|
Trois-Fontaines
Trois-Fontaines Abbey (french: Abbaye de Sainte-Marie des Trois-Fontaines)literally "three fountains"; cf the Trappist abbey of Saints Vincent and Anastasius, near Rome, which is also called the "Abbey of Three Fountains" (''Abbazia delle Tre Fontane'' or ''Trium Fontium ad Aquas Salvias''): se''Catholic Encyclopedia'': "Abbey of Saints Vincent and Anastasius"/ref> was a Cistercian abbey in the present commune of Trois-Fontaines-l'Abbaye in the French department of Marne, in the historic province of Champagne. History It was the first daughter-house founded by Clairvaux Abbey, one of the four Cistercian primary abbeys, and was established north of the head of navigation of the Marne at Saint-Dizier by Bernard of Clairvaux in 1118, on isolated woodland given by Hugh de Vitry, which the monks drained. It was a large community, comprising at its height some 130 monks. The abbey was very active in its first century or so in the settlement of daughter houses: * Lachalade Abbey (112 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trois-Fontaines Ene
Trois-Fontaines Abbey (french: Abbaye de Sainte-Marie des Trois-Fontaines)literally "three fountains"; cf the Trappist abbey of Saints Vincent and Anastasius, near Rome, which is also called the "Abbey of Three Fountains" (''Abbazia delle Tre Fontane'' or ''Trium Fontium ad Aquas Salvias''): se''Catholic Encyclopedia'': "Abbey of Saints Vincent and Anastasius"/ref> was a Cistercian abbey in the present commune of Trois-Fontaines-l'Abbaye in the French department of Marne, in the historic province of Champagne. History It was the first daughter-house founded by Clairvaux Abbey, one of the four Cistercian primary abbeys, and was established north of the head of navigation of the Marne at Saint-Dizier by Bernard of Clairvaux in 1118, on isolated woodland given by Hugh de Vitry, which the monks drained. It was a large community, comprising at its height some 130 monks. The abbey was very active in its first century or so in the settlement of daughter houses: * Lachalade Abbey (1127) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberic Of Trois-Fontaines
Alberic of Trois-Fontaines (french: Aubri or ''Aubry de Trois-Fontaines''; la, Albericus Trium Fontium) (died 1252) was a medieval Cistercian chronicler who wrote in Latin. He was a monk of Trois-Fontaines Abbey in the diocese of Châlons-sur-Marne. He died after 1252. He wrote a chronicle describing world events from the Creation to the year 1241. Life and works Alberic was likely from a noble Liège family which could afford a good education for him. He became a monk of Trois-Fontaines Abbey no later than 1230. In 1232 Alberic began his chronicle ''Chronica Albrici Monachi Trium Fontium'' and continued working on it at least until 1251 since he used a history by Gilles of Orval ''Gesta episcoporum Leodiensium'' ("Deeds of the Bishops of Liège"). His sources also included the universal chronicle of Sigebert of Gembloux and Books 45-49 of Helinand of Froidmont's ''Chronicon''. Alberic's chronicle describes world events from the Creation and contains original writing st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trois-Fontaines-l'Abbaye
