|
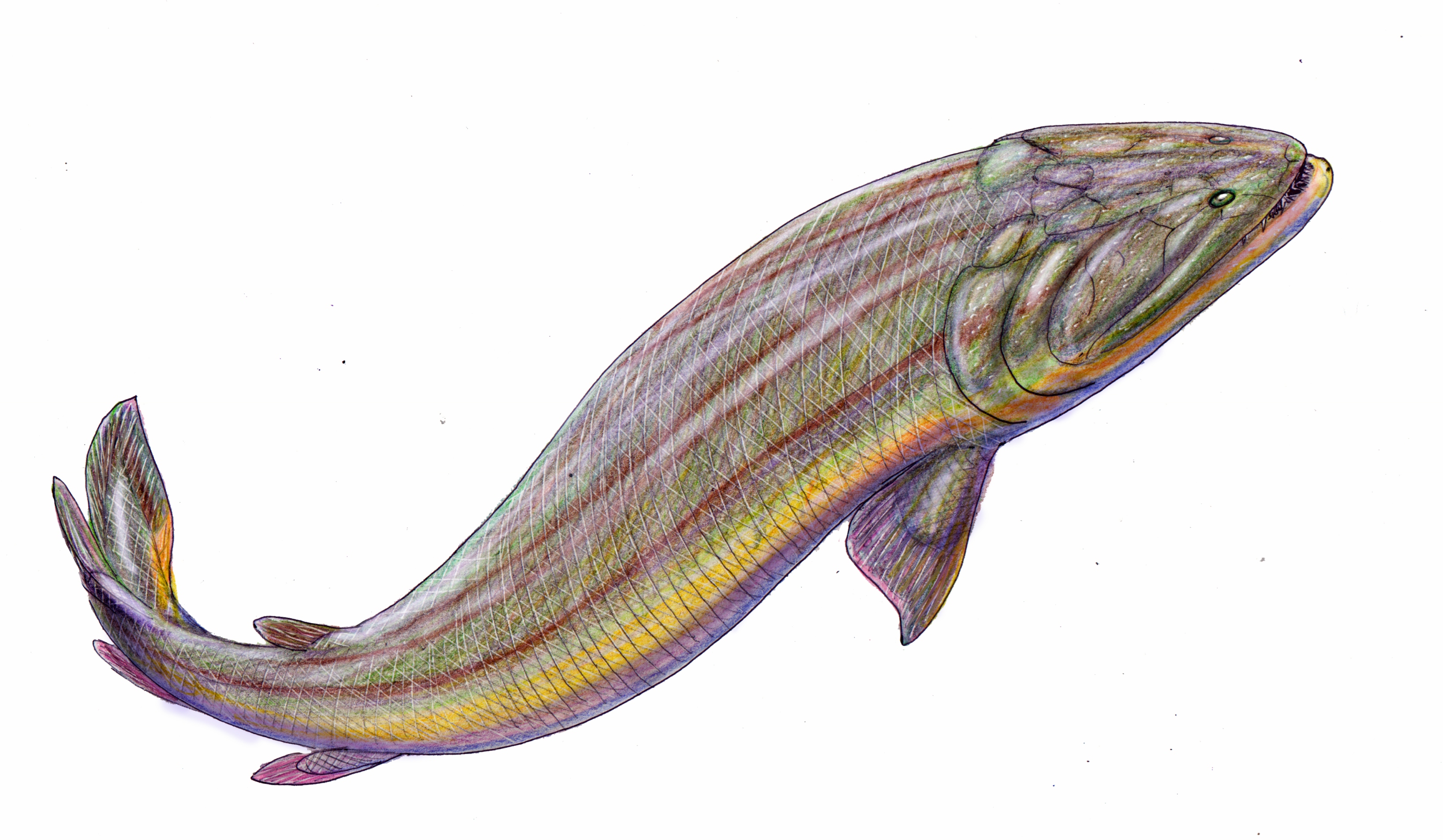
Tristichopteridae
Tristichopterids (Tristichopteridae) were a diverse and successful group of tetrapodomorph fishes living throughout the Middle and Late Devonian. They first appeared in the Eifelian stage of the Middle Devonian. Within the group sizes ranged from a few tens of centimeters ('' Tristichopterus'') to several meters ('' Hyneria'' and '' Eusthenodon''). Some tristichopterids share some of the features of the elpistostegalians, a diverse clade of fishes close to the origin of (and including) tetrapods. This mainly concerns the shape of the skull and a reduction in size of the posterior fins. An old and persistent notion is that '' Eusthenopteron'' was able to crawl onto land using its fins. However, there is no evidence actually supporting this idea.M. Laurin, F. J. Meunier, D. Germain, and M. Lemoine 2007A microanatomical and histological study of the paired fin skeleton of the Devonian sarcopterygian ''Eusthenopteron foordi Journal of Paleontology'' 81: 143–153. All tristichopter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusthenodon
''Eusthenodon'' (Greek for “strong-tooth” – ''eustheno''- meaning “strength”, -''odon'' meaning “tooth”) is an extinct genus of tristichopterid tetrapodomorphs from the Late Devonian period, ranging between 383 and 359 million years ago (Frasnian to Famennian). They are well known for being a cosmopolitan genus with remains being recovered from East Greenland, Australia, Central Russia, South Africa, Pennsylvania, and Belgium. Compared to the other closely related genera of the Tristichopteridae clade, ''Eusthenodon'' was one of the largest lobe-finned fishes (approximately 2.5 meters in length) and among the most derived tristichopterids alongside its close relatives ''Cabonnichthys'' and ''Mandageria''. The large size, predatory ecology, and evolutionarily derived characters possessed by ''Eusthenodon'' likely contributed to its ability to occupy and flourish in the numerous localities across the world mentioned above. ''Eusthenodon'' is attributed to being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristichopteridae
Tristichopterids (Tristichopteridae) were a diverse and successful group of tetrapodomorph fishes living throughout the Middle and Late Devonian. They first appeared in the Eifelian stage of the Middle Devonian. Within the group sizes ranged from a few tens of centimeters ('' Tristichopterus'') to several meters ('' Hyneria'' and '' Eusthenodon''). Some tristichopterids share some of the features of the elpistostegalians, a diverse clade of fishes close to the origin of (and including) tetrapods. This mainly concerns the shape of the skull and a reduction in size of the posterior fins. An old and persistent notion is that '' Eusthenopteron'' was able to crawl onto land using its fins. However, there is no evidence actually supporting this idea.M. Laurin, F. J. Meunier, D. Germain, and M. Lemoine 2007A microanatomical and histological study of the paired fin skeleton of the Devonian sarcopterygian ''Eusthenopteron foordi Journal of Paleontology'' 81: 143–153. All tristichopter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorphs
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorph
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteolepiformes
Osteolepiformes, also known as Osteolepidida, is a group of prehistoric lobe-finned fishes which first appeared during the Devonian period. The order contains the families Canowindridae, Megalichthyidae, Osteolepididae and Tristichopteridae. The order is generally considered to be paraphyletic because the characters that define it are mainly attributes of stem tetrapodomorphs. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... showing the paraphyly of Osteolepiformes compiled and modified from Ahlberg and Johanson (1998). See also Swartz (2012). Osteolepiformes is marked by the green bracket. References External linksTree of Life Tetrapodomorphs Prehistoric fish orders Paraphyletic groups {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platycephalichthys
''Platycephalichthys'' is a genus of tristichopterid lobe-finned fish which lived during the middle Devonian, upper Givetian stage. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... from Swartz, 2012: See also * References Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Eotetrapodiforms Devonian bony fish {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canningius
''Canningius'' is a genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish which belonged to the family Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ... of Tristichopteridae. References External links Classification of Tetrapodomorpha at Fish Index Tristichopterids Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Devonian bony fish {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notorhizodon
''Notorhizodon'' is a genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish which lived during the Devonian period (Givetian stage, about 385 - 391 million years ago). It belonged to the family of Tristichopteridae fishes. Fossils have been found in Antarctica Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ... and described by Young ''et al.'' in 1992. ''Notorhizodon'' probably lived in freshwaters. References Tristichopterids Devonian bony fish Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Prehistoric fish of Antarctica {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristichopterus
''Tristichopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish which lived during the Devonian period. ''Tristichopterus'' belongs to the family Tristichopteridae Tristichopterids (Tristichopteridae) were a diverse and successful group of tetrapodomorph fishes living throughout the Middle and Late Devonian. They first appeared in the Eifelian stage of the Middle Devonian. Within the group sizes ranged fro .... References Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Tristichopterids Devonian bony fish Devonian fish of Europe {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyneria
''Hyneria'' is a genus of large prehistoric predatory lobe-finned fish which lived in freshwater during the Devonian period around 360 million years ago. Etymology The genus name ''Hyneria'' is a reference to the village of Hyner, Pennsylvania, near where the first specimen was found. The species epiphet ''H. lindae'' is derived from the name of the wife of Keith Stewart Thomson, who described this fish. Description ''Hyneria'' was a large fish, with discovered remains estimated between in total length. Its skull had heavy, ornamented dermal bones and its lower jaw was relatively long and shallow. The teeth were stout with those of the premaxilla forming fangs upwards of . Its body was covered by cycloid scales. It had large sensory canals to aid in detection of possible prey, as the freshwater environment it inhabited likely was murky and had low visibility. Adult individuals retained the juvenile features (i.e. partially unossified skeletons), suggesting that they were li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabonnichthys
''Cabonnichthys'' ("Burns' Cabonne fish") is an extinct genus of tristichopterid fish that lived in the Late Devonian period (Famennian The Famennian is the latter of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Epoch. The most recent estimate for its duration estimates that it lasted from around 371.1 million years ago to 359.3 million years ago. An earlier 2012 estimate, still used b ...) of Australia. It has been found in Canowindra and is a medium-sized carnivorous lobe-finned fish. References Tristichopterids Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Late Devonian animals Late Devonian fish Devonian bony fish Prehistoric fish of Australia {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elpistostegalia
Elpistostegalia or Panderichthyida is an order of prehistoric lobe-finned fishes which lived during the Middle Devonian to Late Devonian period (about 385 to 374 million years ago). They represent the advanced tetrapodomorph stock, the fishes more closely related to tetrapods than the osteolepiform fishes. The earliest elpistostegalians, combining fishlike and tetrapod-like characters, are sometimes called fishapods, a phrase coined for the advanced elpistostegalian '' Tiktaalik''. Through a strict cladistic view, the order includes the terrestrial tetrapods. Palaeobiology of the elpistostegalians A rise in global oxygen content allowed for the evolution of large, predatory fish that were able to exploit the shallow tidal areas and swamplands as top predators. Several groups evolved to fill these niches, the most successful were the elpistiostegalians. In such environments, they would have been challenged by periodic oxygen deficiency. In comparable modern aquatic environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |