|
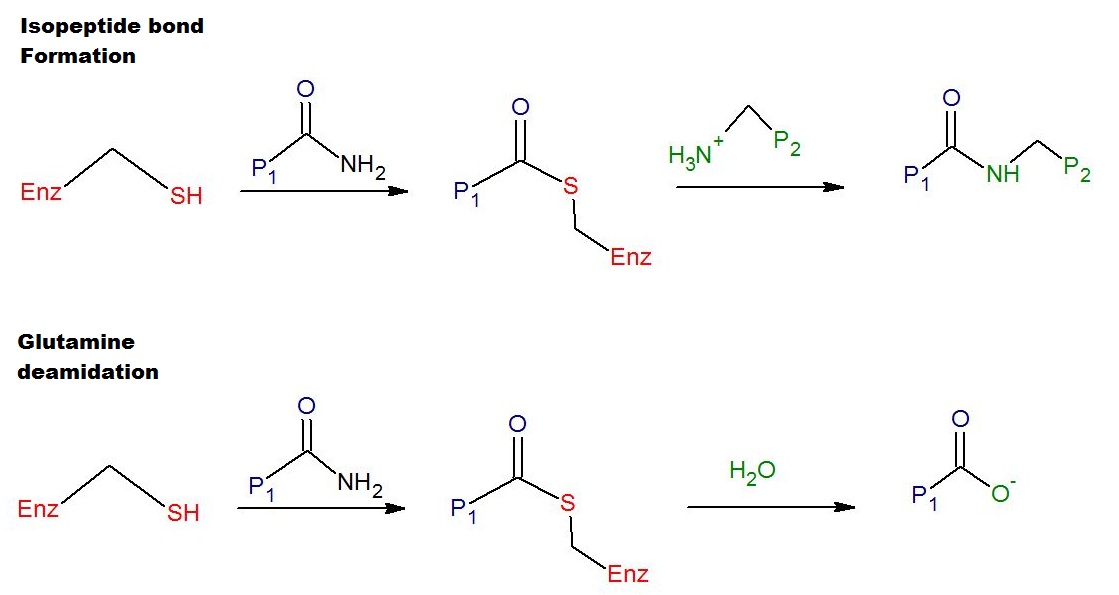
Transglutaminase
Transglutaminases are enzymes that in nature primarily catalyze the formation of an isopeptide bond between γ-carboxamide groups ( -(C=O)NH2 ) of glutamine residue side chains and the ε-amino groups ( -NH2 ) of lysine residue side chains with subsequent release of ammonia ( NH3 ). Lysine and glutamine residues must be bound to a peptide or a protein so that this cross-linking (between separate molecules) or intramolecular (within the same molecule) reaction can happen. Bonds formed by transglutaminase exhibit high resistance to proteolytic degradation (proteolysis). The reaction is :Glutamine, Gln-(C=O)NH2 + Lysine, NH2-Lys → Gln-(C=O)NH-Lys + NH3 Transglutaminases can also join a primary amine ( RNH2 ) to the side chain carboxyamide group of a protein/peptide bound glutamine residue thus forming an isopeptide bond :Gln-(C=O)NH2 + RNH2 → Gln-(C=O)NHR + NH3 These enzymes can also Deamidation, deamidate glutamine residues to glutamic acid residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Mobaraensis
''Streptomyces mobaraensis'' is a spore forming bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces''. ''Streptomyces mobaraensis'' produces bleomycin, detoxin, piericidin A, piericidin B, reticulol and transglutaminase. ''Streptomyces mobaraensis'' is used in the food industry to produce transglutaminase to texture meat and fish products. Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * See also * List of Streptomyces species A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... References External linksType strain of ''Streptomyces mobaraensis'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase mobaraensis Bacteria described in 1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An acid- base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence (primary structure). As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor XIII
Factor XIII or fibrin stabilizing factor is a zymogen found in blood of humans and some other animals. It is activated by thrombin to factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa is an enzyme of the blood coagulation system that crosslinks fibrin. Deficiency of XIII worsens clot stability and increases bleeding tendency. Human XIII is a heterotetramer. It consists of 2 enzymatic A peptides and 2 non-enzymatic B peptides. XIIIa is a dimer of activated A peptides. Function Within blood, thrombins cleave fibrinogens to fibrins during coagulation and a fibrin-based blood clot forms. Factor XIII is a transglutaminase that circulates in human blood as a heterotetramer of two A and two B subunits. Factor XIII binds to the clot via their B units. In the presence of fibrins, thrombin efficiently cleaves the R37– G38 peptide bond of each A unit within a XIII tetramer. A units release their N-terminal activation peptides. Both of the non-covalently bound B units are now able to dissociate from the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism of coagulation involves activation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin. Coagulation begins almost instantly after an injury to the endothelium lining a blood vessel. Exposure of blood to the subendothelial space initiates two processes: changes in platelets, and the exposure of subendothelial tissue factor to plasma factor VII, which ultimately leads to cross-linked fibrin formation. Platelets immediately form a plug at the site of injury; this is called ''primary hemostasis. Secondary hemostasis'' occurs simultaneously: additional coagulation (clotting) factors beyond factor VII ( listed below) respond in a cascade to form fibrin strands, which strengthen the platelet plug. Disorders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papain-like Protease
Papain-like proteases (or papain-like (cysteine) peptidases; abbreviated PLP or PLCP) are a large protein family of cysteine protease enzymes that share structural and enzymatic properties with the group's namesake member, papain. They are found in all domains of life. In animals, the group is often known as cysteine cathepsins or, in older literature, lysosomal peptidases. In the MEROPS protease enzyme classification system, papain-like proteases form Clan CA. Papain-like proteases share a common catalytic dyad active site featuring a cysteine amino acid residue that acts as a nucleophile. The human genome encodes eleven cysteine cathepsins which have a broad range of physiological functions. In some parasites papain-like proteases have roles in host invasion, such as cruzipain from ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. In plants, they are involved in host defense and in development. Studies of papain-like proteases from prokaryotes have lagged their eukaryotic counterparts. In cellular organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transamidation
Transamidation is a chemical reaction in which an amide reacts with an amine to generate a new amide: :RC(O)NR'2 + HNR"2 → RC(O)NR"2 + HNR'2 The reaction is typically very slow, but it can be accelerated with Lewis acid and organometallic catalysts. Primary amides (RC(O)NH2) are more amenable to this reaction. Ureas In contrast to the reluctance of amides as substrates, urea is more susceptible to this exchange process. Transamidation is practiced, sometimes even on an industrial scale, to prepare a variety of N-substituted ureas: :(H2N)2CO + R2NH → (R2N)(H2N)CO + NH3 :(R2N)(H2N)CO + R2NH → (R2N)2CO + NH3 Methylurea, precursor to theobromine, is produced from methylamine and urea. Phenylurea is produced similarly but from anilinium chloride:{{cite journal , authors= , title=Arylureas II. Urea Method p-Ethoxyphenylurea , journal=Org. Synth. , year=1951 , volume=31 , page=11 , doi=10.15227/orgsyn.031.0011 :(H2N)2CO + 6H5NH3l → (C6H5(H)N)(H2N) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transamidation And Deamidation Mechanisms Of Tissue Transglutaminase
Transamidation is a chemical reaction in which an amide reacts with an amine to generate a new amide: :RC(O)NR'2 + HNR"2 → RC(O)NR"2 + HNR'2 The reaction is typically very slow, but it can be accelerated with Lewis acid and organometallic catalysts. Primary amides (RC(O)NH2) are more amenable to this reaction. Ureas In contrast to the reluctance of amides as substrates, urea is more susceptible to this exchange process. Transamidation is practiced, sometimes even on an industrial scale, to prepare a variety of N-substituted ureas: :(H2N)2CO + R2NH → (R2N)(H2N)CO + NH3 :(R2N)(H2N)CO + R2NH → (R2N)2CO + NH3 Methylurea, precursor to theobromine, is produced from methylamine and urea. Phenylurea is produced similarly but from anilinium chloride:{{cite journal , authors= , title=Arylureas II. Urea Method p-Ethoxyphenylurea , journal=Org. Synth. , year=1951 , volume=31 , page=11 , doi=10.15227/orgsyn.031.0011 :(H2N)2CO + 6H5NH3l → (C6H5(H)N)(H2N) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be divided into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Note that some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently) and permanently bound to a protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalian
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 Order (biology), orders. The largest Order (biology), orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, pinniped, seals, and others). In terms of cladistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |