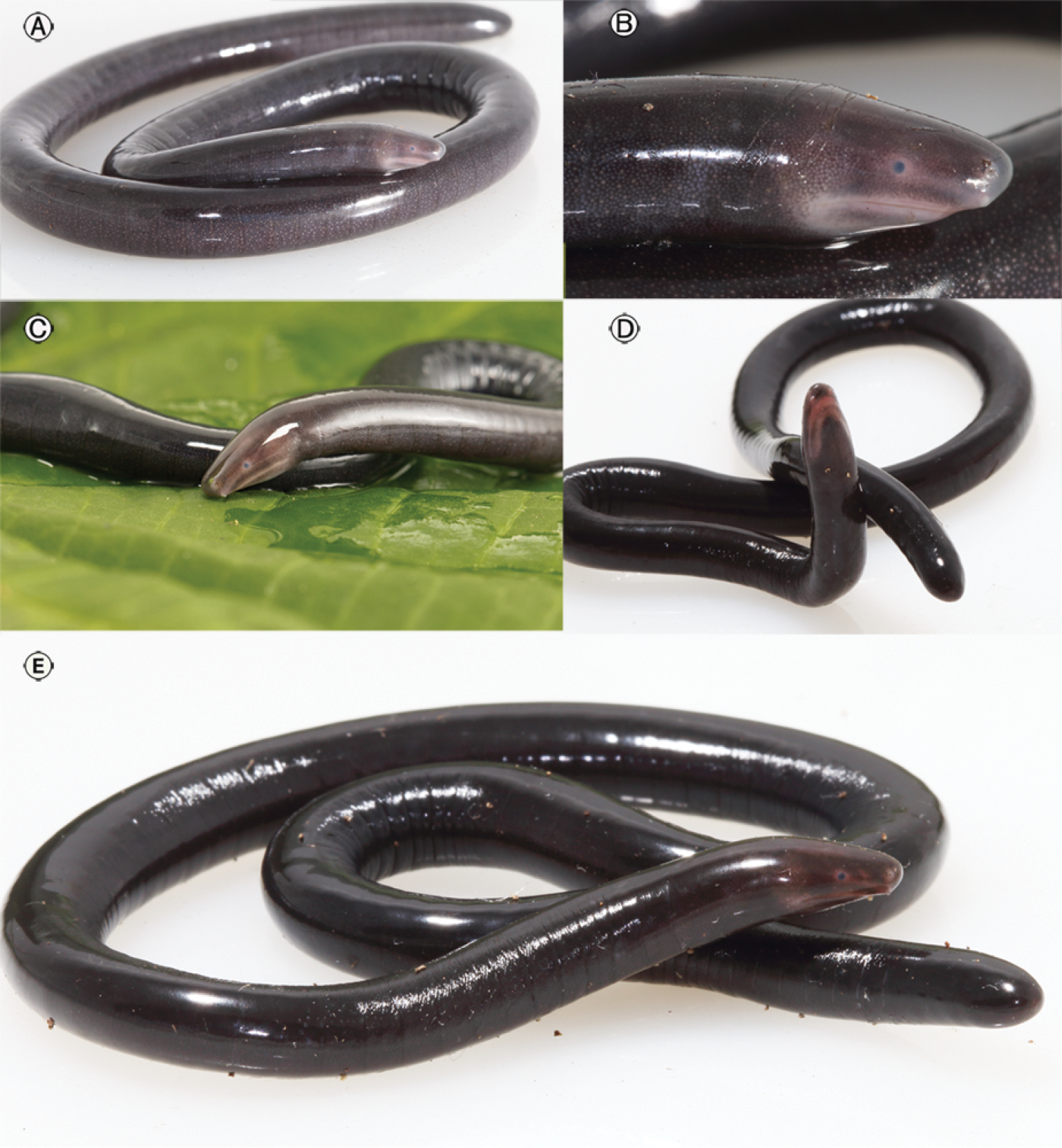
Typhlonectes
''Typhlonectes'' (from el, τῠφλός , 'blind' and el, νηκτῆς , 'swimmer') is a genus of caecilians in the family Typhlonectidae. These fully aquatic amphibians are found in the Amazon Basin and Northern South America, and typically range between in length.Vitt, L.J.; and Caldwell, J.P. (2013). ''Herpetology, Fourth Edition: An Introductory Biology of Amphibians and Reptiles'', p. 453. The genus contains two species: * ''Typhlonectes compressicauda'' (''Typhlonectes cunhai'') * ''Typhlonectes natans ''Typhlonectes natans'', also incorrectly called the rubber eel, is a species of caecilian in the family Typhlonectidae found in Colombia, Venezuela, and possibly Trinidad and Tobago. Its natural habitats are dry savanna, subtropical or tropical ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1992604 Amphibian genera Taxonomy articles created by Polbot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhlonectes Compressicauda
''Typhlonectes compressicauda'', the Cayenne caecilian, is a species of amphibian in the family Typhlonectidae that lives in water. It is found in Amazonian Brazil, Peru, and Colombia as well as in Guyana and French Guiana, and likely Suriname, and according to some sources, Venezuela. It is an aquatic caecilian that inhabits permanent rivers and marshes mainly in the lowland forest zone. Description The Cayenne caecilian is an elongated, dark grey, black or steely blue amphibian with no limbs. The body is flattened laterally and has a number of transverse folds, giving it a segmented appearance. A long fin runs along its back, and it grows to a length of . It has a more highly derived morphology than some more primitive species, showing differences in lung structure, the reproductive organs, and the kidneys. Distribution The Cayenne caecilian occurs in South America, including the Amazon basin and river systems in the Guianas. It is found at altitudes of up to above sea level. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhlonectes Cunhai
''Typhlonectes compressicauda'', the Cayenne caecilian, is a species of amphibian in the family Typhlonectidae that lives in water. It is found in Amazonian Brazil, Peru, and Colombia as well as in Guyana and French Guiana, and likely Suriname, and according to some sources, Venezuela. It is an aquatic caecilian that inhabits permanent rivers and marshes mainly in the lowland forest zone. Description The Cayenne caecilian is an elongated, dark grey, black or steely blue amphibian with no limbs. The body is flattened laterally and has a number of transverse folds, giving it a segmented appearance. A long fin runs along its back, and it grows to a length of . It has a more highly derived morphology than some more primitive species, showing differences in lung structure, the reproductive organs, and the kidneys. Distribution The Cayenne caecilian occurs in South America, including the Amazon basin and river systems in the Guianas. It is found at altitudes of up to above sea level. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhlonectes Natans
''Typhlonectes natans'', also incorrectly called the rubber eel, is a species of caecilian in the family Typhlonectidae found in Colombia, Venezuela, and possibly Trinidad and Tobago. Its natural habitats are dry savanna, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, subtropical or tropical seasonally wet or flooded lowland grassland, and rivers. The ''T. natans'' is commonly kept as an aquarium pet, and is sometimes sold as a "fish" in aquarium stores. A specimen of ''T. natans'' was found in October 2019 in Miami-Dade County, Florida, making it the first caecilian to be collected in North America. They grow to in length. They are dark grey to black in color. While ''T. natans'' can and occasionally does breathe air at the surface, most of its respiration takes place through its skin. The species is ovoviviparous Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhlonectes
''Typhlonectes'' (from el, τῠφλός , 'blind' and el, νηκτῆς , 'swimmer') is a genus of caecilians in the family Typhlonectidae. These fully aquatic amphibians are found in the Amazon Basin and Northern South America, and typically range between in length.Vitt, L.J.; and Caldwell, J.P. (2013). ''Herpetology, Fourth Edition: An Introductory Biology of Amphibians and Reptiles'', p. 453. The genus contains two species: * ''Typhlonectes compressicauda'' (''Typhlonectes cunhai'') * ''Typhlonectes natans ''Typhlonectes natans'', also incorrectly called the rubber eel, is a species of caecilian in the family Typhlonectidae found in Colombia, Venezuela, and possibly Trinidad and Tobago. Its natural habitats are dry savanna, subtropical or tropical ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1992604 Amphibian genera Taxonomy articles created by Polbot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhlonectidae
Typhlonectidae, also known as aquatic caecilians or rubber eels, are a family of caecilians found east of the Andes in South America. They are viviparous animals, giving birth to young that possess external gills. Of the five genera in the family, ''Atretochoana'', ''Potamotyphlus'' and ''Typhlonectes'' are entirely aquatic, while ''Chthonerpeton'' and ''Nectocaecilia'' are semiaquatic. ''Atretochoana'' reaches in length, but other species in the family range from . Taxonomy *Genus ''Atretochoana'' **''Atretochoana eiselti'' *Genus ''Chthonerpeton'' **''Chthonerpeton arii'' **''Chthonerpeton braestrupi'' **''Chthonerpeton exile'' **''Chthonerpeton indistinctum'' **''Chthonerpeton noctinectes'' **''Chthonerpeton onorei'' **''Chthonerpeton perissodus'' **''Chthonerpeton viviparum'' *Genus ''Nectocaecilia'' **''Nectocaecilia petersii'' *Genus ''Potamotyphlus'' **''Potamotyphlus kaupii'' *Genus ''Typhlonectes'' **''Typhlonectes compressicauda'' **''Typhlonectes natans ''Typhlon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform or serpentine amphibians. They mostly live hidden in the ground and in stream substrates, making them the least familiar order of amphibians. Caecilians are mostly distributed in the tropics of South and Central America, Africa, and southern Asia. Their diet consists of small subterranean creatures such as earthworms. All modern caecilians and their closest fossil relatives are grouped as a clade, Apoda , within the larger group Gymnophiona , which also includes more primitive extinct caecilian-like amphibians. The name derives from the Greek words γυμνος (''gymnos'', naked) and οφις (''ophis'', snake), as the caecilians were originally thought to be related to snakes. The body is cylindrical dark brown or bluish black in colour. The skin is slimy and bears grooves or ringlike markings. Description Caecilians completely lack limbs, making the smaller species resemble worms, while the larger species, with lengths up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial animal, terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian Genera
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
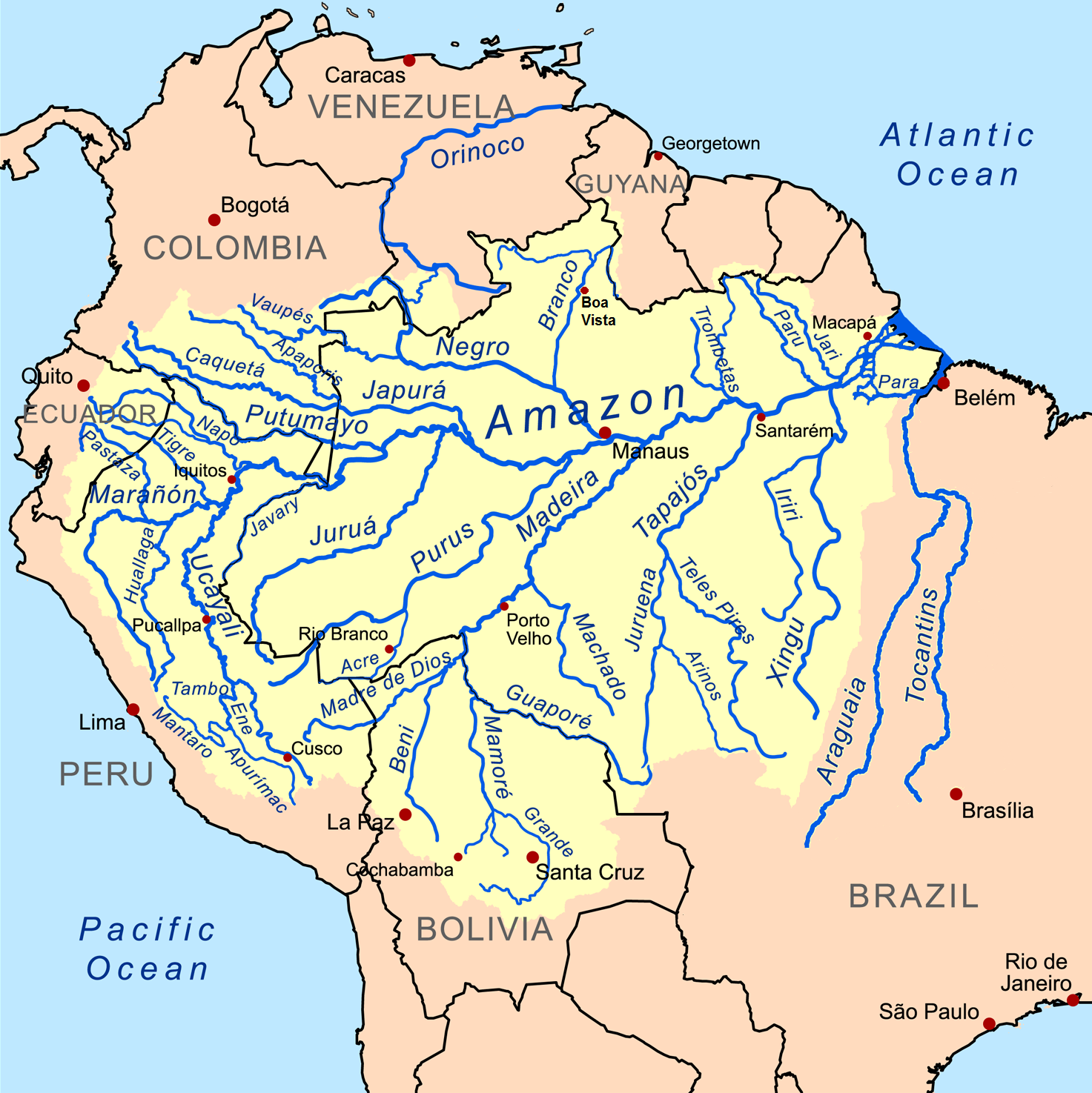
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)