|
Twin Clutch SST
Twin Clutch SST (Sport- or Sportronic Shift Transmission) is the brand name of a six-speed dual-clutch automatic transmission, developed by Getrag for Mitsubishi Motors."SS-T: The Magic Inside the Evo X" ''The Motor Report'', April 14, 2008 The system was first incorporated in the 2008 Lancer Evolution X, and was designed to be a more performance-oriented system than that developed by rival manufacturers,"Technical A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brand Name
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create and store value as brand equity for the object identified, to the benefit of the brand's customers, its owners and shareholders. Brand names are sometimes distinguished from Generic brand, generic or store brands. The practice of branding - in the original literal sense of marking by burning - is thought to have begun with the ancient Egyptians, who are known to have engaged in livestock branding as early as 2,700 BCE. Branding was used to differentiate one person's cattle from another's by means of a distinctive symbol burned into the animal's skin with a hot branding iron. If a person stole any of the cattle, anyone else who saw the symbol could deduce the actual owner. The term has been extended to mean a strategic personality for a produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-AWC
S-AWC (Super All Wheel Control) is the brand name of an advanced full-time four-wheel drive system developed by Mitsubishi Motors. The technology, specifically developed for the new 2007 Lancer Evolution,"Mitsubishi Motors develops S-AWC vehicle dynamics control system" , Mitsubishi Motors press release, July 10, 2007 the 2010 Outlander (if equipped), the 2014 Outlander (if equipped), the Outlander PHEV and the Eclipse Cross have an advanced version of Mitsubishi Motors' AWC system."All Wheel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
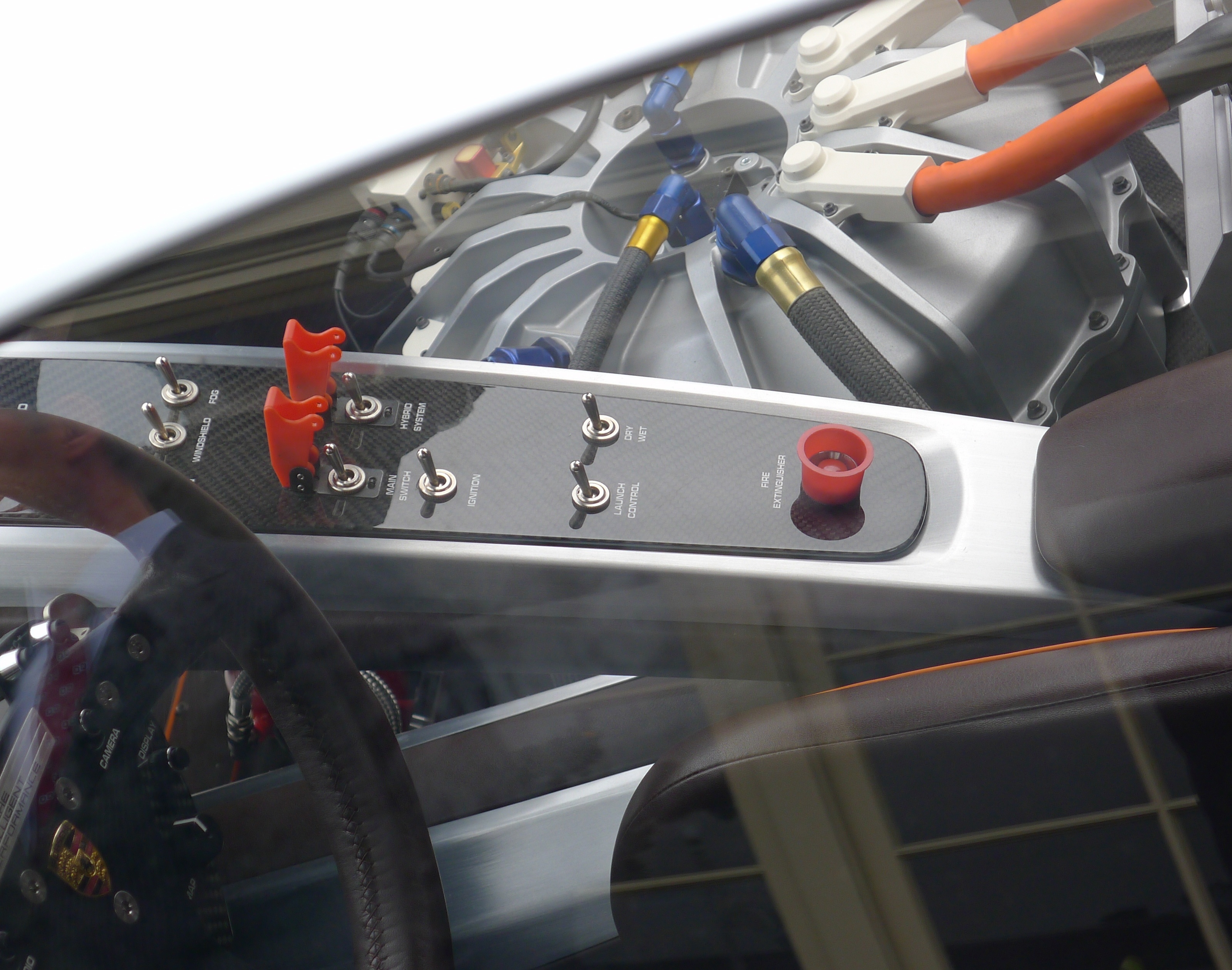
Launch Control (automotive)
Launch control is an electronic aid to assist drivers of both racing and street cars to accelerate from a standing start. Motorcycles have been variously fitted with mechanical and electronic devices for both street and race. Popular automobiles with launch control include the BMW M series, certain marques of the Volkswagen Group with Direct-Shift Gearbox (most notably the Bugatti Veyron), Porsche 911 (sport+ mode), Panamera Turbo, Alfa Romeo with TCT gearbox and certain General Motors products. Mitsubishi also incorporated launch control into their Twin Clutch SST gearbox, on its "S-Sport" mode, but the mode is only available in the Evolution X MR and MR Touring (USDM). The Jaguar F-Type includes launch control. The Nissan GT-R has electronics to control launch but the company does not use the term "launch control" since some owners have equated the term with turning off the stability control to launch the car, which may void the warranty of the drivetrain. One version of Nissa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Braking
Engine braking occurs when the retarding forces within an engine are used to slow down a motor vehicle, as opposed to using additional external braking mechanisms such as friction brakes or magnetic brakes. The term is often confused with several other types of braking, most notably compression-release braking or "jake braking" which uses a different mechanism. Traffic regulations in many countries require trucks to always drive with an engaged gear, which in turn provides a certain amount of engine braking (viscous losses to the engine oil and air pumped through the engine and friction losses to the cylinder walls and bearings) when no accelerator pedal is applied. Type Gasoline engines The term "engine braking" refers to the braking effect that occurs in gasoline engines when the accelerator pedal is released. This causes fuel injection to cease and the throttle valve to close almost completely, greatly restricting forced airflow from, for example, a turbocharger. The rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiator
Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics. A radiator is always a source of heat to its environment, although this may be for either the purpose of heating this environment, or for cooling the fluid or coolant supplied to it, as for automotive engine cooling and HVAC dry cooling towers. Despite the name, most radiators transfer the bulk of their heat via convection instead of thermal radiation. History The Roman hypocaust is an early example of a type of radiator for building space heating. Franz San Galli, a Prussian-born Russian businessman living in St. Petersburg, is credited with inventing the heating radiator around 1855, having received a radiator patent in 1857, but American Joseph Nason developed a primitive radiator in 1841 and received a number of U.S. patents for hot water and steam heating. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
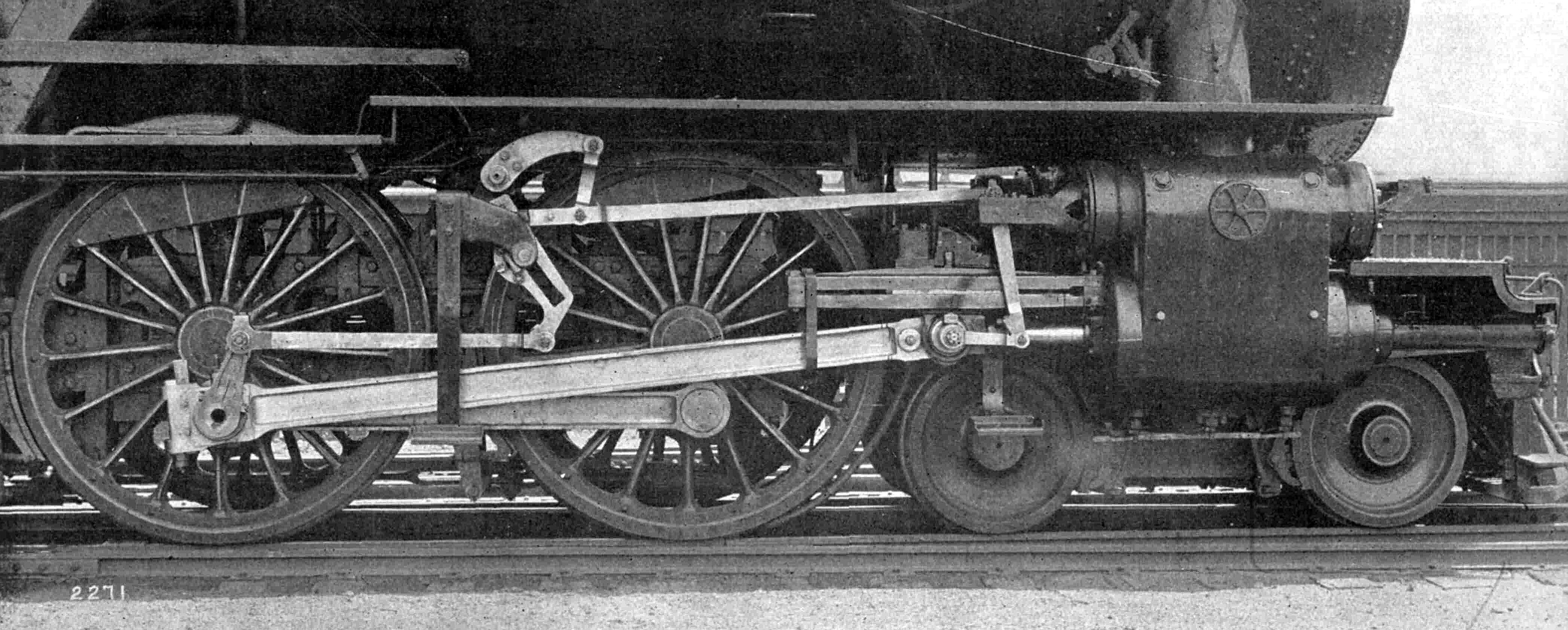
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solenoids
upright=1.20, An illustration of a solenoid upright=1.20, Magnetic field created by a seven-loop solenoid (cross-sectional view) described using field lines A solenoid () is a type of electromagnet formed by a helix, helical coil of wire whose length is substantially greater than its diameter, which generates a controlled magnetic field. The coil can produce a uniform magnetic field in a volume of space when an electric current is passed through it. The term ''solenoid'' was coined in 1823 by André-Marie Ampère. The helical coil of a solenoid does not necessarily need to revolve around a straight-line axis; for example, William Sturgeon's electromagnet of 1824 consisted of a solenoid bent into a horseshoe shape (not unlike an arc spring). Solenoids provide magnetic focusing of electrons in vacuums, notably in television camera tubes such as vidicons and image orthicons. Electrons take helical paths within the magnetic field. These solenoids, focus coils, surround nearly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
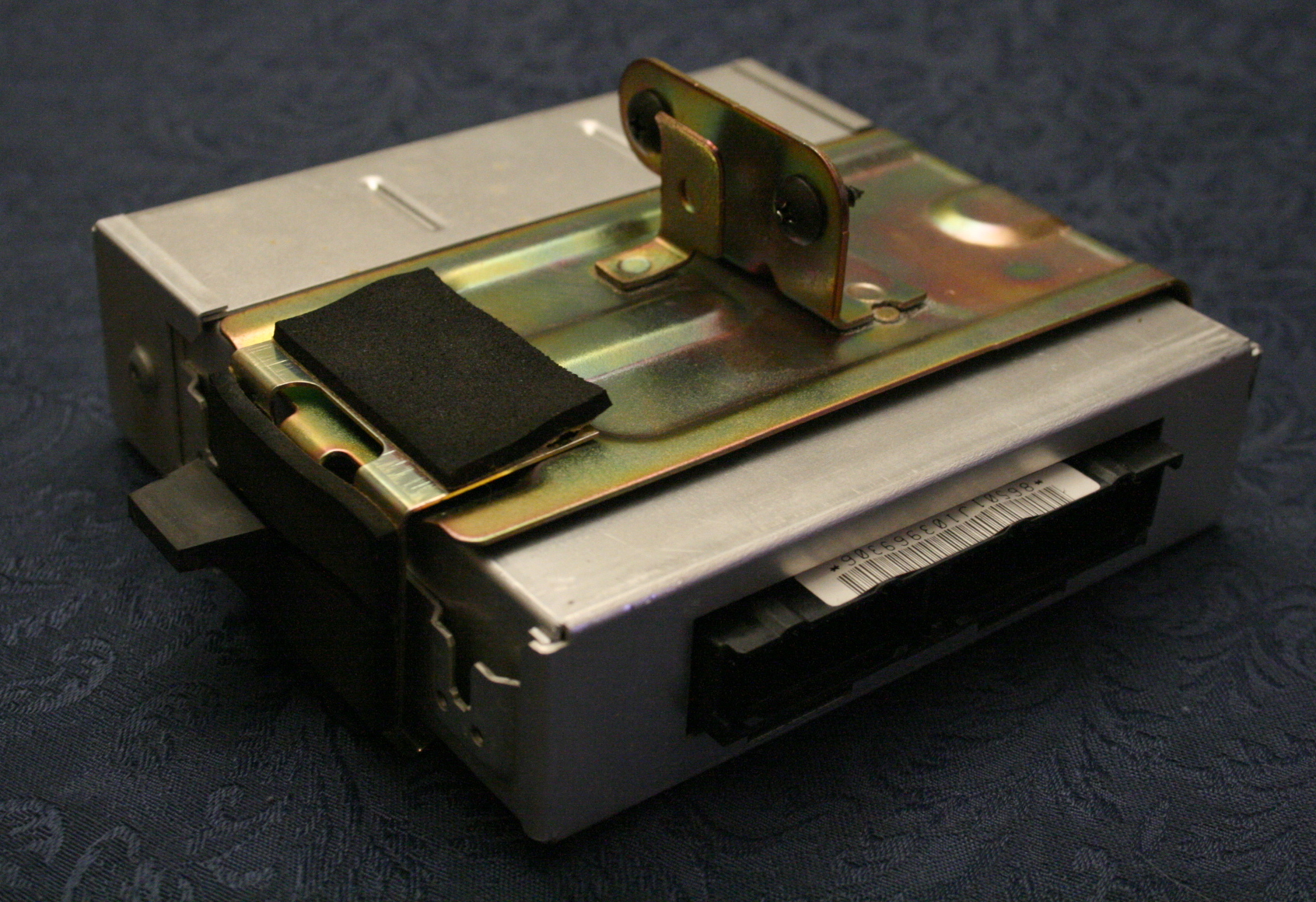
Electronic Control Unit
An electronic control unit (ECU), also known as an electronic control module (ECM), is an embedded system in automotive electronics that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a car or other motor vehicle. Modern vehicles have many ECUs, and these can include some or all of the following: engine control module (ECM), powertrain control module (PCM), transmission control module (TCM), brake control module (BCM or EBCM), central control module (CCM), central timing module (CTM), general electronic module (GEM), body control module (BCM), and suspension control module (SCM). These ECUs together are sometimes referred to collectively as the car's computer though technically they are all separate computers, not a single one. Sometimes an assembly incorporates several individual control modules (a PCM often controls both the engine and the transmission). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Case
A transfer case is a part of the drivetrain of four-wheel-drive, all-wheel-drive, and other multiple powered axle vehicles. The transfer case transfers power from the transmission to the front and rear axles by means of drive shafts. It also synchronizes the difference between the rotation of the front and rear wheels, and may contain one or more sets of low range gears for off-road use. Functions * The transfer case receives power from the transmission and sends it to both the front and rear axles, or just one (usually the rear.) This can be done with gears, hydraulics, or chain drive. On some vehicles, such as four-wheel-drive trucks or vehicles intended for off-road use, this feature is controlled by the driver. The driver can put the transfer case into either "two-wheel-drive" or "four-wheel-drive" mode. This is sometimes accomplished by means of a shifter, similar to that in a manual transmission. On some vehicles, this may be electronically operated by a switch inste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocar (magazine)
''Autocar'' (originally ''The Autocar'') is a weekly British automobile magazine published by the Haymarket Media Group. It was first published in 1895 and refers to itself as "the world's oldest car magazine". There are now several international editions, including for China, India, New Zealand, and South Africa. History The publication was launched as ''The Autocar'' by Iliffe and Son Ltd. "in the interests of the mechanically propelled road carriage" on 2 November 1895 when, it is believed, there were only six or seven cars in the United Kingdom. L. J. K. Setright suggests that the magazine was set up by Henry Sturmey as an organ of propaganda for Harry J. Lawson, founder of the Daimler Company and a journalist on the magazine in its early days. Henry Sturmey stood down as editor of ''The Autocar'' magazine and left the company in 1901. ''Autocar'' claims to have invented the road test in 1928 when it analysed the Austin 7 Gordon England Sunshine Saloon. ''Aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stick Shift
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear changes require the driver to manually select the gears by operating a gear stick and clutch (which is usually a foot pedal for cars or a hand lever for motorcycles). Early automobiles used ''sliding-mesh'' manual transmissions with up to three forward gear ratios. Since the 1950s, ''constant-mesh'' manual transmissions have become increasingly commonplace and the number of forward ratios has increased to 5-speed and 6-speed manual transmissions for current vehicles. The alternative to a manual transmission is an automatic transmission; common types of automatic transmissions are the hydraulic automatic transmission (AT), and the continuously variable transmission (CVT), whereas the automated manual transmission (AMT) and dual-clutch transmissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)