Trois-Fontaines-l'Abbaye () is a commune in the northeastern French department of Marne. See also *Communes of the Marne department The following is a list of the 613 communes in the French department of Marne. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Troisfontaineslabbaye {{Marne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Guérin De Tencin
Pierre-Paul Guérin de Tencin (Grenoble, 22 August 1679 – 2 March 1758), French ecclesiastic, was archbishop of Embrun and Lyon, and a cardinal. His sister was Claudine Guérin de Tencin. Biography After studying with the Oratorians in his native Grenoble, he entered the Sorbonne, where he became prior in 1702, and obtained the doctorate in 1705. He was then appointed Vicar-General of the diocese of Sens and, in 1721, accompanied Cardinal de Rohan to Rome as his conclavist, to support the candidacy of Cardinal Conti (Innocent XIII), from whom he had obtained a promise to bestow the purple on the French minister Guillaume Dubois. He remained at Rome as French ''chargé d'affaires'', with the appointment '' in commendam'' of abbot of Trois-Fontaines to support him (1739–1753), until Benedict XIII, with whom he was on cordial terms of intimacy and very influential, consecrated him Archbishop of Embrun (26 June 1724). On 22 February 1739, Guérin de Tencin was created ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Of Pecorara
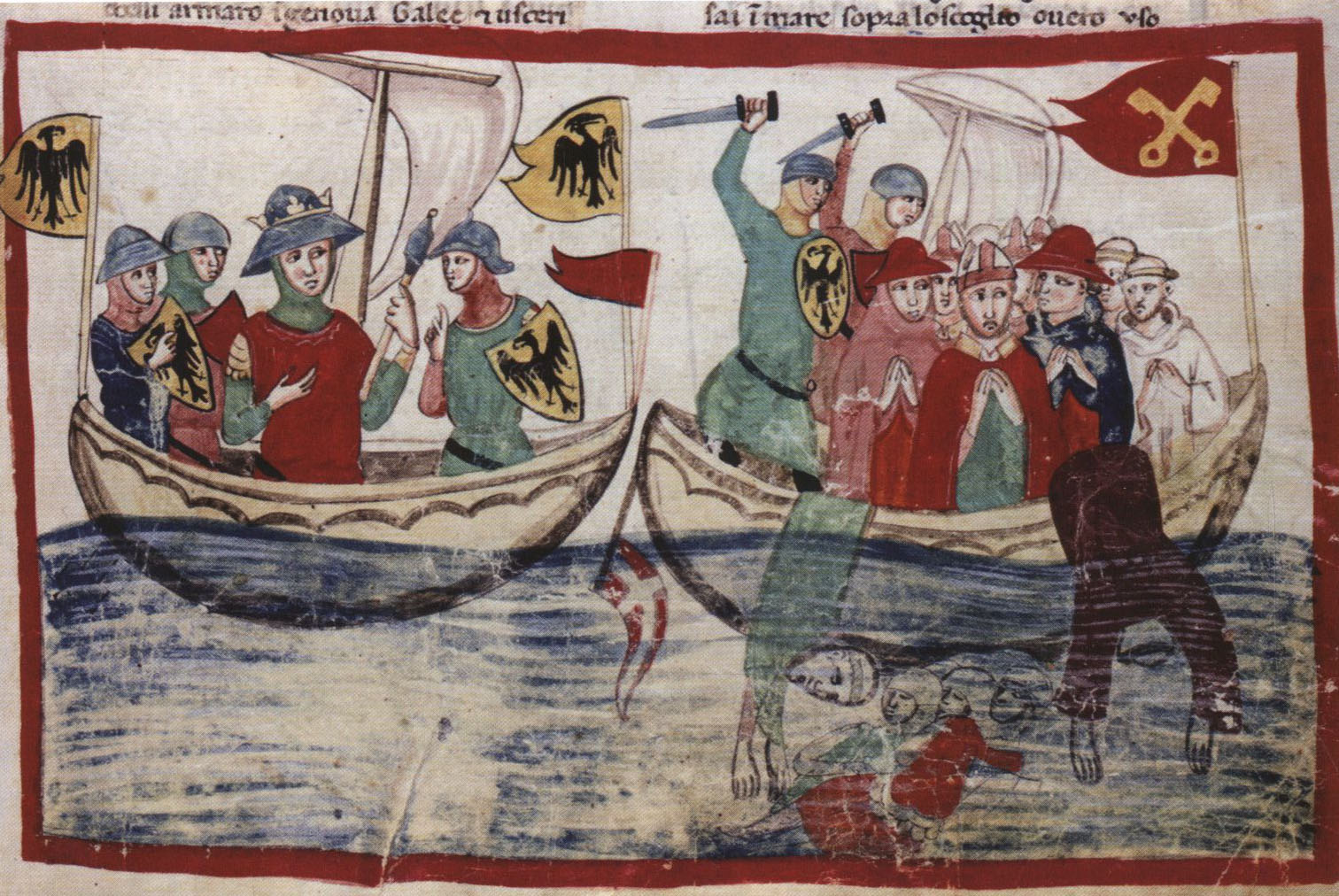
James of Pecorara or Giacomo da Pecorara (1170s – June 1244) was an Italian monk, Catholic cardinal, cardinal and diplomat. James was a cleric in the Archdiocese of Ravenna, church of Ravenna before he joined the Cistercians in 1215, becoming abbot of Trois-Fontaines in France in 1223. Cardinals created by Gregory IX, Created a cardinal by Pope Gregory IX in 1231 and given the Cardinal-bishop of Palestrina, diocese of Palestrina, he served as a papal legate in Lombardy (1232), Kingdom of Hungary (1000–1301), Hungary (1232–1234), March of Tuscany, Tuscany (1235), Lombardy a second time (1236–1237) and France (1239–1241). He was the Cardinal Vicar, vicar of the city of Rome on two occasions (1238–1239, 1243–1244). He was captured by the emperor and imprisoned for two years on account of his efforts towards an anti-imperial alliance (1241–1243). Early life James was born between 1170 and 1180. His father was Torniello of Pecorara. His family took its name, ''de Pecora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthiers-en-Argonne Abbey
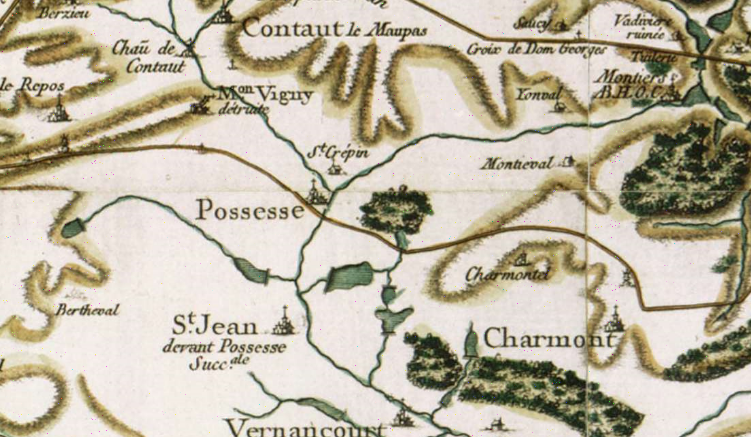
