|
Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy
Transmissible mink encephalopathy (TME) is a rare sporadic disease that affects the central nervous system of ranch-raised adult mink. It is a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, caused by proteins called prions. Clinical signs This illness has a minimum incubation period of 7 months with a maximum of 12 months. This disease results in mortality of adult animals. Medical sign, Clinical signs of TME include behavioural changes such as confusion, loss of cleanliness, and aimless circling. An affected animal shows signs of weight loss, might develop matted fur, hindquarter ataxia, and its tail arched over its back. Seizures may very rarely occur. Near-death stages include the animal showing signs of drowsiness and unresponsiveness. Diagnosis Currently, no tests are available to detect signs of this illness in live animals. However, veterinary pathologists can confirm this illness by Microscopy, microscopic examination of the brain tissue in animals suspected to have died of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinary Pathologist
Veterinary pathologists are veterinarians who specialize in the diagnosis of diseases through the examination of animal tissue and body fluids. Like medical pathology, veterinary pathology is divided into two branches, anatomical pathology and clinical pathology. Other than the diagnosis of disease in food-producing animals, companion animals, zoo animals and wildlife, veterinary pathologists also have an important role in drug discovery and safety as well as scientific research. Veterinary anatomical pathology Anatomical pathology (''Commonwealth'') or ''Anatomic pathology'' (''U.S.'') is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the gross examination, microscopic, and molecular examination of organs, tissues, and whole bodies (necropsy). The Indian, European, Japanese and American Colleges of Veterinary Pathologists certify veterinary pathologists through a certifying exam. The American College of Veterinary Pathologist certification exam consists of four parts - gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrapie
Scrapie () is a fatal, degenerative disease affecting the nervous systems of sheep and goats. It is one of several transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), and as such it is thought to be caused by a prion. Scrapie has been known since at least 1732 and does not appear to be transmissible to humans. However, new studies suggest a link between scrapie and sporadic CJD. The name scrapie is derived from one of the clinical signs of the condition, wherein affected animals will compulsively scrape off their fleeces against rocks, trees or fences. The disease apparently causes an itching sensation in the animals. Other clinical signs include excessive lip smacking, altered gaits and convulsive collapse. Scrapie is infectious and transmissible among conspecifics, so one of the most common ways to contain it (since it is incurable) is to quarantine and kill those affected. However, scrapie tends to persist in flocks and can also arise apparently spontaneously in flocks that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuru (disease)
Kuru is a rare, incurable, and fatal Neurological disorder, neurodegenerative disorder that was formerly common among the Fore people of Papua New Guinea. Kuru is a form of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) caused by the transmission of abnormally folded proteins (prions), which leads to symptoms such as tremors and loss of coordination from neurodegeneration. The term kuru derives from the Fore language, Fore word ''kuria'' or ''guria'' ("to shake"), due to the body tremors that are a classic symptom of the disease. ''Kúru'' itself means "trembling". It is also known as the "laughing sickness" due to the pathologic bursts of laughter which are a symptom of the disease. It is now widely accepted that kuru was transmitted among members of the Fore tribe of Papua New Guinea via Endocannibalism, funerary cannibalism. Deceased family members were traditionally cooked and eaten, which was thought to help free the spirit of the dead. Women and children usually consumed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
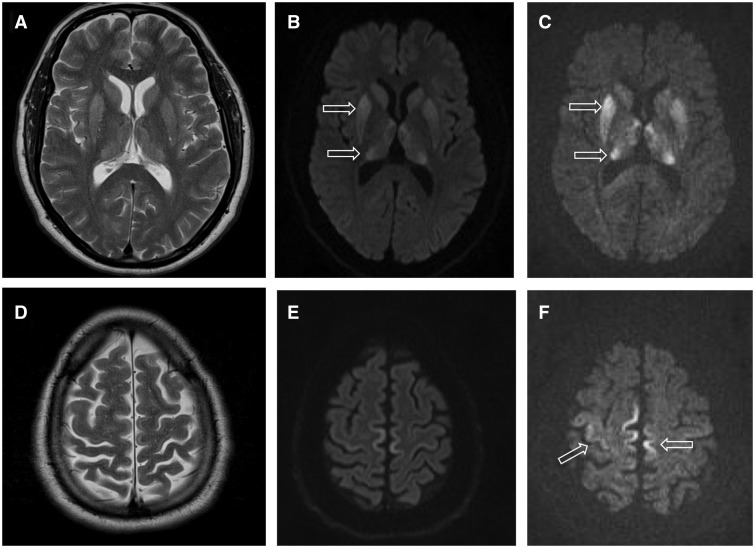
Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), also known as subacute spongiform encephalopathy or neurocognitive disorder due to prion disease, is an invariably fatal degenerative brain disorder. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, and visual disturbances. Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, weakness, and coma. About 70% of people die within a year of diagnosis. The name Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease was introduced by Walther Spielmeyer in 1922, after the German neurologists Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob. CJD is caused by a type of abnormal protein known as a prion. Infectious prions are misfolded proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded. About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread. There is no evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stetsonville, Wisconsin
Stetsonville is a village in Taylor County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 541 at the 2010 census. Geography Stetsonville is located at (45.076413, -90.313952). According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , all of it land. History Stetsonville began when the Wisconsin Central Railway built its line through the area in 1872, heading north for Ashland. The stop was initially called "63." In 1875 Isiah Stetson built the first sawmill in town. The town was later named after him. The people of Stetsonville drew water from private wells until the 1980s, when petroleum contamination began to appear in some of them. A complete cleanup of the source was impossible, so in 2010 the village established a municipal water system, with help from the DNR, the USDA, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, and other sources. Demographics 2010 census As of the census of 2010, there were 541 people, 242 households, and 156 families livi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
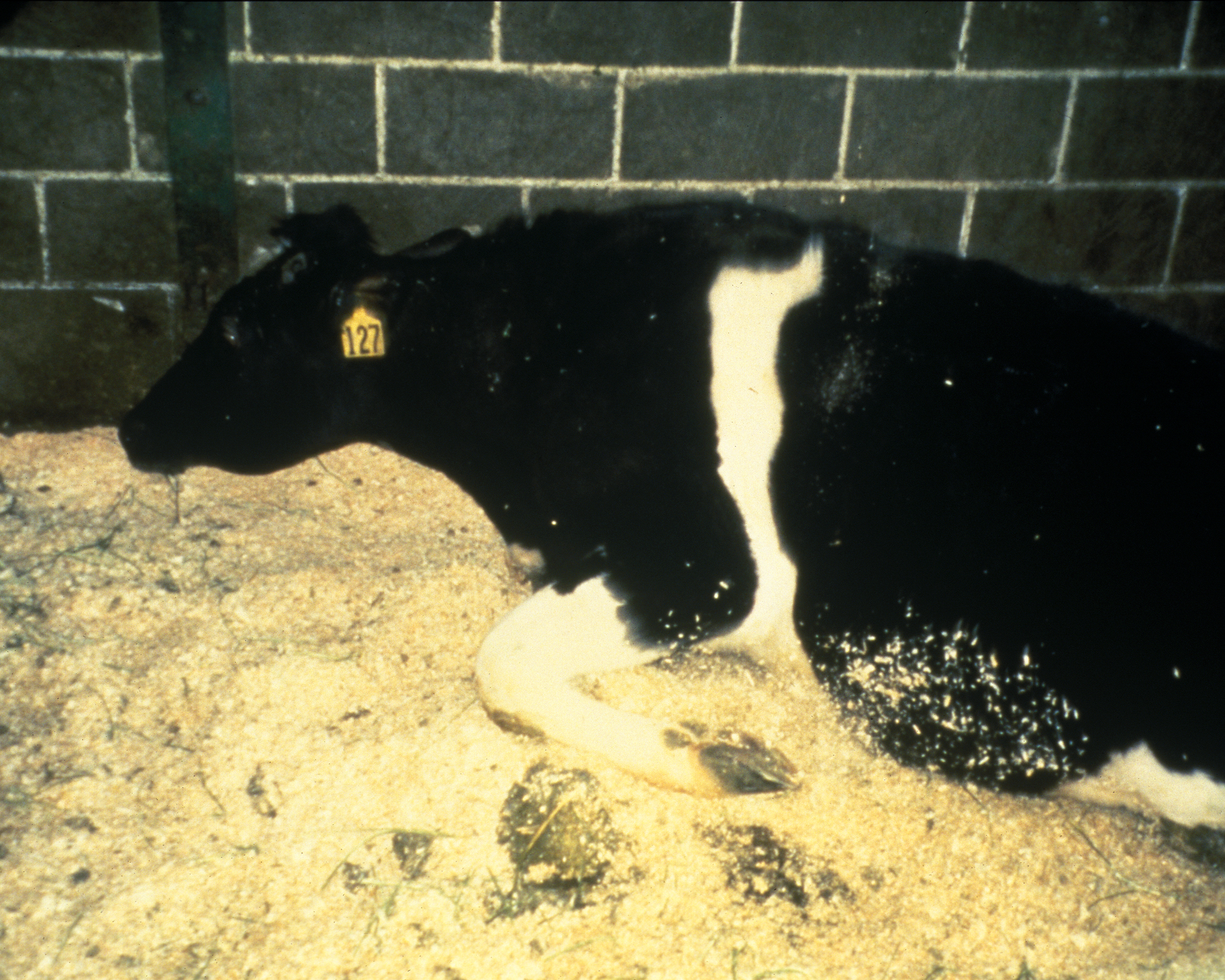
Downer (animal)
