|
Tricetin 3',4',5'-O-trimethyltransferase
Tricetin 3',4',5'-O-trimethyltransferase (, ''FOMT'', ''TaOMT1'', ''TaCOMT1'', ''TaOMT2'') is an enzyme with List of enzymes, systematic name ''S-adenosyl-L-methionine:tricetin 3',4',5'-O-trimethyltransferase''. This enzyme catalysis, catalyses the following chemical reaction : 3 S-adenosyl-L-methionine + tricetin \rightleftharpoons 3 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 3',4',5'-O-trimethyltricetin (overall reaction) :(1a) S-adenosyl-L-methionine + tricetin \rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 3'-O-methyltricetin :(1b) S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 3'-O-methyltricetin \rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 3',5'-O-dimethyltricetin :(1c) S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 3',5'-O-dimethyltricetin \rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 3',4',5'-O-trimethyltricetin The enzyme from ''Triticum aestivum'' catalyses the sequential O-methylation of tricetin via 3'-O-methyltricetin, 3',5'-O-methyltricetin to 3',4',5'-O-trimethyltricetin. References External links * {{Por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
This article lists enzymes by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. * List of EC numbers (EC 5) * List of EC numbers (EC 6) :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) (Oxidoreductase) *Dehydrogenase * Luciferase *DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) **Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase **Diacetyl reductase **Glycerol dehydrogenase **Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase **L-xylulose reductase **Lactate dehydrogenase **Malate dehydrogenase **Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) **Glucose oxidase **L-gulonolactone oxidase **Thiamine oxidase **Xanthine oxidase * :EC 1.1.4 (with a disul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
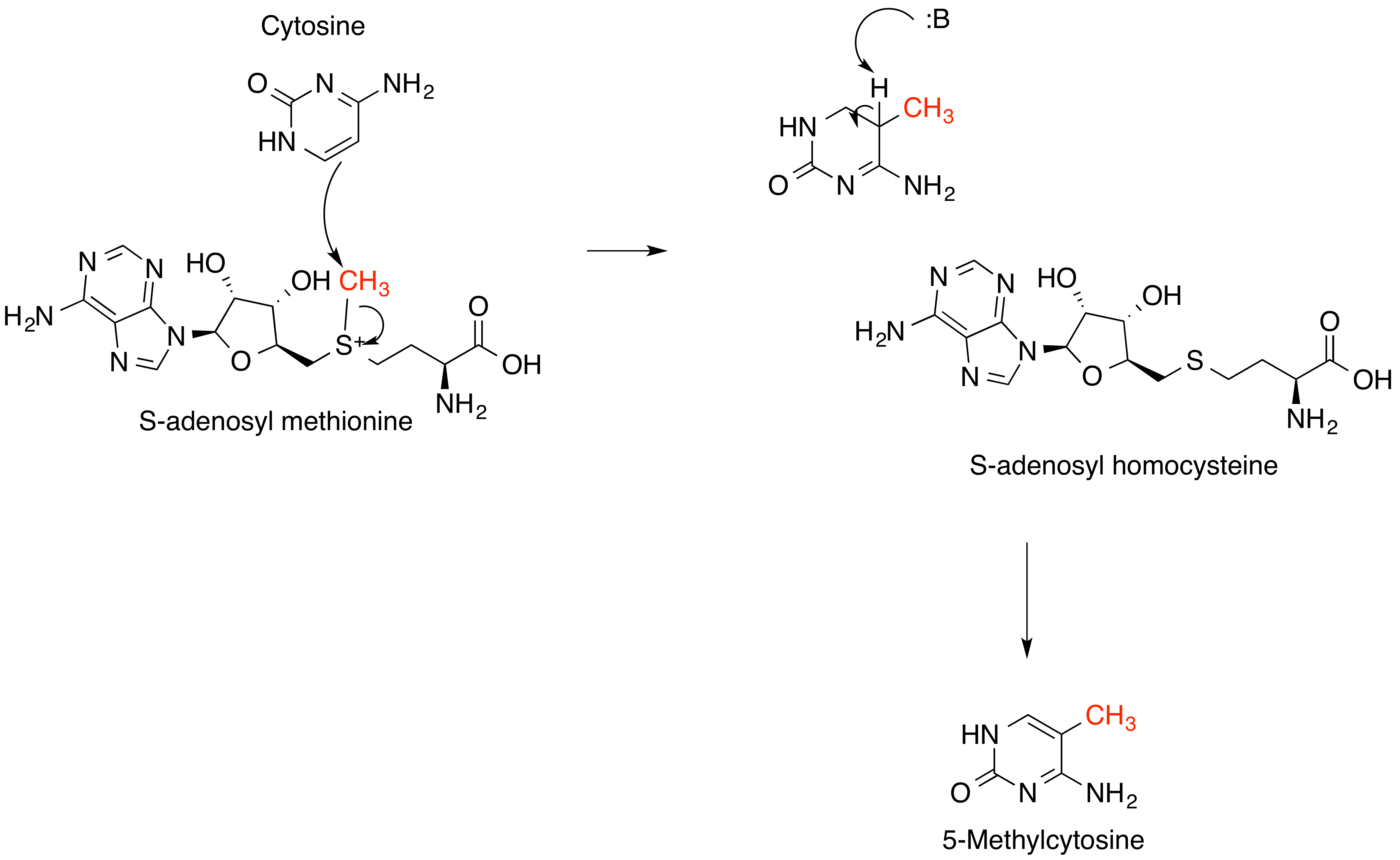
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone and sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricetin
Tricetin is a flavone, a type of flavonoid. It is a rare aglycone found in the pollen of members of the Myrtaceae, subfamily Leptospermoideae, such as ''Eucalyptus globulus''. This compound shows anticancer effects on human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells. Moreover. a potent anti-inflammatory effect of tricetin has also been demonstrated in a model of acute pancreatitis. This observation was explained by the compound's radical scavenging effects, its inhibitory effect on the DNA damage sensor enzyme poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP1) and PARP1-mediated cell death and suppression of inflammatory gene expression. See also * Tricin synthase produces tricin Tricin is a chemical compound. It is an O-methylated flavone, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in rice bran and sugarcane. Glycosides * Tricin 4'-glucoside (Tricin-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranaoside, CAS number 71855-50-0) * Tricin 5-glucoside (T ... or tricetin 3′,5′-dimethyl ether * Tricetin 3′,4′,5′-''O'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triticum Aestivum
Common wheat (''Triticum aestivum''), also known as bread wheat, is a cultivated wheat species. About 95% of wheat produced worldwide is common wheat; it is the most widely grown of all crops and the cereal with the highest monetary yield. Taxonomy Numerous forms of wheat have evolved under human selection. This diversity has led to confusion in the naming of wheats, with names based on both genetic and morphological characteristics. List of common cultivars * Albimonte * Manital Phylogeny Bread wheat is an allohexaploid (an allopolyploid with six sets of chromosomes: two sets from each of three different species). Of the six sets of chromosomes, two come from ''Triticum urartu'' (einkorn wheat) and two from a species related to ''Aegilops speltoides''. This spontaneous hybridisation created the tetraploid species ''Triticum turgidum'' (an ancestor of wild emmer wheat and durum wheat) 580,000–820,000 years ago. The last two sets of chromosomes came from wild goat-gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |