|
Treaty Of Saint Petersburg (1875)
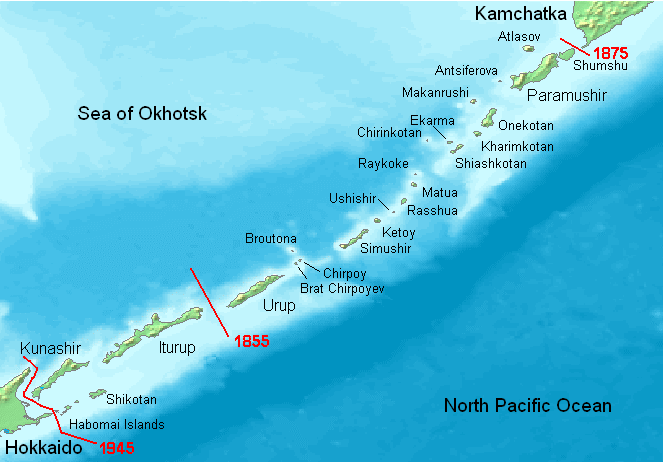
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg ( ja, жЁәеӨӘгғ»еҚғеі¶дәӨжҸӣжқЎзҙ„, Karafuto-Chishima KЕҚkan JЕҚyaku; russian: РҹРөСӮРөСҖРұСғСҖРіСҒРәРёР№ РҙРҫРіРҫРІРҫСҖ) between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire was signed on 7 May 1875, and its ratifications exchanged at Tokyo on 22 August 1875. The treaty itself went into effect in 1877. Its terms stipulated that Japan cedes to Russia the part of Sakhalin island it then owned in exchange for the group of the Kuril Islands owned by Russia (between Iturup island and the Kamchatka Peninsula). Consequently, Sakhalin island as a whole became Russian territory, and the entire Kuril archipelago Japanese territory. The authentic text of the treaty is written in French. Differences with its Japanese translation contributed to the controversy on what constitutes the Kuril islands, claims to which Japan renounced in 1951 by the Treaty of San Francisco. The Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875) is part of an ongoing, and long-standing, territorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, РЎР°РҪРәСӮ-РҹРөСӮРөСҖРұСғСҖРі, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ЛҲsankt pКІЙӘtКІЙӘrЛҲburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914вҖ“1924) and later Leningrad (1924вҖ“1991), is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia. It is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iturup
, other_names = russian: РҳСӮСғСҖСғМҒРҝ; ja, жҠһжҚүеі¶ , location = Sea of Okhotsk , coordinates = , archipelago = Kuril Islands , total_islands = , major_islands = , area_km2 = 3139 , length_km = 200 , width_km = 27 , coastline = , highest_mount = Stokap , elevation_m = 1634 , country_claim = , country_claim_divisions_title_1 = Prefecture , country_claim_divisions_1 = Hokkaido , country_claim_divisions_title_2 = Subprefecture , country_claim_divisions_2 = Nemuro , country = , country_admin_divisions_title_1 = Federal subject , country_admin_divisions_1 = Sakhalin Oblast , country_admin_divisions_title_2 = District , country_admin_divisions_2 = Kurilsky , population = 7,500 , population_as_of = 2003 , density = , ethnic_groups = , additional_info = Iturup (russian: РһСҒСӮСҖРҫРІ РҳСӮСғСҖСғМҒРҝ, Ostrov IturГәp; ain, гӮЁгғ„гӮҡгғІгғӯгҮ·гӮҡ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SovietвҖ“Japanese Joint Declaration Of 1956
The Soviet Union did not sign the Treaty of Peace with Japan in 1951. On October 19, 1956, Japan and the Soviet Union signed a Joint Declaration providing for the end of the state of war and for the restoration of diplomatic relations between both countries. They also agreed to continue negotiations for a peace treaty. In addition, the Soviet Union pledged to support Japan for UN membership and to waive all World War II reparations claims. The joint declaration was accompanied by a trade protocol, which granted reciprocal most favored nation status and provided for the development of trade. Japan derived few apparent gains from the normalization of diplomatic relations. The second half of the 1950s saw an increase in cultural exchanges. Territorial provisions The Joint Declaration provided in Article 9 for the continuation of negotiations for the conclusion of a peace treaty after the restoration of diplomatic relations between the countries and further stipulated that "in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Gromyko
Andrei Andreyevich Gromyko (russian: РҗРҪРҙСҖРөР№ РҗРҪРҙСҖРөРөРІРёСҮ Р“СҖРҫРјСӢРәРҫ; be, РҗРҪРҙСҖСҚР№ РҗРҪРҙСҖСҚРөРІС–СҮ Р“СҖамСӢРәР°; вҖ“ 2 July 1989) was a Soviet communist politician and diplomat during the Cold War. He served as Minister of Foreign Affairs (1957вҖ“1985) and as Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet (1985вҖ“1988). Gromyko was responsible for many top decisions on Soviet foreign policy until he retired in 1988. In the 1940s Western pundits called him ''Mr Nyet'' ("Mr No") or "Grim Grom", because of his frequent use of the Soviet veto in the United Nations Security Council. Gromyko's political career started in 1939 in the People's Commissariat for Foreign Affairs (renamed Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1946). He became the Soviet ambassador to the United States in 1943, leaving that position in 1946 to become the Soviet Permanent Representative to the United Nations in New York. Upon his return to Moscow he became a Deputy Minister o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939вҖ“1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy. Its principal members by 1941 were the United Kingdom, United States, Soviet Union, and China. Membership in the Allies varied during the course of the war. When the conflict broke out on 1 September 1939, the Allied coalition consisted of the United Kingdom, France, and Poland, as well as their respective dependencies, such as British India. They were soon joined by the independent dominions of the British Commonwealth: Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Consequently, the initial alliance resembled that of the First World War. As Axis forces began invading northern Europe and the Balkans, the Allies added the Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, Greece, and Yugoslavia. The Soviet Union, which initially ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Peace Treaty
The , also called the , re-established peaceful relations between Japan and the Allied Powers on behalf of the United Nations by ending the legal state of war and providing for redress for hostile actions up to and including World War II. It was signed by 49 nations on 8 September 1951, in San Francisco, California, U.S. at the War Memorial Opera House. Italy and China were not invited, the latter due to disagreements on whether the Republic of China or the People's Republic of China represented the Chinese people. Korea was also not invited due to a similar disagreement on whether South Korea or North Korea represented the Korean people. The treaty came into force on 28 April 1952. It ended Japan's role as an imperial power, allocated compensation to Allied nations and former prisoners of war who had suffered Japanese war crimes during World War II, ended the Allied post-war occupation of Japan, and returned full sovereignty to it. This treaty relied heavily on the United Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, ж—ҘйңІжҲҰдәү, Nichiro sensЕҚ, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Р СғМҒСҒСҒРәРҫ-СҸРҝГіРҪСҒРәР°СҸ РІРҫР№РҪГЎ, RГәssko-yapГіnskaya voynГЎ) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1905 over rival imperialism, imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major theatres of military operations were located in Liaodong Peninsula and Shenyang, Mukden in Southern Manchuria, and the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia sought a Port#Warm-water port, warm-water port on the Pacific Ocean both for its navy and for maritime trade. Vladivostok remained ice-free and operational only during the summer; LГјshunkou, Port Arthur, a naval base in Liaodong Province leased to Russia by the Qing dynasty of China from 1897, was operational year round. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy east of the Urals, in Siberia and the Russian Far East, Far East, since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. Since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Portsmouth
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyinskoye, Sakhalin Oblast
Ilyinskoye (russian: РҳР»СҢРёРҪСҒРәРҫРө, until 1946 Kusunai or is a rural locality ( selo) in Tomarinsky District, Sakhalin Oblast, Russia. A settlement on the western coast of Sakhalin Island, by the mouth of the Kusunai River was founded in 1853 by Dmitry Orlov, however, it was later abandoned when all Russian settlements were removed from the island due to the Crimean War. A successor settlement, known as Ilyinsky Post or Kusunai Post, was founded at the same location by Nikolay Rudanovsky on 20 August 1857. In the 1860s this was one of the two settlements on Sakhalin, along with Due, which had a permanent Russian population. In 1906, after the Russo-Japanese War, following the Treaty of Portsmouth, the Southern Sakhalin was transferred to Japan. Ilyinskoye was renamed Kusunai and became part of Karafuto Prefecture. In 1945, following World War II, it was reoccupied by the Soviet Union. Administratively, on 2 February 1946 South Sakhalin Oblast was created, which was part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