A downer is an animal, usually livestock, that cannot stand on its own and therefore is to be killed. A downed animal, one that is unable to stand, is not necessarily a downer. Causes The animal's inability to stand may be caused by illness or injury. In nearly all cases it is considered by most farmers to be both humane and cost-effective to kill the animal when it becomes a downer, rather than keeping it alive and unhealthy. Once killed, and depending on how the animal became a downer and how it was killed, the animal may then be incinerated, buried, rendered, or slaughtered. Because of mad cow disease, the slaughter of downer cattle is a topic of great concern. There are many possible reasons for an animal staying down, including: *Mastitis *Metritis *Hypomagnesaemia * Postparturient Hypocalcemia * Ketosis *Dystocia **Nerve damage **Pelvic fracture *Long bone fracture *Neurological disease Use of certain animal feed additives has been linked to downers such as the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown County, Wisconsin
Brown County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 268,740, making it the fourth-most populous county in Wisconsin. The county seat is Green Bay, making it one of three Wisconsin counties on Lake Michigan not to have a county seat with the same name. Brown County is part of the Green Bay, WI Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Brown County is one of Wisconsin's two original counties, along with Crawford County. It originally spanned the entire eastern half of the state when formed by the Michigan Territorial legislature in 1818. It was named for Major General Jacob Brown, a military leader during the War of 1812. Several towns along the Fox River vied for the position of county seat in Brown County's early years. The first county seat was located at Menomoneeville (now a part of Allouez) in 1824. In 1837, a public referendum relocated the county seat to De Pere. The location was put up for the popular vote again in 1854, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Tissue
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drowsiness
Somnolence (alternatively sleepiness or drowsiness) is a state of strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods (compare hypersomnia). It has distinct meanings and causes. It can refer to the usual state preceding falling asleep, the condition of being in a drowsy state due to circadian rhythm disorders, or a symptom of other health problems. It can be accompanied by lethargy, weakness and lack of mental agility. Somnolence is often viewed as a symptom rather than a disorder by itself. However, the concept of somnolence recurring at certain times for certain reasons constitutes various disorders, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, shift work sleep disorder, and others; and there are medical codes for somnolence as viewed as a disorder. Sleepiness can be dangerous when performing tasks that require constant concentration, such as driving a vehicle. When a person is sufficiently fatigued, microsleeps may be experienced. In individuals deprived of sleep, somno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |