|
Trichys
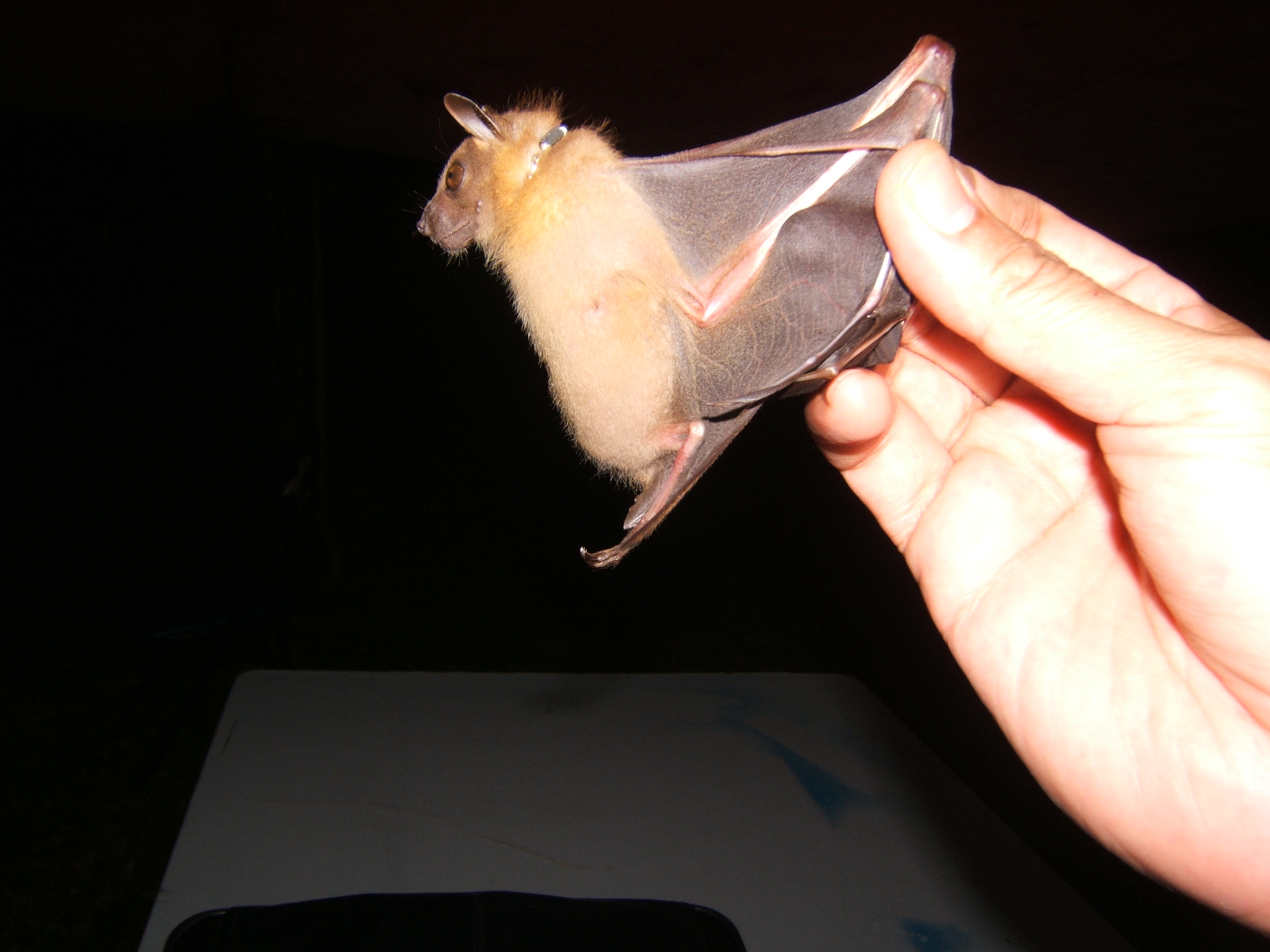
The long-tailed porcupine (''Trichys fasciculata'') is a species of rodent in the family Hystricidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Trichys'', and is found in Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia. Physical appearance Long-tailed porcupines’ appearances are somewhat rat-like. Their weight is usually around 1.7-2.3 kg but can be as small as 1.5 kg and their length can be between 27.9-48 cm excluding their tail which is usually up to 24 cm. To save themselves from predators including larger mammals, snakes and birds, their tails can be lost when grabbed but will not be regenerated. Long-tailed porcupine's broad paws allow them to be good climbers, hence they are able to climb trees and shrubs to search for food. Their front legs consist of four toes while the back legs consist of five toes. Long-tailed porcupines are commonly black or brown in colour while their underbody is usually white. The short dark brown flattened spines with white base cover their entire body with bristl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World Porcupine
The Old World porcupines, or Hystricidae, are large terrestrial rodents, distinguished by the spiny covering from which they take their name. They range over the south of Europe and the Levant, most of Africa, India, and Southeast Asia as far east as Flores. Although both the Old World and New World porcupine families belong to the infraorder Hystricognathi of the vast order Rodentia, they are quite different and are not particularly closely related. Characteristics Old World porcupines are stout, heavily built animals, with blunt, rounded heads, fleshy, mobile snouts, and coats of thick cylindrical or flattened spines, which form the whole covering of their bodies, and are not intermingled with ordinary hairs. The habits of most species are strictly terrestrial. They vary in size from the relatively small long–tailed porcupine with body lengths of , and a weight of , to the much larger crested porcupines, which are long, discounting the tail, and weigh from . The various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Brunei
This is a list of the mammal species recorded in Brunei. The following tags are used to highlight each species' conservation status as assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature: Some species were assessed using an earlier set of criteria. Species assessed using this system have the following instead of near threatened and least concern categories: Order: Sirenia (manatees and dugongs) ---- Sirenia is an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit rivers, estuaries, coastal marine waters, swamps, and marine wetlands. All four species are endangered. *Family: Dugongidae **Genus: ''Dugong'' ***Dugong, ''D. dugon'' Order: Scandentia (treeshrews) ---- The treeshrews are small mammals native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. Although called treeshrews, they are not true shrews and are not all arboreal. *Family: Tupaiidae (tree shrews) **Genus: '' Tupaia'' ***Long-footed treeshrew, ''T. longipes'' *** Painted treeshrew, ''T. picta'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Borneo
The mammal species of Borneo include 288 species of terrestrial and 91 species of marine mammals recorded within the territorial boundaries of Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia. The terrestrial mammals are dominated by the chiroptera (102 species of bats) and rodents (61 species of rats and mice). Introduction The high diversity and endemicity of mammals is related to the many niches found in the tropical rain forest of Borneo and past Pleistocene events within the Sundaland region. During interglacial and post-glacial periods, there was migration of animal from the Asian mainland into Borneo and into Sulawesi via the Philippines. Due to lack of favourable habitats and small founder population, some species of animals have become extinct and others have radiated into endemic species. Of the 57 mammal species that were identified from archaeological remains in the Niah Caves, Sarawak, 13 were bats. Four of these were megachiropterans, ''Pteropus vampyrus'', ''Rousettus amplexicauda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folivore
In zoology, a folivore is a herbivore that specializes in eating leaves. Mature leaves contain a high proportion of hard-to-digest cellulose, less energy than other types of foods, and often toxic compounds.Jones, S., Martin, R., & Pilbeam, D. (1994) ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Human Evolution''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press For this reason, folivorous animals tend to have long digestive tracts and slow metabolisms. Many enlist the help of symbiotic bacteria to release the nutrients in their diet. Additionally, as has been observed in folivorous primates, they exhibit a strong preference for immature leaves, which tend to be easier to masticate, tend to be higher in energy and protein, and lower in fibre and poisons than more mature fibrous leaves. Evolution Herbivory has evolved several times among different groups of animals. The first vertebrates were small fish that consumed protists and invertebrates. After these fish, the next group of vertebrates to evolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodents Of Indonesia
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Described In 1801
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
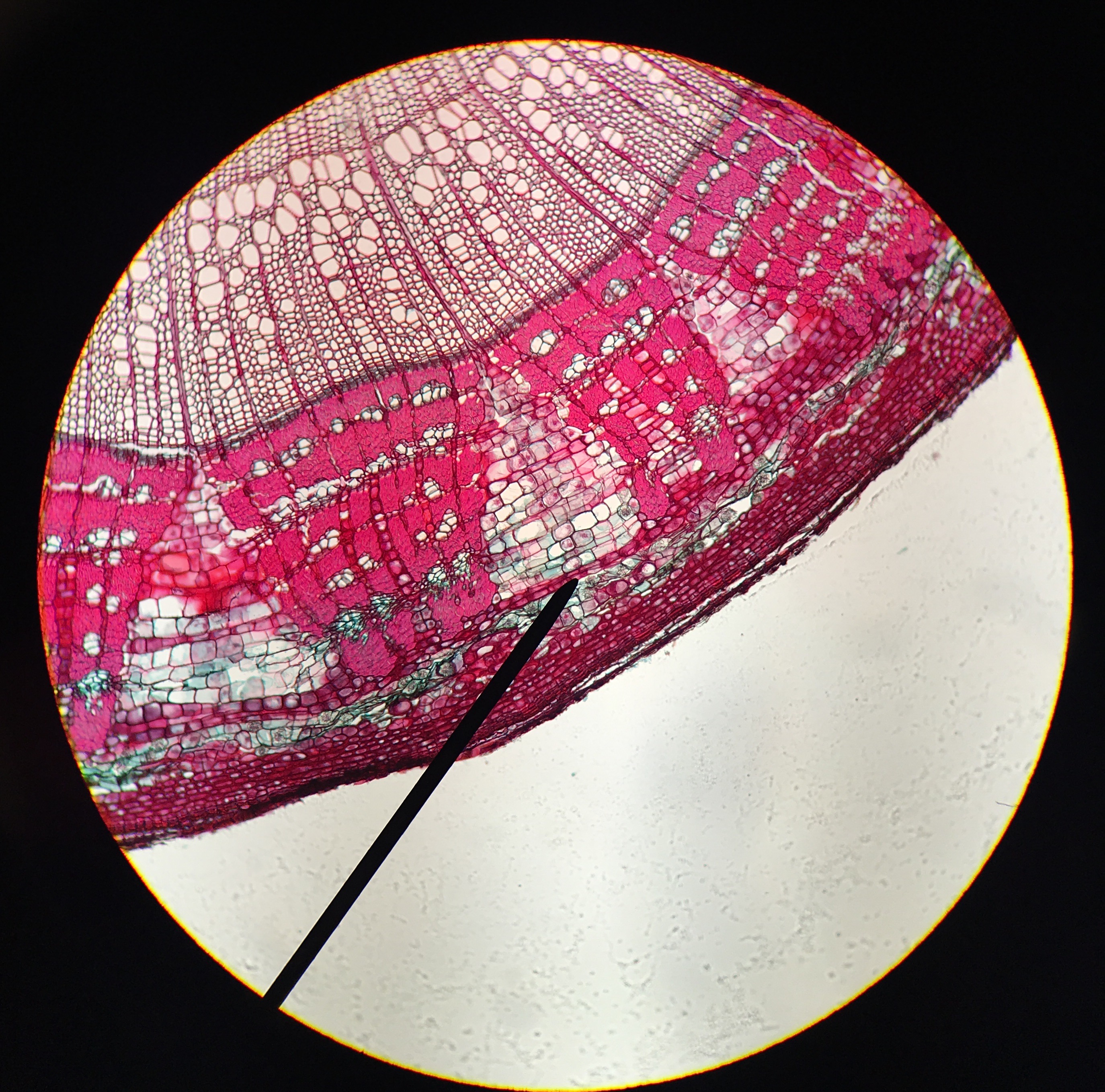
Cambium
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or cooke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms and cnidarians. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 50 μm (0.002 in) rotifers to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the invertebrates paraphyletic, so the term has little meaning in taxonomy. Etymology The word "invertebrate" comes from the Latin word ''vertebra'', whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (adaxial) and lower ( abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll that is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert C
Albert may refer to: Companies * Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic * Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands * Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia * Albert Productions, a record label * Albert Computers, Inc., a computer manufacturer in the 1980s Entertainment * ''Albert'' (1985 film), a Czechoslovak film directed by František Vláčil * ''Albert'' (2015 film), a film by Karsten Kiilerich * ''Albert'' (2016 film), an American TV movie * ''Albert'' (Ed Hall album), 1988 * "Albert" (short story), by Leo Tolstoy * Albert (comics), a character in Marvel Comics * Albert (''Discworld''), a character in Terry Pratchett's ''Discworld'' series * Albert, a character in Dario Argento's 1977 film ''Suspiria'' Military * Battle of Albert (1914), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1916), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1918), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France People * Albert (given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)