The Abbey of Monthiers-en-Argonne (also spelled Montiers-en-Argonne, from Latin ''Monasterium in Argona'', "monastery in the Argonne") was a Cistercian monastery located in Possesse in the diocese of Châlons-sur-Marne in the County of Champagne. A daughter house of Trois-Fontaines and of the lineage of Clairvaux, it was dedicated to Saints Nicholas and Mary (Notre-Dame). According to Leopold Janauschek, its order number was 194. It was founded at the site called "Vieux Montiers" (Old Monastery) by its first abbot, Eustache, around 1135. Originally a house of Augustinian canons, it adopted the Cistercian rule on 30 May 1144. The monastery was moved to its final location, where its ruins are still found, around 1155. Eustache was assisted by a co-abbot, Gervais, and together they greatly expanded the abbey's temporalities. Towards the end of the century, the abbey was embroiled in controversy over land with the lords of Possesse and Dampierre-en-Astenois, especially Lord Renard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clairvaux Abbey
Clairvaux Abbey (, ; la, Clara Vallis) was a Cistercian monastery in Ville-sous-la-Ferté, from Bar-sur-Aube. The original building, founded in 1115 by St. Bernard, is now in ruins; the present structure dates from 1708. Clairvaux Abbey was a good example of the general layout of a Cistercian monastery. The abbey has been listed since 1926 as a historical monument by the French Ministry of Culture. The grounds are now occupied and used by Clairvaux Prison, a high-security prison. History In 1115 Bernard, a Benedictine monk of the Abbaye de Saint-Nicolas-lès-Cîteaux, was sent with a group of twelve other monks to found a new house at Vallée d'Absinthe. Hughes I, Count of Troyes, donated this valley to the colony of Cistercians.Gildas, Marie. "Abbey of Clairvaux." The Catholic Encyclopedia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szentgotthárd Abbey
Szentgotthárd Abbey Janauschek number 470 is a former Cistercian monastery and church in Szentgotthárd Hungary that is now a Roman Catholic parish church. In hu, Szentgotthárdi ciszterci apátság; german: Kloster Sankt Gotthard; la, Abbatia Sancti Gotthardi, sl, Monoštrska cistercijanska opatija, Prekmurje Slovene: ''Monošterski cistercijánski klošter'') The first Szentgotthárd church and abbey was built in 1183 and demolished in 1604. The second church was built in the mid 1600s, but went out of use 100 years later. The current third church was built in 1748 and is still in use today. History First church In 1183, Hungarian King Béla III (1173–1196) founded a monastery in honor of Saint Gotthard at the confluence of the Rába and Lapincs rivers. Twelve Cistercian monks from Trois-Fontaines Abbey, France arrived in Hungary to staff the new Szentgotthárd monastery. The king hoped that the monks would provide technical aid to local farmers and also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orval Abbey
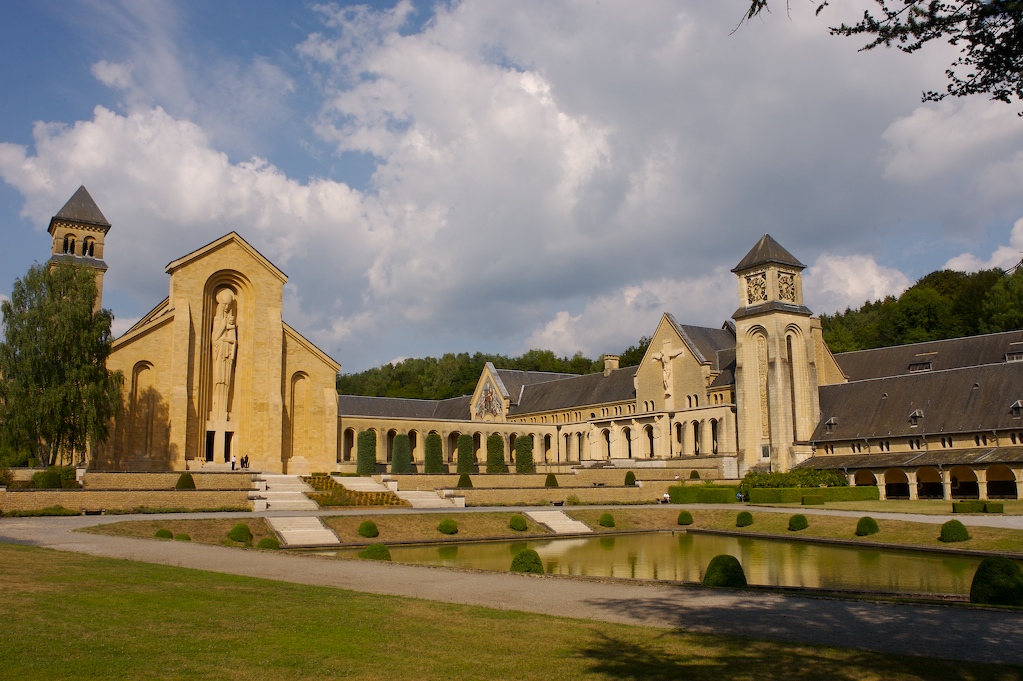
Orval Abbey (Abbaye Notre-Dame d'Orval) is a Cistercian monastery founded in 1132 in the Gaume region of Belgium and is located in Villers-devant-Orval, part of Florenville, Wallonia in the province of Luxembourg. The abbey is well known for its history and spiritual life but also for its local production of the Trappist beer Orval and a specific cheese. History First foundation The site has been occupied since the Merovingian period, and there is evidence that there was already a chapel here in the 10th century. In 1070, a group of Benedictine monks from Calabria settled here, at the invitation of Arnould, Count of Chiny, and Conrad I, Count of Luxembourg, and began construction of a church and a monastery, but after some forty years, possibly because of the death of Count Arnould, they moved away again. They were replaced by a community of Canons Regular, who completed the construction work: the abbey church was consecrated on 30 September 1124. In 1132, a group of Cis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Of Clairvaux
Bernard of Clairvaux, O. Cist. ( la, Bernardus Claraevallensis; 109020 August 1153), venerated as Saint Bernard, was an abbot, mystic, co-founder of the Knights Templars, and a major leader in the reformation of the Benedictine Order through the nascent Cistercian Order. He was sent to found Clairvaux Abbey at an isolated clearing in a glen known as the ''Val d'Absinthe'', about southeast of Bar-sur-Aube. In the year 1128, Bernard attended the Council of Troyes, at which he traced the outlines of the Rule of the Knights Templar, which soon became an ideal of Christian nobility. On the death of Pope Honorius II in 1130, a schism arose in the church. Bernard was a major proponent of Pope Innocent II, arguing effectively for his legitimacy over the Antipope Anacletus II. In 1139, Bernard attended the Second Council of the Lateran and criticized Peter Abelard vocally. Bernard advocated crusades in general and convinced many to participate in the unsuccessful Second Crusade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by his grand-uncle Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was chief minister from 1726 until his death in 1743, at which time the king took sole control of the kingdom. His reign of almost 59 years (from 1715 to 1774) was the second longest in the history of France, exceeded only by his predecessor, Louis XIV, who had ruled for 72 years (from 1643 to 1715). In 1748, Louis returned the Austrian Netherlands, won at the Battle of Fontenoy of 1745. He ceded New France in North America to Great Britain and Spain at the conclusion of the disastrous Seven Years' War in 1763. He incorporated the territories of the Duchy of Lorr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Capital
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects other than the capitals of the columns. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon: the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations. The name ''Corinthian'' is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by the Templ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)