|
Trinchera Cave Archeological District
The Trinchera Cave Archeological District ( 5LA9555) is an archaeological site in Las Animas County, Colorado with artifacts primarily dating from 1000 BC to AD 1749, although there were some Archaic period artifacts found. The site was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2001 and is located on State Trust Lands. Geography Trinchera Cave is located within the Trinchera Creek canyon Black, Kevin. D''An Archaeological Survey of the Trinchera Cave Area, Southeastern Colorado.''Southwestern Lore: Contents and Abstracts. pp. 12-30. Retrieved 9-30-2011. in south central Colorado, east of Interstate 25. The climate zones and topography vary significantly in the 3,147 square mile Trinchera data analysis area (State of Colorado). Elevations range from , the lowest being at the San Francisco Creek to the height at Blanca Peak. Between the two points are low rolling hills, valleys, ridges, steep mountain slopes and cliffs. At the lowest elevation there is less than 6& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinchera, Colorado
Trinchera is an unincorporated community and a U.S. Post Office located in Las Animas County, Colorado Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ..., United States. The Trinchera Post Office has the ZIP Code 81081. A post office called Trinchera has been in operation since 1889. Trinchera is a name derived from Spanish meaning "trench". Geography Trinchera is located at (37.042847,-104.047565). References {{authority control Unincorporated communities in Las Animas County, Colorado Unincorporated communities in Colorado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
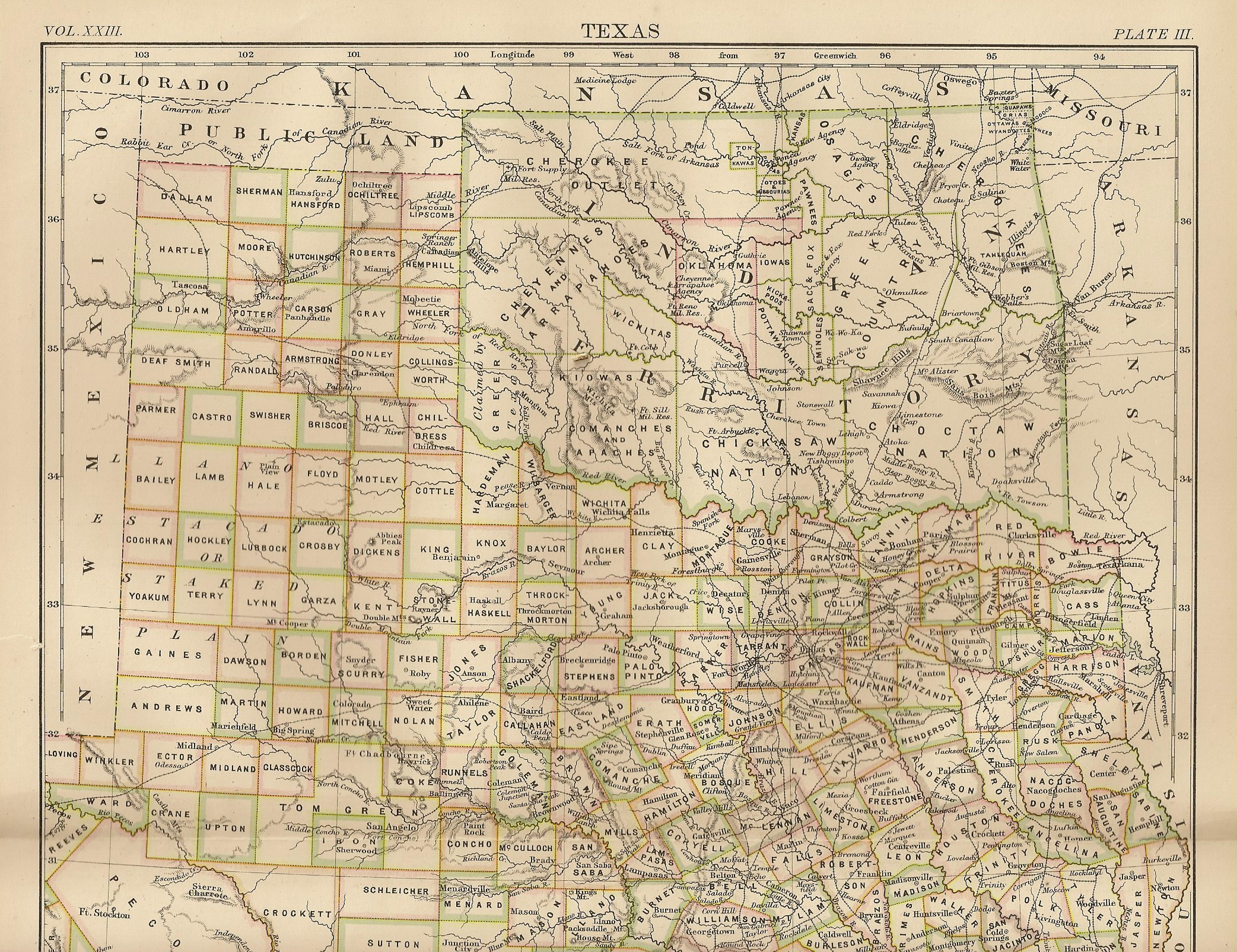
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad State Junior College
Trinidad State College is a public community college in Trinidad, Colorado. It was founded in 1925, making it the first community college in the state of Colorado. Trinidad State operates a satellite campus in the nearby city of Alamosa, Colorado. The college offers 49 degree programs in vocational fields. Academics TSC offers courses in many diverse areas, including gunsmithing, aquaculture, cosmetology, welding, nursing, as well as traditional arts and STEM subjects such as English, biology, and chemistry. Additionally, TSC trains first-responders with both an affiliated Emergency medical services training center in Grand Junction, Colorado, and its own on-campus Peace Officer Standards and Training program. Trinidad State has been continually accredited by the Higher Learning Commission since 1962. Athletics As a member of the NJCAA, Trinidad State College offers 11 athletic programs, including: * Baseball * Men's Basketball * Women's Basketball * Men's Cross Country * Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United States in Colorado, specifically the Arkansas River Valley. The headwaters derive from the snowpack in the Sawatch and Mosquito mountain ranges. It flows east into the Midwest via Kansas, and finally into the South through Oklahoma and Arkansas. At , it is the sixth-longest river in the United States, the second-longest tributary in the Mississippi–Missouri system, and the 45th longest river in the world. Its origin is in the Rocky Mountains in Lake County, Colorado, near Leadville. In 1859, placer gold discovered in the Leadville area brought thousands seeking to strike it rich, but the easily recovered placer gold was quickly exhausted. The Arkansas River's mouth is at Napoleon, Arkansas, and its drainage basin covers nearly .See wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franktown Cave
Franktown Cave is located 25 miles south of Denver, Colorado on the north edge of the Palmer Divide. It is the largest rock shelter documented on the Palmer Divide, which contains artifacts from many prehistoric cultures. Prehistoric hunter-gatherers occupied Franktown Cave intermittently for 8000 years beginning about 6400 B.C. The site held remarkable lithic and ceramic artifacts, but it is better known for its perishable artifacts, including animal hides, wood, fiber and corn. Material goods were produced for their comfort, task-simplification and religious celebration. There is evidence of the site being a campsite or dwelling as recent as AD 1725. Geography Franktown Cave is a rock shelter above Willow Creek, a tributary of Cherry Creek (Colorado), Cherry Creek that flows into the South Platte River at Denver, Colorado, 25 miles to the north. It is more than in elevation. Situated on Palmer Divide, which separates the South Platte River basin from the Arkansas River basin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter Gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, honey, or anything safe to eat, and/or by hunting game (pursuing and/or trapping and killing wild animals, including catching fish), roughly as most animal omnivores do. Hunter-gatherer societies stand in contrast to the more sedentary agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful competitive adaptation in the natural world, occupying at least 90 percent of human history. Following the invention of agriculture, hunter-gatherers who did not change were displaced or conquered by farming or pastoralist groups in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cord-marked Pottery
Cord-marked pottery or Cordmarked pottery is an early form of a simple earthenware pottery made in precontact villages. It allowed food to be stored and cooked over fire. Cord-marked pottery varied slightly around the world, depending upon the clay and raw materials that were available. It generally coincided with cultures moving to an agrarian and more settled lifestyle, like that of the Woodland period, as compared to a strictly hunter-gatherer lifestyle. Making cord-marked pottery Pottery was made by gathering clay from hillsides or streams. Other material—shells, stone, sand, plant fibers, crushed fired clay—added to the clay tempers it to prevent cracking and shrinking when dried and fired. Several methods were used to create the rough shape of the vessel: pinching and shaping, paddling, or coiling, the latter of which means to build up a pot with coils of rolled clay. Layers of coiled clay are then pinched, thinned, and smoothed. Another method, paddling, is accomplis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamper Site
The Stamper site, designated by the Smithsonian trinomial 34TX1, is an archaeological site in rural Texas County, Oklahoma. The site has historic significance for the role its finds have played in the development of archaeologists' understanding of cultural contact and migration in the southern plains. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1964. Description The Stamper site is south of the town of Optima, on a terrace overlooking the North Canadian River but below a higher escarpment. The site takes its name from Charles Stamper, who homesteaded the area in 1886. Its major features are eighteen "rooms" or walled structures, whose remnants are visible on the surface. The site has yielded stone projectiles, pottery fragments, and evidence of human burials. The site had been known locally as a significant prehistoric site for many years before it was brought to the attention of professional archaeologists. In 1929 J. Willis Stovall of the University of Oklahoma (OU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacal
The jacal (həˈkɑːl; Mexican Spanish from Nahuatl ''xacalli'' contraction of ''xamitl calli''; literally "hut") is an adobe-style housing structure historically found throughout parts of the Southwestern United States and Mexico. This type of structure was employed by some aboriginal people of the Americas prior to European colonization and was later employed by both Hispanic and Non-Hispanic settlers in Texas and elsewhere. Typically, a jacal consisted of slim close-set poles tied together and filled out with mud, clay and grasses. More sophisticated structures, such as those constructed by the Ancestral Pueblo people, incorporated adobe bricks—sun-baked mud and sandstone. Jacal construction is similar to wattle and daub. However, the "wattle" portion of jacal structures consists mainly of vertical poles lashed together with cordage and sometimes supported by a pole framework, as in the pit-houses of the Basketmaker III period of the Ancestral Puebloan (a.k.a. Anasazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puebloan Peoples
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zuni, and Hopi are the best-known. Pueblo people speak languages from four different language families, and each Pueblo is further divided culturally by kinship systems and agricultural practices, although all cultivate varieties of maize. Pueblo peoples have lived in the American Southwest for millennia and descend from Ancestral Pueblo peoples. The term ''Anasazi'' is sometimes used to refer to ancestral Pueblo people but it is now largely minimized. ''Anasazi'' is a Navajo word that means ''Ancient Ones'' or ''Ancient Enemy'', hence Pueblo peoples' rejection of it (see exonym). ''Pueblo'' is a Spanish term for "village." When Spaniards entered the area, beginning in the 16th-century with the founding of Nuevo México, they came across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by metropolitan area are Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson. Prior to 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of Nuevo México's Pueblos and Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854. While the region's boundaries are not officially defined, there have been attempts to do so. One such definition is from the Mojave Desert in California in the west (117° west longitude) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. It is the southern and main part of the Interior Plains, which also include the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. The term Western Plains is used to describe the ecoregion of the Great Plains, or alternatively the western portion of the Great Plains. The Great Plains lies across both Central United States and Western Canada, encompassing: * The entirety of the U.S. states of Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota and South Dakota; * Parts of the U.S. states of Colorado, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Wyoming; * The southern portions of the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)