|
Tricarina
''Tricarina'' is an extinct genus of crustaceans in order Isopoda, known from a single incomplete fossil specimen from the Cretaceous of western Iran. It has a flattened body with three longitudinal ridges, which give it its name. Sources The single known specimen of ''Tricarina'' was discovered in a well core that had been bored at a site on the Khuzestan Plain in south-western Iran, at , and at a depth of . The rocks that contain it are calcareous shales, which form part of the Gadvan Formation, and are part of the main sequence of rocks for the production oil and gas around the Persian Gulf. Examination of the foraminiferan fossils show that the shales are Barremian to Aptian in age. Description The fossil of ''Tricarina gadvanensis'' is known from a part and counterpart from a core drilled to make an oil well. It has been deposited in the Carnegie Museum of Natural History, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, as specimen number CM 54197. A segment of the cylindrical core was cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achelata
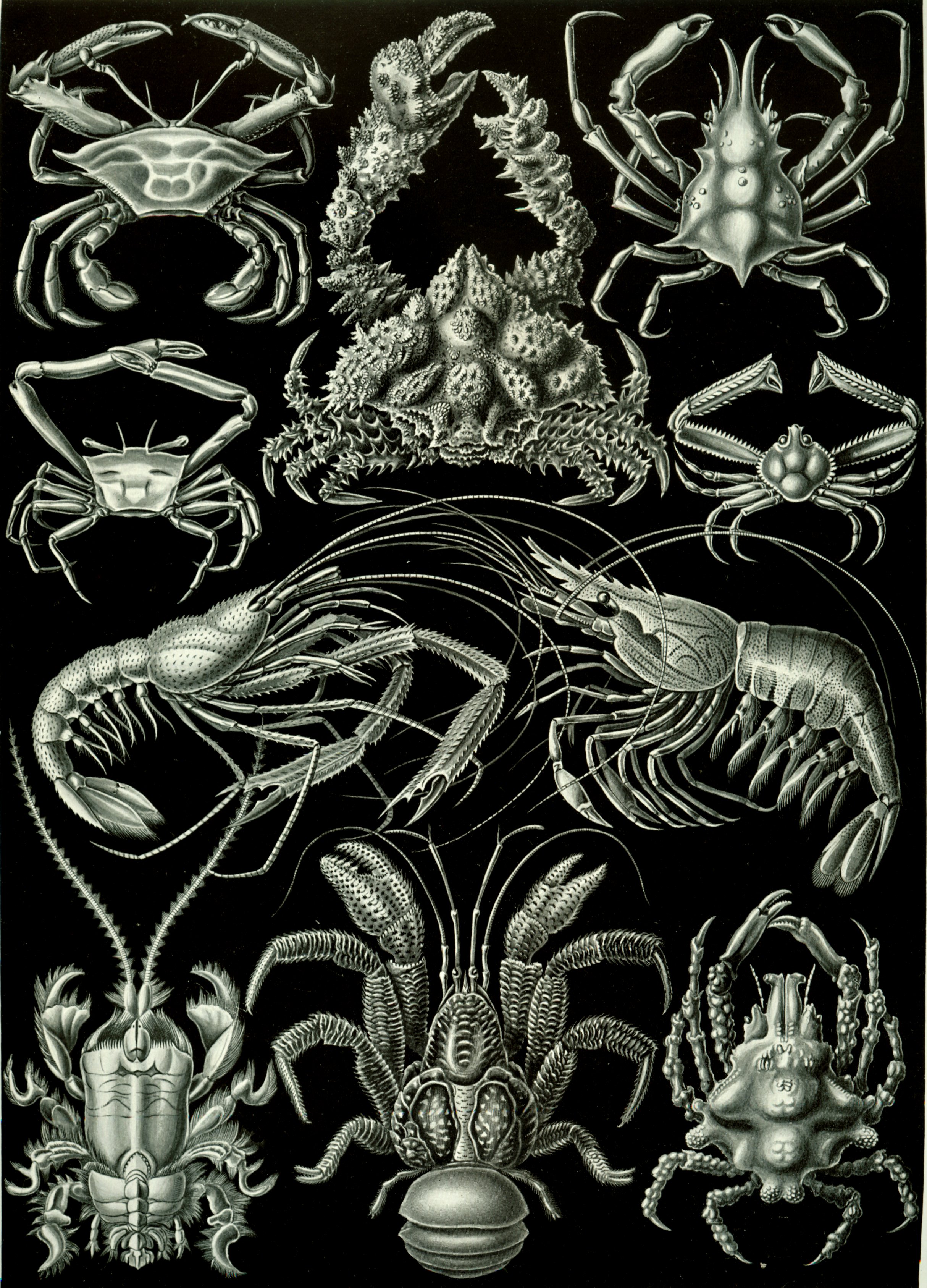
The Achelata is an infra-order of the decapod crustaceans, holding the spiny lobsters, slipper lobsters and their fossil relatives. Description The name "Achelata" derives from the fact that all the members of this group lack the chelae (claws) that are found on almost all other decapods (from the Ancient Greek , = "not", , = "claw"). They are further united by the great enlargement of the second antennae, by the special "phyllosoma" form of the larva, and by a number of other characters. Classification and fossil record The infraorder Achelata belongs to the group Reptantia, which consists of the walking/crawling decapods (lobsters and crabs). The cladogram below shows Achelata's placement within the larger order Decapoda, from analysis by Wolfe ''et al.'', 2019. Achelata contains the spiny lobsters (Palinuridae), the slipper lobsters (Scyllaridae) and the furry lobsters (Synaxidae, now usually included in Palinuridae), as well as two extinct families, Cancrinidae a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Museum Of Natural History
The Carnegie Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as CMNH) is a natural history museum in the Oakland neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was founded by Pittsburgh-based industrialist Andrew Carnegie in 1896. Housing some 22 million specimens, the museum features one of the finest paleontological collections in the world. Description and history The museum consists of organized into 20 galleries as well as research, library, and office space. It holds some 22 million specimens, of which about 10,000 are on view at any given time and about 1 million are cataloged in online databases. In 2008 it hosted 386,300 admissions and 63,000 school group visits. Museum education staff also actively engage in outreach by traveling to schools all around western Pennsylvania. The museum gained prominence in 1899 when its scientists unearthed the fossils of ''Diplodocus carnegii''. Notable dinosaur specimens include one of the world's very few fossils of a juvenile ''Apatosauru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiny Lobster
Spiny lobsters, also known as langustas, langouste, or rock lobsters, are a family (Palinuridae) of about 60 species of achelate crustaceans, in the Decapoda Reptantia. Spiny lobsters are also, especially in Australia, New Zealand, Ireland, South Africa, and The Bahamas, called crayfish, sea crayfish, or crawfish ("kreef" in South Africa), terms which elsewhere are reserved for freshwater crayfish. Classification The furry lobsters (''e.g.'' ''Palinurellus'') were previously separated into a family of their own, the Synaxidae, but are usually considered members of the Palinuridae. The slipper lobsters (Scyllaridae) are their next-closest relatives, and these two or three families make up the Achelata. Genera of spiny lobsters include ''Palinurus'' and a number of anagrams thereof: ''Panulirus'', ''Linuparus'', ''etc.'' (Palinurus was a helmsman in Virgil's ''Æneid''.) In total, 12 extant genera are recognised, containing around 60 living species: *''Jasus'' Parker, 1883 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity (taxonomy)
Affinity (taxonomy) – mainly in life sciences or natural history – refers to resemblance suggesting a common descent, phylogenetic relationship, or type. The term does, however, have broader application, such as in geology (for example, in descriptive and theoretical works), and similarly in astronomy (for example, see "Centaur object" in the context of 2060 Chiron's close affinity with icy comet nuclei."Centaur object." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica 2007 Ultimate Reference Suite . Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2011.) Basis In taxonomy the basis of any particular type of classification is the ''way in which objects in the domain resemble each other''. A resemblance of a type that seems appropriate to the classification that we propose, we may call an ''affinity'', and when we decide how to classify say, a specimen of rock or butterfly, we justify our decision according to the affinities that we observe. Other resemblances we dismiss as being out o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychelida
Polychelida is an infraorder of decapod crustaceans. Fossil representatives are known dating from as far back as the Upper Triassic. A total of 38 extant species, all in the family Polychelidae, and 55 fossil species have been described. History Polychelida had traditionally been included in the infraorder Palinura, alongside the spiny lobsters and slipper lobsters (now in the infraorder Achelata). In 1995, Gerhard Scholtz and Stefan Richter of the carried out a phylogenetic study of the "Reptantia", and concluded that "Palinura" was paraphyletic. They therefore abandoned that taxon and introduced instead the new clade Polychelida. Classification Polychelida belongs to the group Reptantia, which consists of the walking/crawling decapods (lobsters and crabs). Polychelida is the sister clade to the infraorder Astacidea, which contains the "true" lobsters and crayfish. The cladogram below shows Polychelida's placement within the larger order Decapoda, from analysis by Wolfe '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scyllaridae
Slipper lobsters are a family (Scyllaridae) of about 90 species of achelate crustaceans, in the Decapoda clade Reptantia, found in all warm oceans and seas. They are not true lobsters, but are more closely related to spiny lobsters and furry lobsters. Slipper lobsters are instantly recognisable by their enlarged antennae, which project forward from the head as wide plates. All the species of slipper lobsters are edible, and some, such as the Moreton Bay bug and the Balmain bug (''Ibacus peronii'') are of commercial importance. Description Slipper lobsters have six segments in their heads and eight segments in the thorax, which are collectively covered in a thick carapace. The six segments of the abdomen each bear a pair of pleopods, while the thoracic appendages are either walking legs or maxillipeds. The head segments bear various mouthparts and two pairs of antennae. The first antennae, or ''antennules'', are held on a long flexible stalk, and are used for sensing the env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapoda
The Decapoda or decapods (literally "ten-footed") are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, including many familiar groups, such as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp (about 3,000 species) and Anomura including hermit crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters (about 2500 species) making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossil decapod is the Devonian ''Palaeopalaemon''. Anatomy Decapods can have as many as 38 appendages, arranged in one pair per body segment. As the name Decapoda (from the Greek , ', "ten", and , '' -pod'', "foot") implies, ten of these appendages are considered legs. They are the pereiopods, found on the last five thoracic segments. In many decapods, one pair of these "legs" has enlarged pincers, called chelae, with the legs be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chela (organ)
A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer (biology), pincer-like organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through New Latin '. The plural form is chelae. Legs bearing a chela are called chelipeds. Another name is ''claw'' because most chelae are curved and have a sharp point like a claw. Chelae can be present at the tips of arthropod legs as well as their pedipalps. Chelae are distinct from spider chelicerae in that they do not contain venomous glands and cannot distribute venom. See also * Pincer (biology) * Pincer (tool) References Arthropod anatomy {{Arthropod-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pereiopod
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (biology)
Antennae ( antenna), sometimes referred to as "feelers", are paired appendages used for sensing in arthropods. Antennae are connected to the first one or two segments of the arthropod head. They vary widely in form but are always made of one or more jointed segments. While they are typically sensory organs, the exact nature of what they sense and how they sense it is not the same in all groups. Functions may variously include sensing touch, air motion, heat, vibration (sound), and especially smell or taste. Antennae are sometimes modified for other purposes, such as mating, brooding, swimming, and even anchoring the arthropod to a substrate. Larval arthropods have antennae that differ from those of the adult. Many crustaceans, for example, have free-swimming larvae that use their antennae for swimming. Antennae can also locate other group members if the insect lives in a group, like the ant. The common ancestor of all arthropods likely had one pair of uniramous (unbranched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapace
A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron. Crustaceans In crustaceans, the carapace functions as a protective cover over the cephalothorax (i.e., the fused head and thorax, as distinct from the abdomen behind). Where it projects forward beyond the eyes, this projection is called a rostrum (anatomy), rostrum. The carapace is Calcification, calcified to varying degrees in different crustaceans. Zooplankton within the phylum Crustacea also have a carapace. These include Cladocera, ostracods, and Isopoda, isopods, but isopods only have a developed "cephalic shield" carapace covering the head. Arachnids In arachnids, the carapace is formed by the fusion of prosomal tergites into a single Plate (animal anatomy), plate which carries the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |